吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2): 289-297.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230204
幽门螺杆菌感染性慢性胃炎模型小鼠肠道各区域的菌群分布特征及其机制
覃艳春1,黄衍强1,陆钢2( ),黄干荣1,唐华英1(
),黄干荣1,唐华英1( ),戴园园1
),戴园园1
- 1.右江民族医学院基础医学院病原生物学与免疫学教研室,广西 百色 533000
2.右江民族医学院 附属医院烧伤整形与创面修复外科,广西 百色 533000
Distribution characteristics of micrflora in various regions of intestinal tract of mice with chronic gastritis infected with Helicobacter Pylori andits mechannism
Yanchun QIN1,Yanqiang HUANG1,Gang LU2( ),Ganrong HUANG1,Huaying TANG1(
),Ganrong HUANG1,Huaying TANG1( ),Yuanyuan DAI1
),Yuanyuan DAI1
- 1.Department of Pathogenic Biology and Immunology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities,Baise 533000,China
2.Department of Burn Plastic and Wound Repair Surgery,Affiliated Hospital,Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities,Baise 533000,China
摘要:
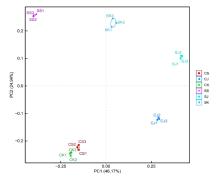
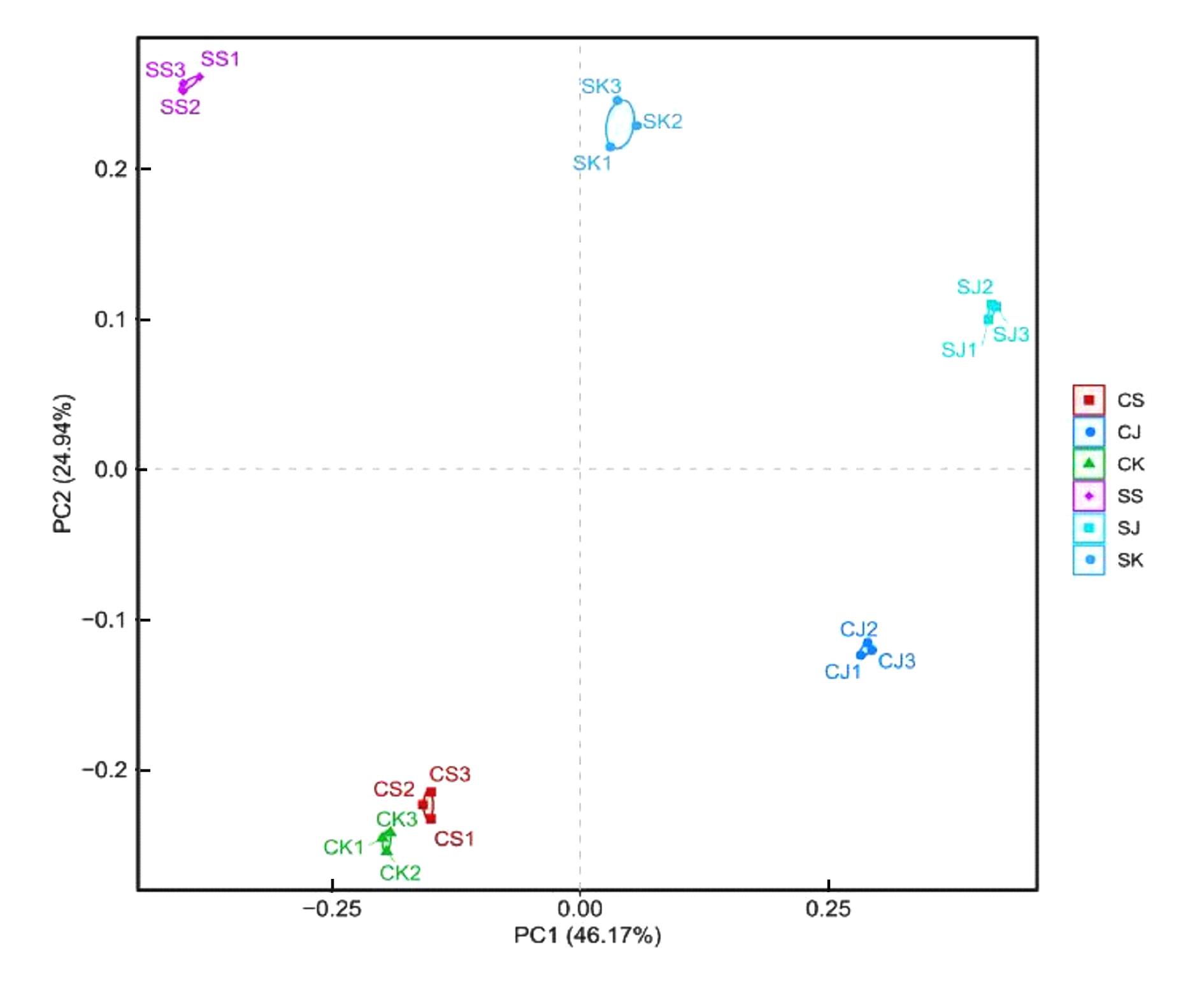
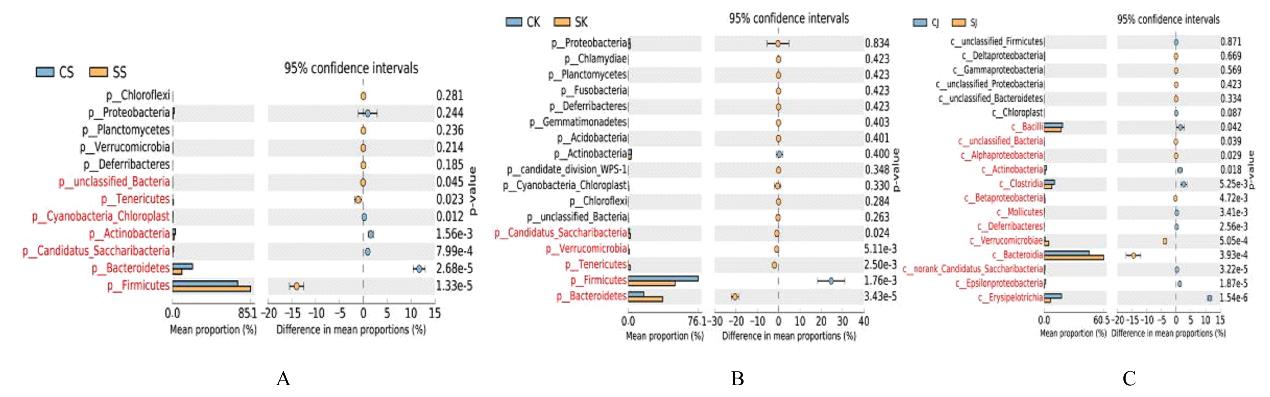
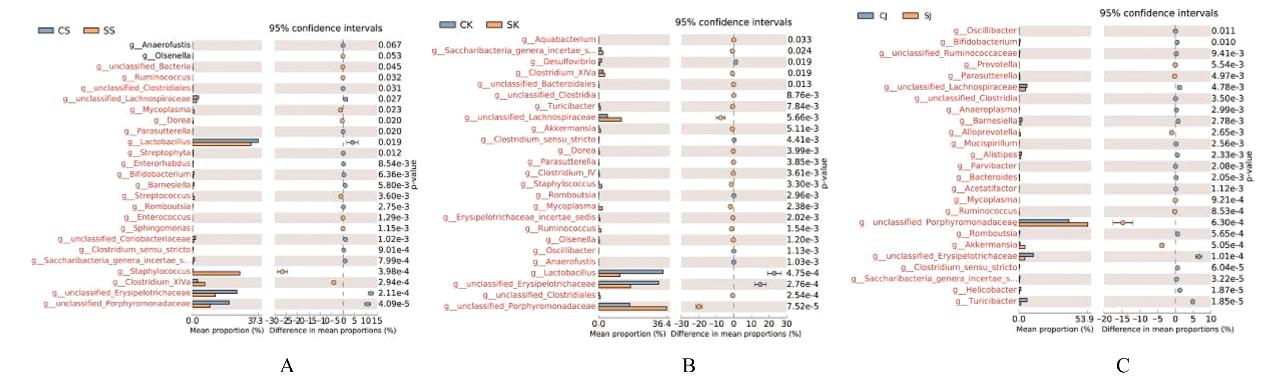
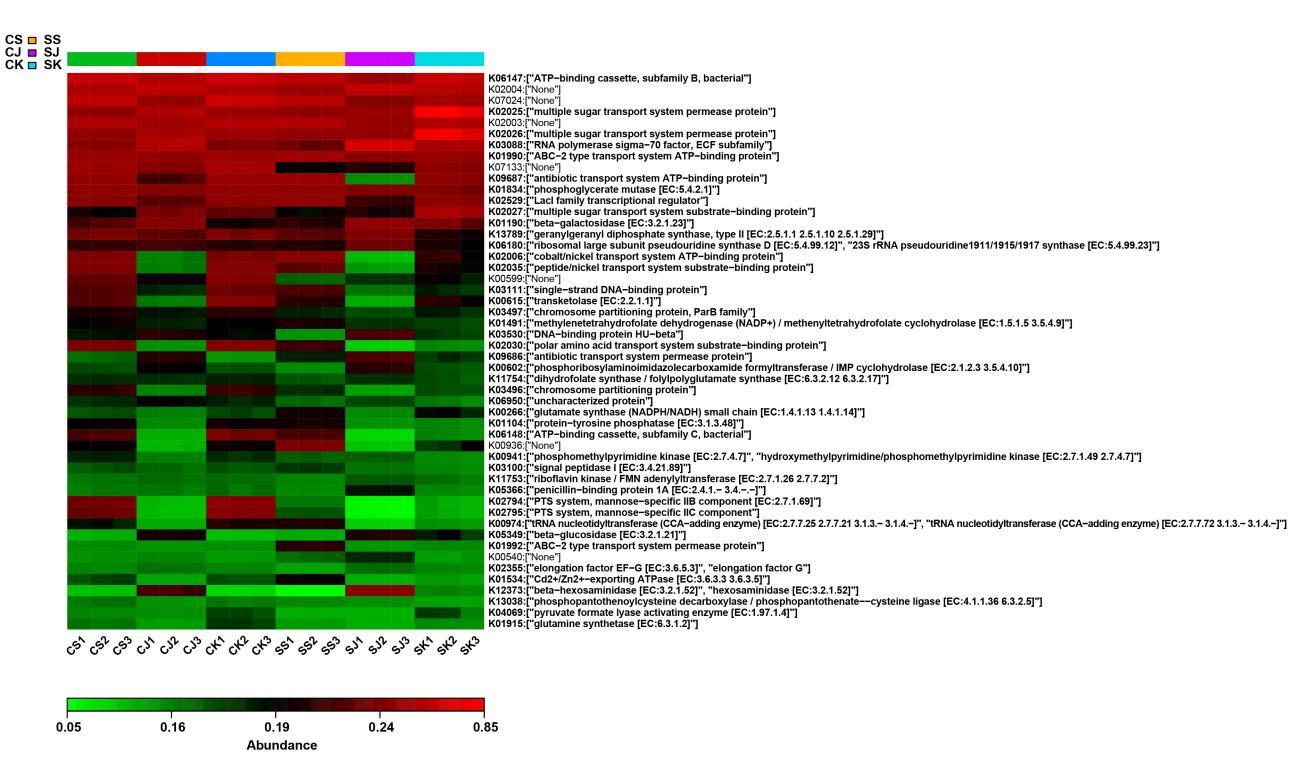
目的 探讨幽门螺杆菌(Hp)感染性慢性胃炎模型小鼠肠道各区域菌群种类、特征和菌群差异,并阐明其相关机制。 方法 30只C57BL/6小鼠随机分为对照组和感染组,每组15只。对照组小鼠以生理盐水灌胃,感染组小鼠以浓度为1×109CFU·mL-1的Hp菌悬液灌胃,确认建模成功后采集2组小鼠的十二指肠、空肠和结肠内容物提取总DNA,PCR法扩增,采用高通量测序技术对样本16SrRNAV3-V4区进行测序,通过α和β多样性分析对照组和感染组小鼠肠道菌群的特征、差异和多样性。 结果 2组样本聚类分析共产生的操作单元分类(OTU)数目为211个。在门水平,2组样本主要有厚壁菌门、拟杆菌门、放线菌门、变形菌门和疣微菌门5个优势菌门;与对照组比较,感染组小鼠十二指肠、空肠和结肠中的放线菌门丰度明显降低(P<0.05)。在属水平,2组样本主要有乳酸菌属、葡萄球菌属、梭状芽孢杆菌属ⅩⅣa菌属、Turicibacter菌属、阿克曼菌属、双歧杆菌属、Saccharibacteria-genera-incertae-sedis菌属、巴恩斯氏菌属、脱硫弧菌属、另枝菌属和支原体等21个优势菌属;与对照组比较,感染组小鼠十二指肠和结肠中的乳酸菌属及双歧杆菌属丰度明显降低(P<0.05),支原体丰度明显升高(P<0.05)。OTU主成分分析(PCA),2组间主成分比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。Alpha多样性分析,shannon指数,对照组与感染组小鼠的十二指肠和空肠菌群多样性比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),感染组菌群多样性降低;simpson指数,对照组与感染组小鼠的十二指肠、空肠和结肠菌群多样性比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),感染组菌群多样性降低。Welch’s t-test分析,2组小鼠肠道各区域多数菌群丰度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 Hp感染性慢性胃炎小鼠肠道各区域中菌群种类和特征发生改变,益生菌丰度降低,支原体丰度升高,其机制可能与Hp的定植改变肠道微环境有关。
中图分类号:
- R378