吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 580-589.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230305
薏苡附子散对小鼠心肌缺血和血管内皮功能损伤的保护作用及其机制
李畅1,2,马梓珊1,2,黄汕梅1,2,银帮巧2,陈枝凡1,2,聂莎1,2,张子谦3,李力3,刘鹰1( ),唐耀平2,4(
),唐耀平2,4( )
)
- 1.广西中医药大学研究生院,广西 南宁 530200
2.广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院心血管内科,广西 南宁 530200
3.广西中医药大学科学实验中心 ;广西 南宁 530200
4.广西壮族自治区高发传染病 中西医结合转化医学重点实验室,广西 南宁 530200
Protective effect of Yiyi Fuzisan on myocardium ischemia and vascular endothelial function injury in mice and its mechanism
Chang LI1,2,Zishan MA1,2,Shanmei HUANG1,2,Bangqiao YIN2,Zhifan CHEN1,2,Sha NIE1,2,Ziqian ZHANG3,Li LI3,Ying LIU1( ),Yaoping TANG2,4(
),Yaoping TANG2,4( )
)
- 1.Graduate School, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
2.Affiliated Ruikang Hospital, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, China
3.Center of Scientific Research, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
4.Key Laboratory of Translational Medicine for Treating High-Incidence Infectious Diseases with Integrative Medicine, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Nanning 530200, China
摘要:
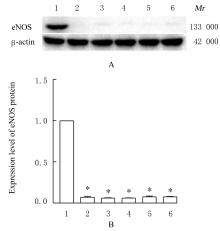
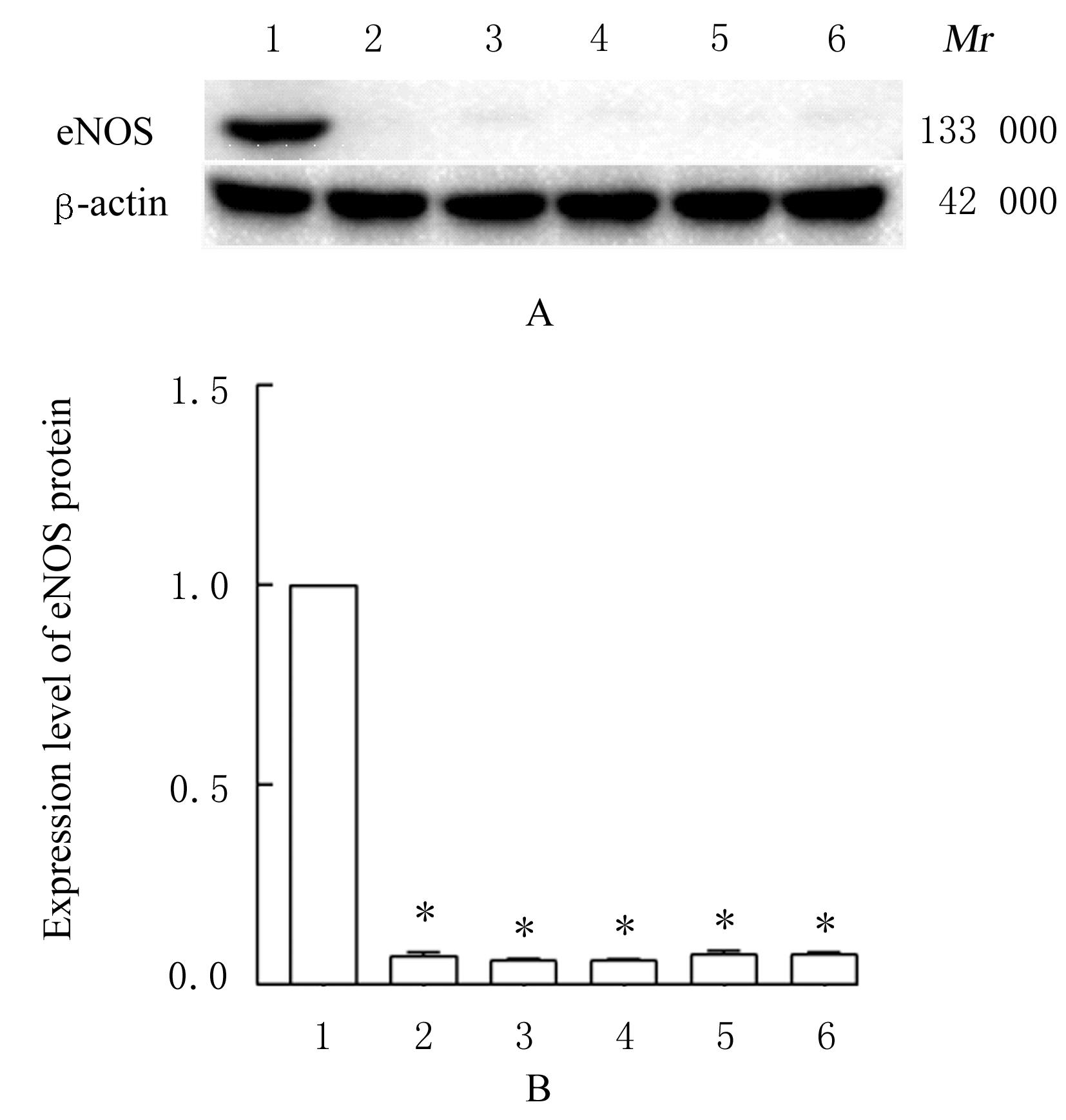
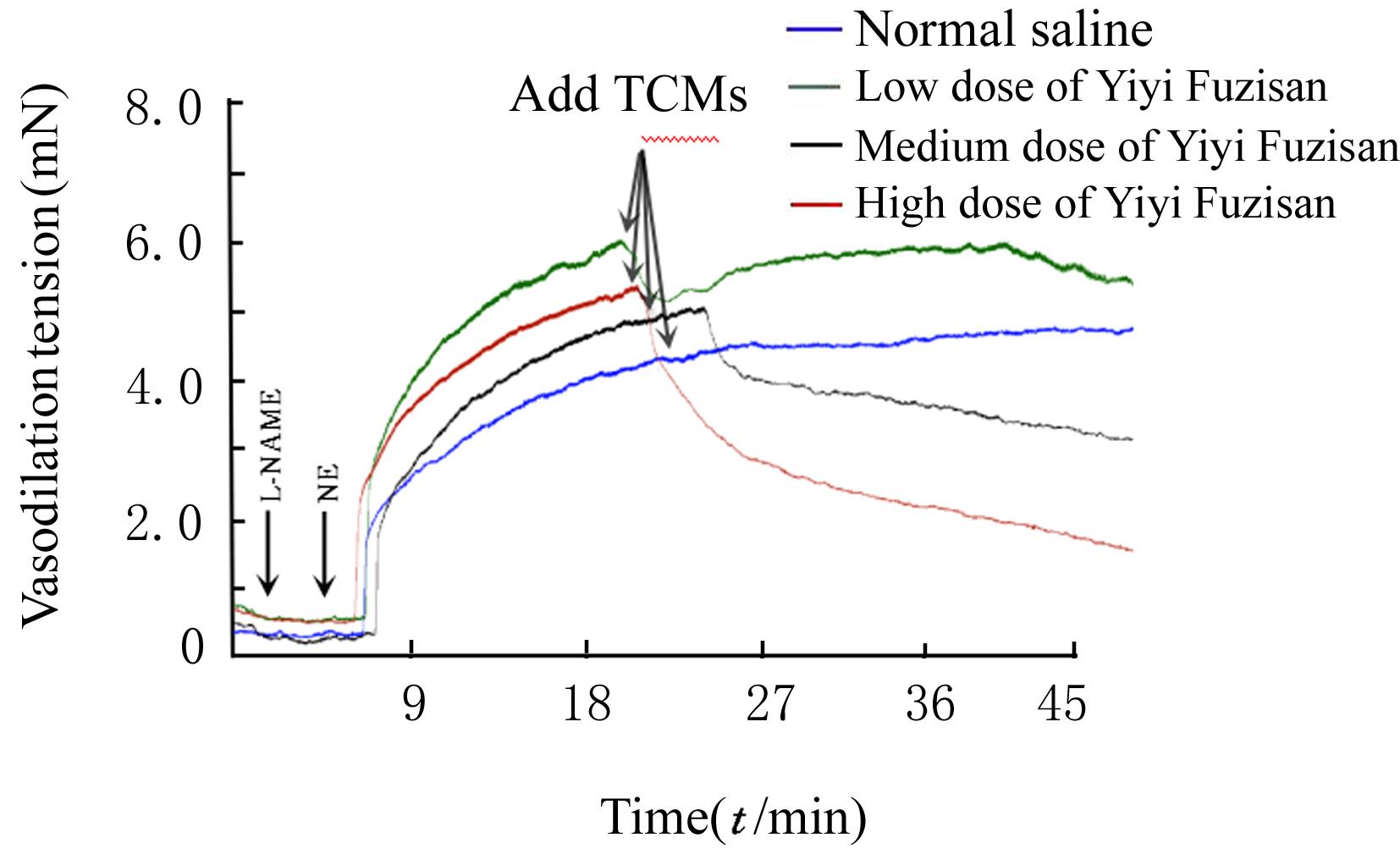
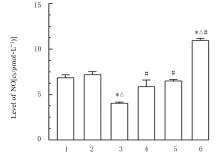
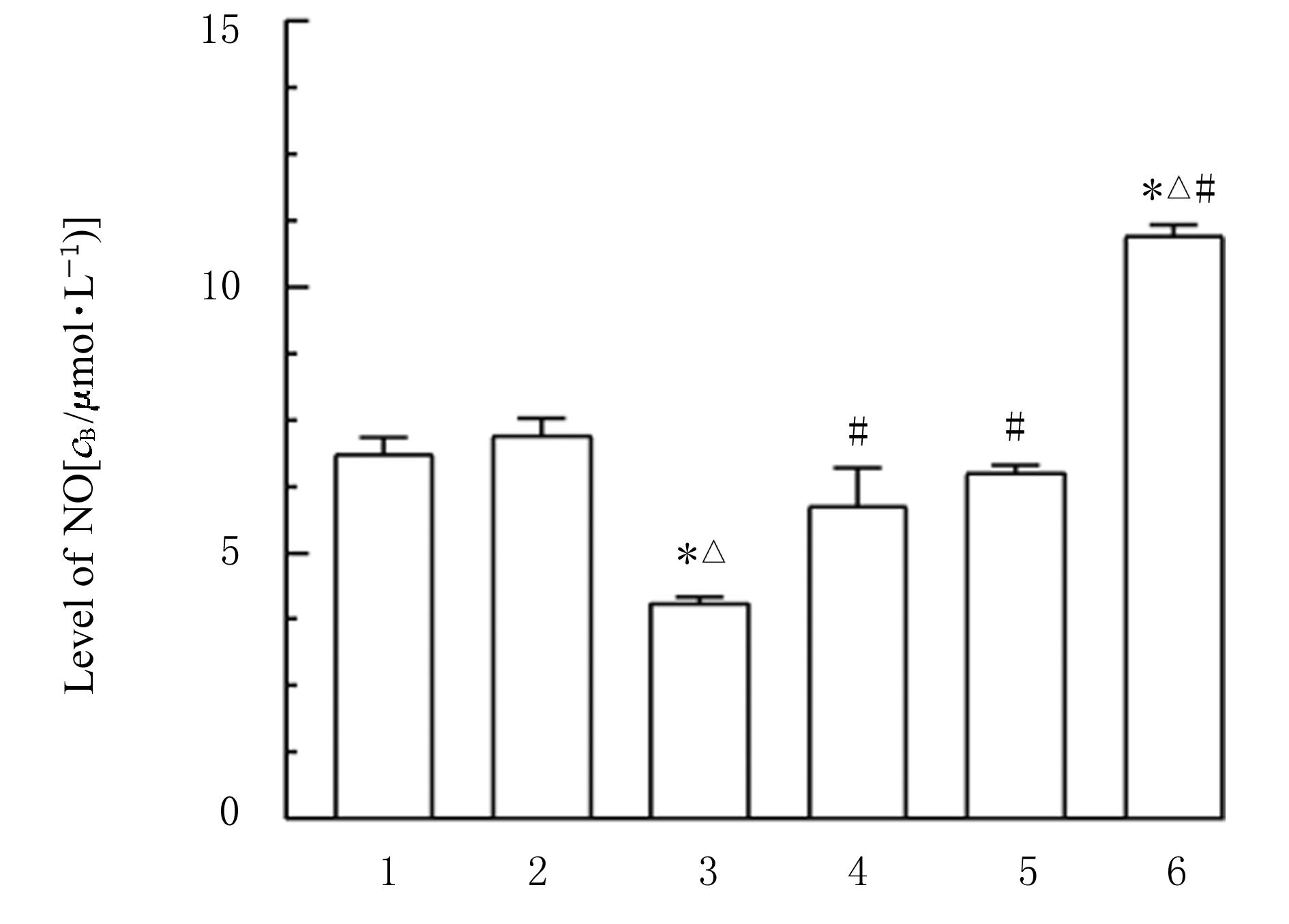
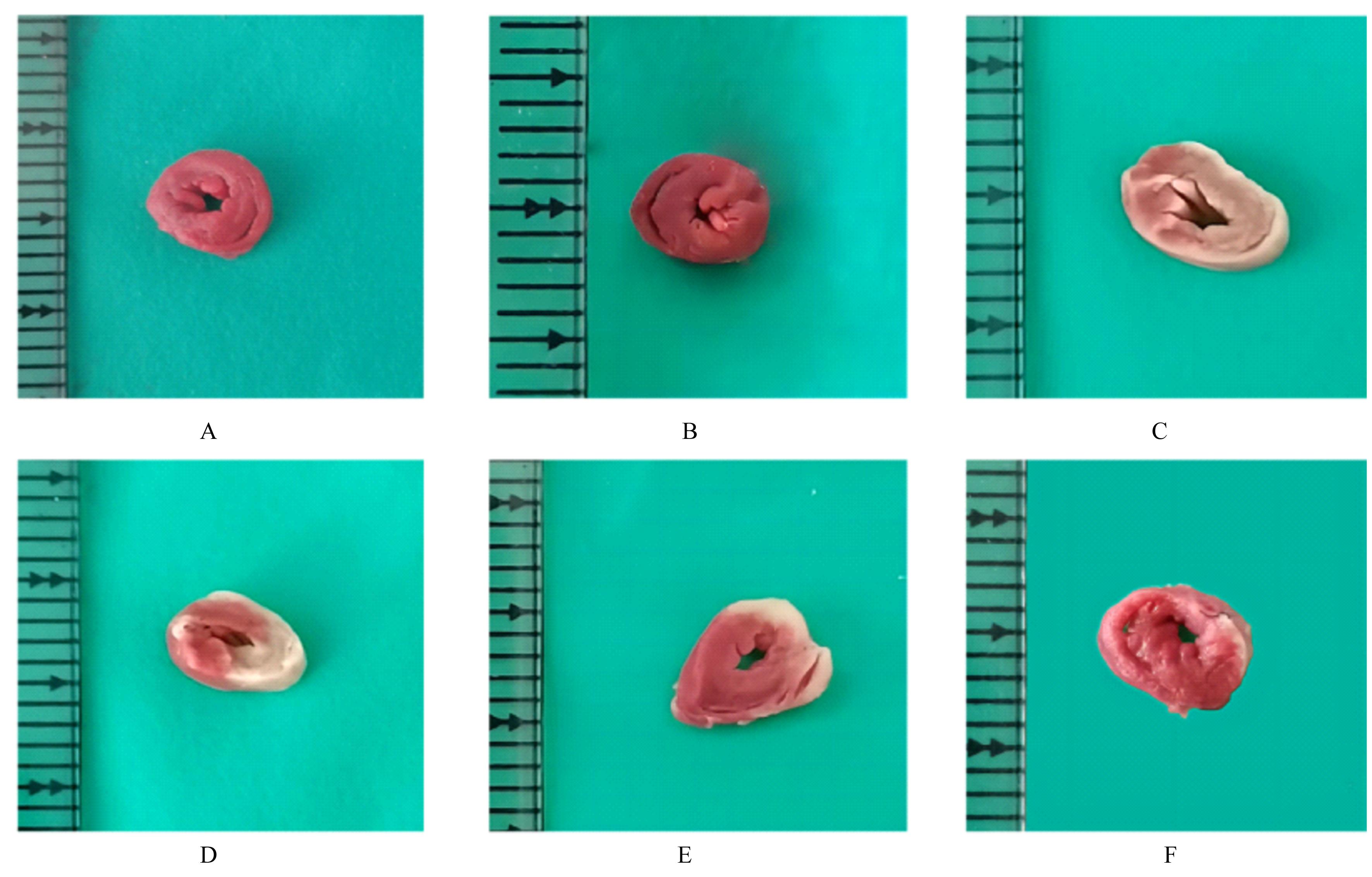
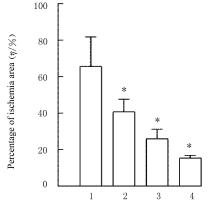
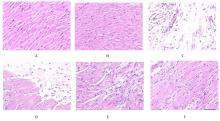
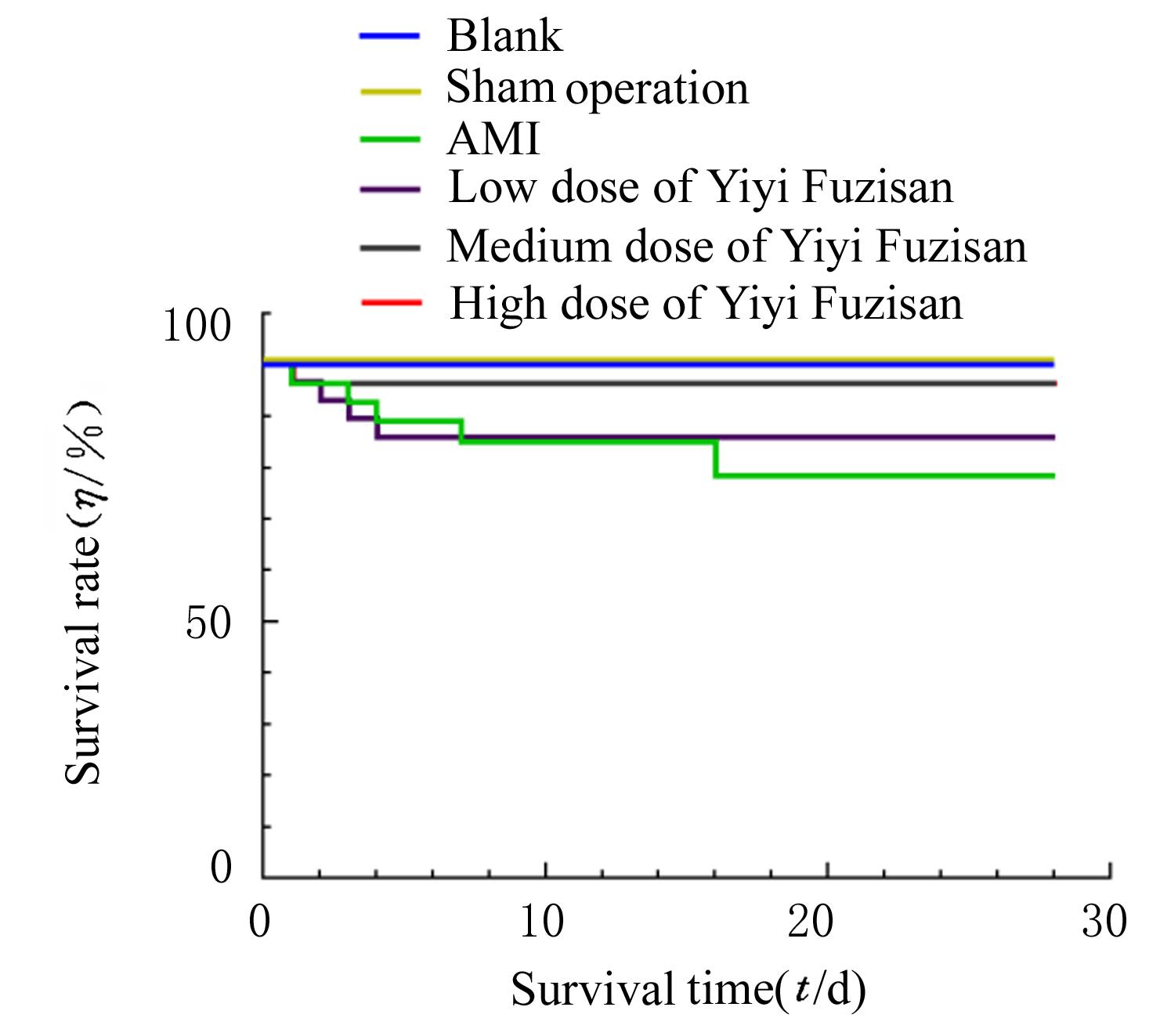
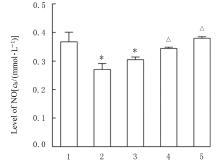
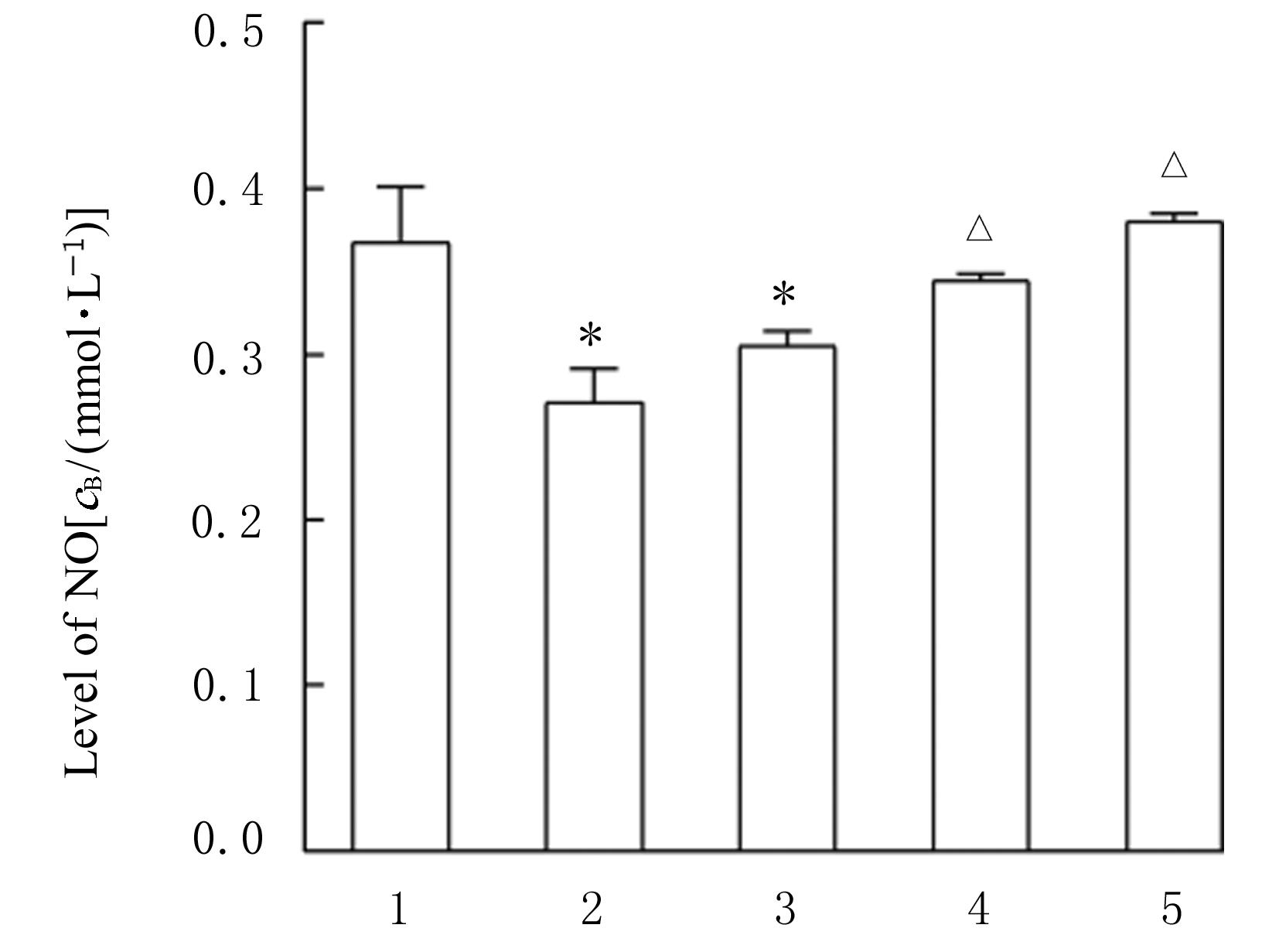
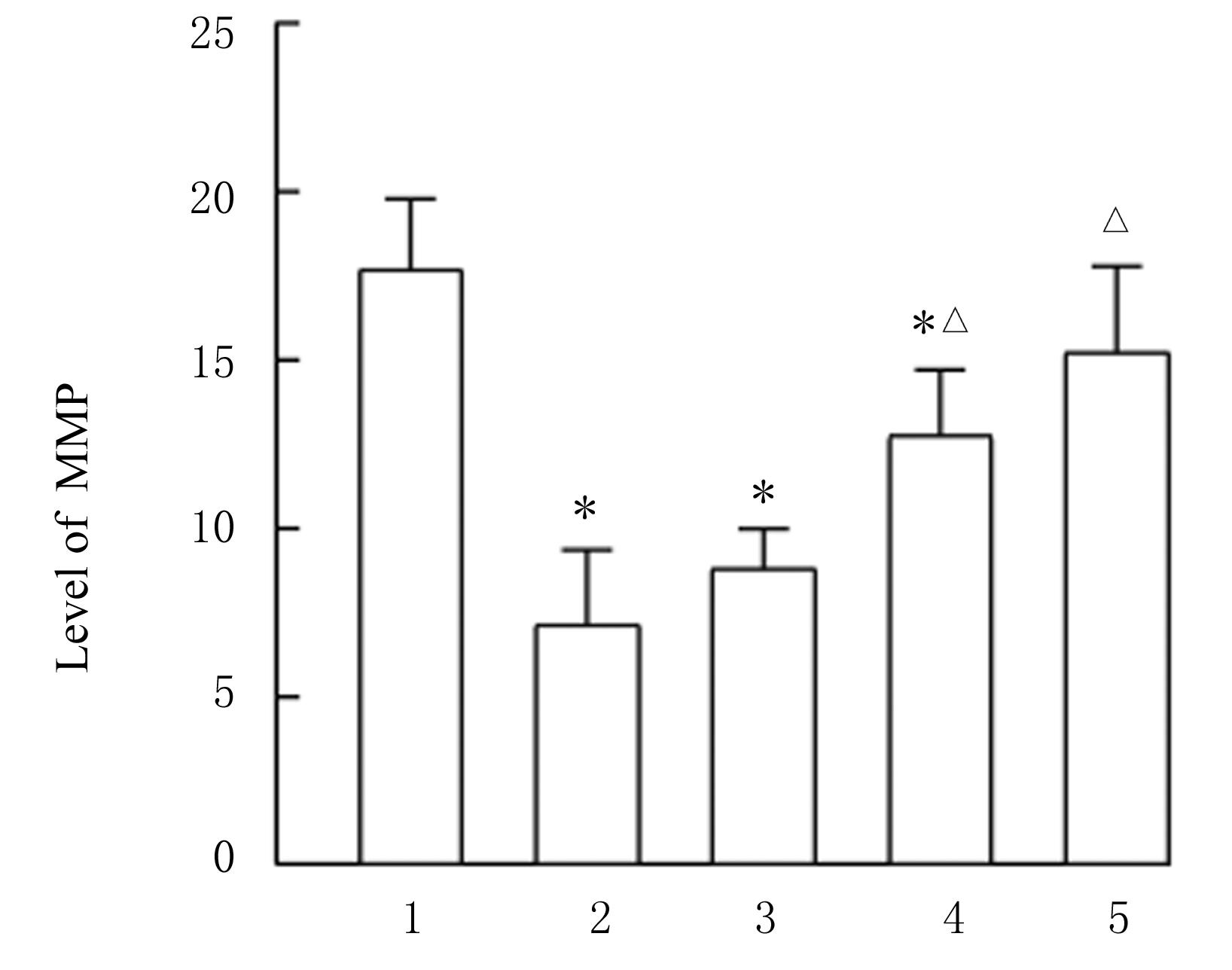
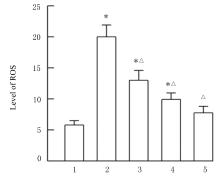
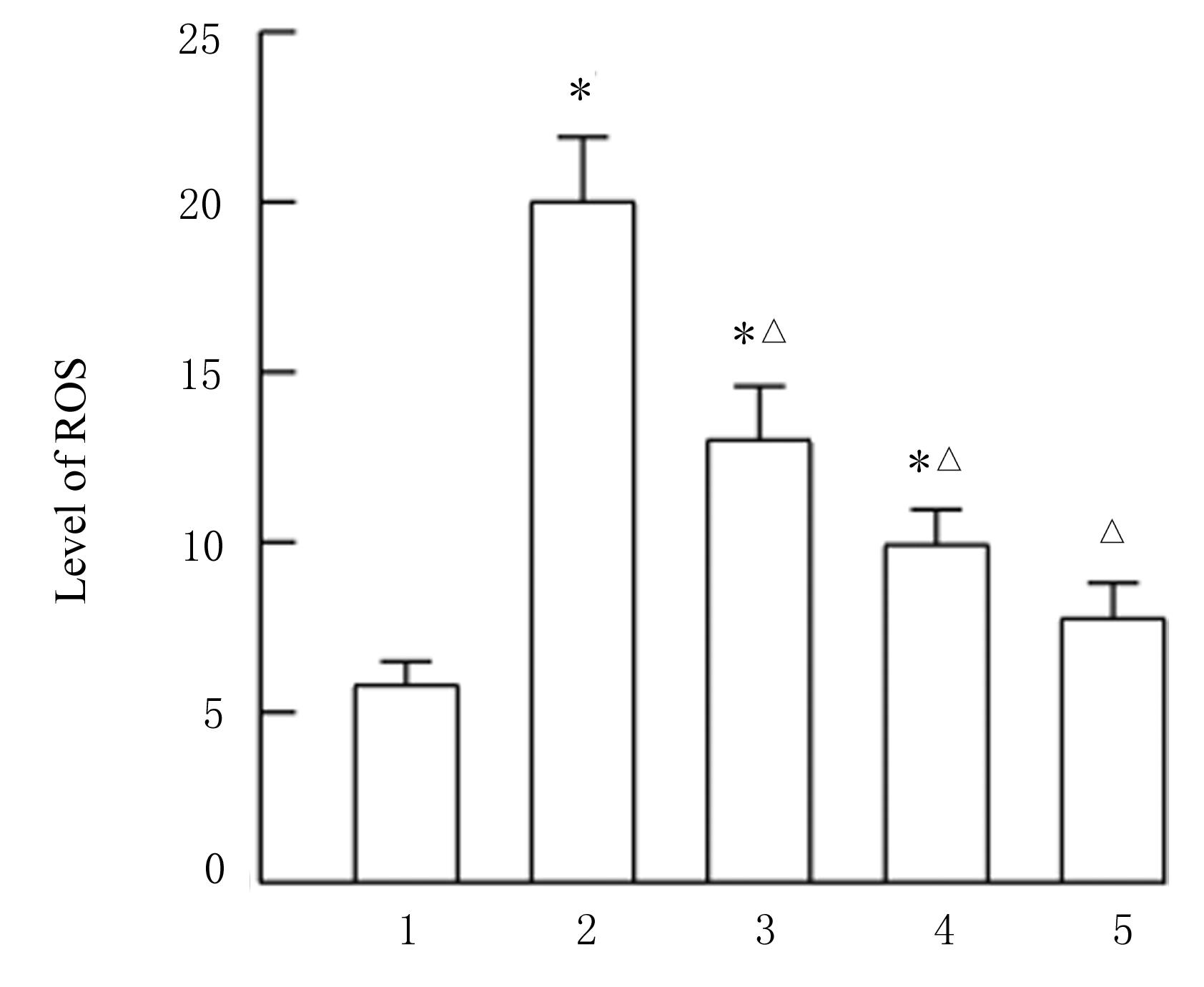
目的 探讨薏苡附子散对小鼠心肌缺血和血管内皮功能损伤的保护作用,阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 60只雄性SPF级C57BL/6J小鼠,随机分为空白组、假手术组、急性心肌缺血(AMI)组、低剂量薏苡附子散组、中剂量薏苡附子散组和高剂量薏苡附子散组,每组10只;另取40只C57BL/6J小鼠随机分为生理盐水组、低剂量薏苡附子散组、中剂量薏苡附子散组和高剂量薏苡附子散组,每组10只。采用冠脉左前降支(LAD)结扎法建立AMI小鼠模型后进行相应的药物干预处理28 d。采用Western blotting法检测小鼠心肌组织中一氧化氮合酶(eNOS)蛋白表达水平,动脉张力检测法检测各组小鼠离体胸主动脉血管张力和舒张率,总一氧化氮(NO)检测试剂盒检测各组小鼠血清中NO水平,氯化三苯基四氮唑(TTC)染色观察各组小鼠心肌组织缺血面积,HE染色观察各组小鼠心肌组织病理形态表现,观察各组小鼠术后存活率。人冠脉内皮细胞(HCAECs)随机分为空白组、缺氧组、缺氧+低剂量薏苡附子散组、缺氧+中剂量薏苡附子散组和缺氧+高剂量薏苡附子散组,除空白组外,其余各组细胞采用三气培养箱培养24 h建立缺氧模型。Griess实验检测各组HCAECs中NO水平,荧光染色法检测各组HCAECs中线粒体膜电位(MMP)和活性氧(ROS)水平。 结果 与建立AMI模型前比较,建立AMI模型后小鼠心电图ST段明显抬高。Western blotting法检测,与空白组比较,注射N-硝基-L-精氨酸甲酯(L-NAME)后假手术组、AMI组和低、中及高剂量薏苡附子散组小鼠心肌组织中eNOS蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。与生理盐水组比较,低、中和高剂量薏苡附子散组小鼠胸主动脉舒张率升高(P<0.05)。与空白组和假手术组比较,AMI组小鼠血清中NO水平降低(P<0.05),高剂量薏苡附子散组小鼠血清中NO水平升高(P<0.05);与AMI组比较,低、中和高剂量薏苡附子散组小鼠血清中NO水平升高(P<0.05)。TTC染色观察,与空白组和假手术组比较,AMI组和低、中及高剂量薏苡附子散组小鼠心肌组织均有不同程度心肌缺血;与AMI组比较,低、中和高剂量薏苡附子散组小鼠心肌组织缺血面积减少,心肌组织缺血面积百分率降低(P<0.05)。HE染色,空白组和假手术组小鼠心肌细胞排列整齐,胞核清晰完整,大小均匀,未见炎性细胞浸润;AMI组小鼠可见明显的心肌组织损伤,心肌细胞排列紊乱、破裂坏死,有炎性细胞浸润;低、中和高剂量薏苡附子散组小鼠可见心肌组织病理性损伤恢复。药物干预第28天,空白组和假手术组小鼠生存率为100%;与AMI组比较,低、中和高剂量薏苡附子散组小鼠生存率升高(χ2=15.03,P=0.010 2)。Griess实验检测,与空白组比较,缺氧组和缺氧+低剂量组薏苡附子散组HCAECs中NO水平降低(P<0.05);与缺氧组比较,缺氧+中剂量薏苡附子散组和缺氧+高剂量薏苡附子散组HCAECs中NO水平升高(P<0.05)。荧光染色法检测,与空白组比较,缺氧组、缺氧+低剂量薏苡附子散组和缺氧+中剂量薏苡附子散组HCAECs中MMP水平降低(P<0.05),ROS水平升高(P<0.05);与缺氧组比较,缺氧+中剂量薏苡附子散组和缺氧+高剂量薏苡附子散组HCAECs中MMP水平升高(P<0.05),缺氧+低剂量薏苡附子散组、缺氧+中剂量薏苡附子散组和缺氧+高剂量薏苡附子散组HCAECs中ROS水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 薏苡附子散可通过增强NO生物活性,增加主动脉血管活性,改善心肌缺血病理状态,恢复MMP,减少ROS的生成,改善线粒体及血管内皮细胞功能障碍。
中图分类号:
- R541