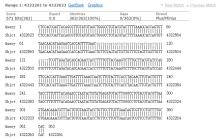
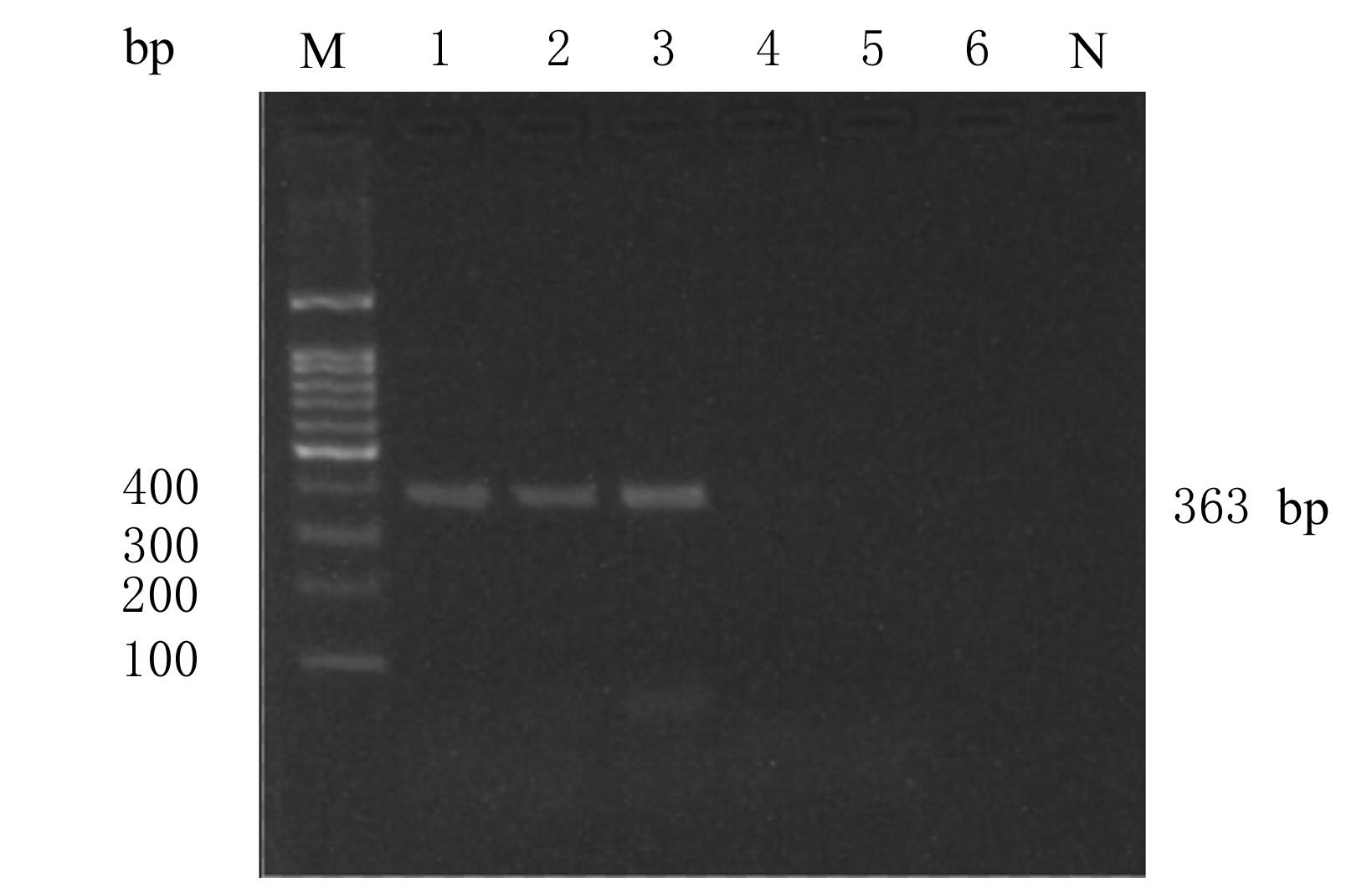
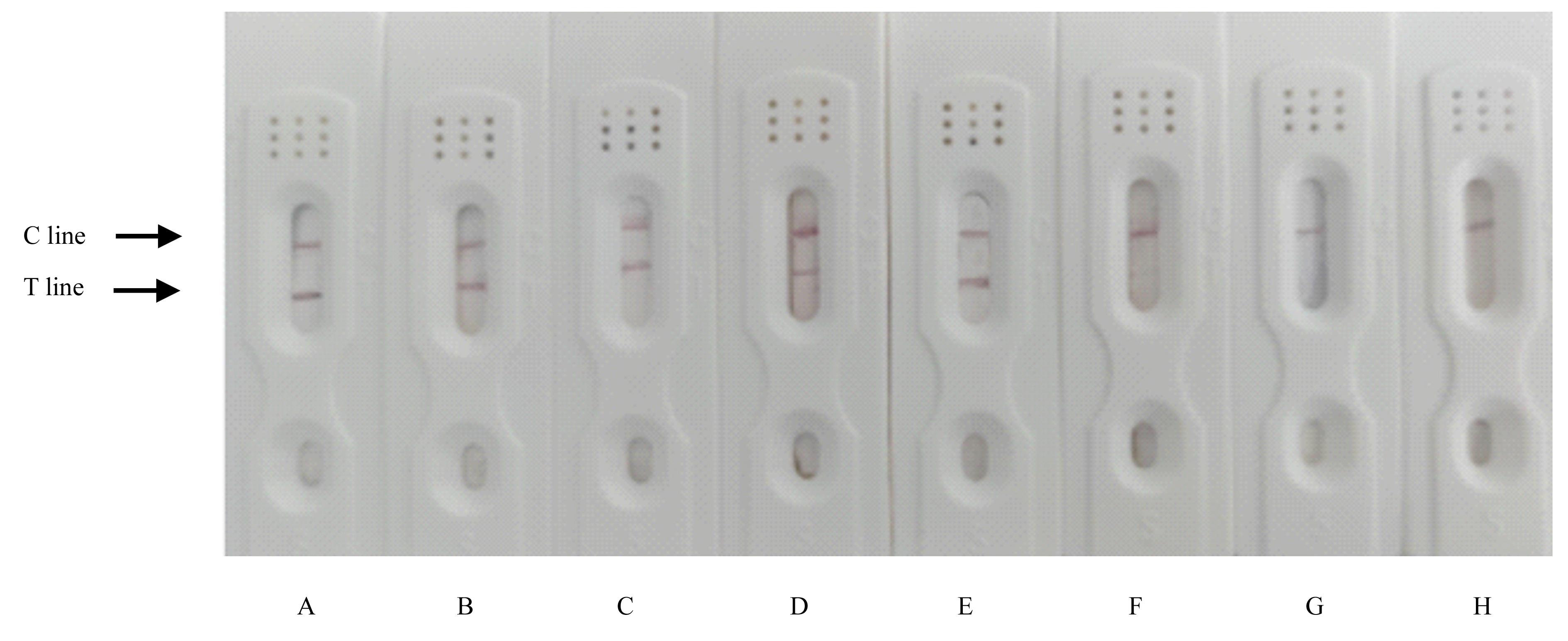
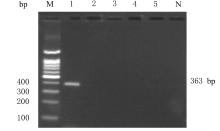
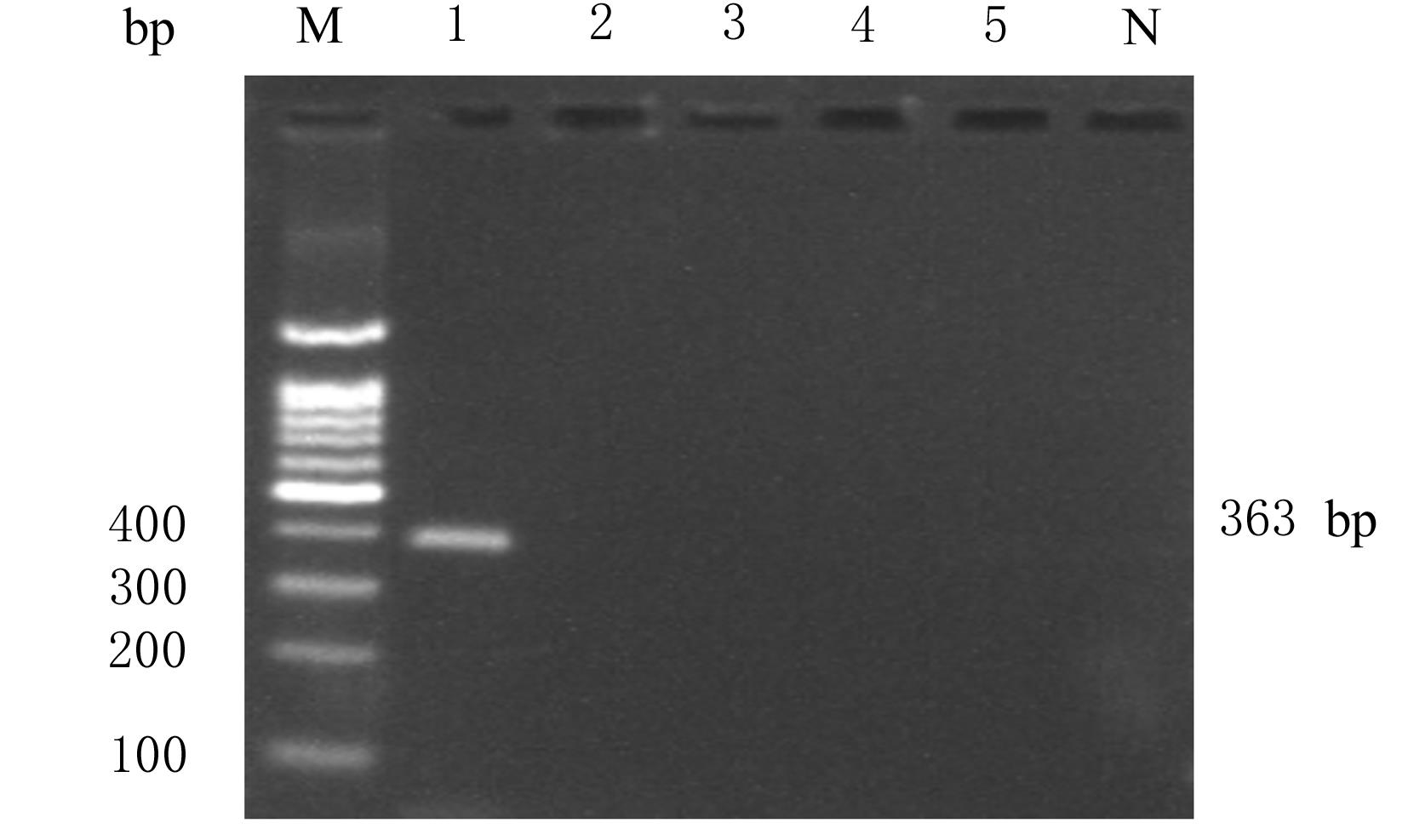
| 1 |
国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准食品微生物学检验蜡样芽孢杆菌检验: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
|
| 2 |
张玲艳, 宋丽丽, 贾伟娟, 等. 蜡样芽孢杆菌检测方法的研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(4): 1360-1372.
|
| 3 |
MESSELHÄUßER U, BUSCH U, BUTZENLECHNER M. Toxingen-profiling Bei bakterien der Bacillus cereus-gruppe[J]. BIOspektrum, 2014, 20(4): 390-392.
|
| 4 |
TRAN S L, GUILLEMET E, GOHAR M, et al. CwpFM (EntFM) is a Bacillus cereus potential cell wall peptidase implicated in adhesion, biofilm formation, and virulence[J]. J Bacteriol, 2010, 192(10): 2638-2642.
|
| 5 |
CUI Y F, MÄRTLBAUER E, DIETRICH R, et al. Multifaceted toxin profile, an approach toward a better understanding of probiotic Bacillus cereus [J]. Crit Rev Toxicol, 2019, 49(4): 342-356.
|
| 6 |
张慧娟,张恩民,贺金荣,等. 蜡样芽胞杆菌快速检测及其毒力基因筛选[J].疾病监测,2019, 34(8): 767-770.
|
| 7 |
秦丽云,吕国平,蔡 箴,等. 石家庄市131株食源性蜡样芽胞杆菌毒力基因的分布[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2015, 27(4): 358-362.
|
| 8 |
章乐怡,张秀尧,李 毅,等. 婴幼儿奶粉和米粉中蜡样芽胞杆菌及其毒素、毒力基因的调查研究[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志, 2014, 26(6): 600-604.
|
| 9 |
RAMARAO N, TRAN S L, MARIN M, et al. Advanced methods for detection of Bacillus cereus and its pathogenic factors[J]. Sensors (Basel),2020,20(9):2667.
|
| 10 |
FORGHANI F, SINGH P, SEO K H, et al. A novel pentaplex real time (RT)- PCR high resolution melt curve assay for simultaneous detection of emetic and enterotoxin producing Bacillus cereus in food[J]. Food Control, 2016, 60: 560-568.
|
| 11 |
龚真莉, 蒋 韬, 祁淑芸, 等. 口蹄疫病毒核酸试纸条检测方法的建立[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2015, 42(9): 2292-2297.
|
| 12 |
王宪国. 两种不同应用领域POCT快速检测试剂的研制[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2015.
|
| 13 |
戚衍博, 袁周恩, 王兆林, 等. 蜡样芽胞杆菌呕吐毒素的幼猫试验[J]. 微生物学杂志, 1984, 4(1): 28-30.
|
| 14 |
TSILIA V, DEVREESE B, DE BAENST I, et al. Application of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the detection of enterotoxins produced by pathogenic strains of the Bacillus cereus group[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2012, 404(6/7): 1691-1702.
|
| 15 |
HÄGGBLOM M M, APETROAIE C, ANDERSSON M A,et al. Quantitative analysis of cereulide, the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus, produced under various conditions[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2002, 68(5): 2479-2483.
|
| 16 |
张秀尧, 蔡欣欣, 李 毅. 超高效液相色谱串联质谱法检测食品中蜡样芽胞杆菌呕吐毒素Cereulide[J]. 分析化学, 2012, 40(8): 1267-1273.
|
| 17 |
ZHU K, DIETRICH R, DIDIER A, et al. Recent developments in antibody-based assays for the detection of bacterial toxins[J]. Toxins, 2014, 6(4): 1325-1348.
|
| 18 |
张力支, 魏亚楠, 王雪辉, 等. 基于纳米金核酸探针的新型试纸条对灿烂弧菌快速检测[J]. 生物工程学报, 2021, 37(9): 3323-3333.
|
| 19 |
王之莹, 于文杰, 谢瑞彬, 等. 利用侧流核酸试纸条快速检测非洲猪瘟病毒[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020,36(4): 294-299.
|
| 20 |
QIN P Z, QIAO D Q, XU J G, et al. Rapid visual sensing and quantitative identification of duck meat in adulterated beef with a lateral flow strip platform[J]. Food Chem, 2019, 294: 224-230.
|
| 21 |
TRAN S L, CORMONTAGNE D, VIDIC J, et al. Structural modeling of cell wall peptidase CwpFM (EntFM) reveals distinct intrinsically disordered extensions specific to pathogenic Bacillus cereus strains[J]. Toxins, 2020, 12(9): 593.
|
| 22 |
BLACKMAN S A, SMITH T J, FOSTER S J. The role of autolysins during vegetative growth of Bacillus subtilis 168[J].Microbiology (Reading),1998,144(Pt 1): 73-82.
|
| 23 |
CHICA J S, CORREA M M, ACEVES-DIEZ A E, et al. Genomic and toxigenic heterogeneity of Bacillus cereus sensu lato isolated from ready-to-eat foods and powdered milk in day care centers in Colombia[J]. Foodborne Pathog Dis, 2020, 17(5): 340-347.
|
| 24 |
ZHAO S J, CHEN J L, FEI P, et al. Prevalence, molecular characterization, and antibiotic susceptibility of Bacillus cereus isolated from dairy products in China[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2020, 103(5): 3994-4001.
|
| 25 |
PARK K M, KIM H J, JEONG M, et al. Enterotoxin genes, antibiotic susceptibility, and biofilm formation of low-temperature-tolerant Bacillus cereus isolated from green leaf lettuce in the cold chain[J].Foods,2020,9(3): 249.
|
 )
)
 )
)