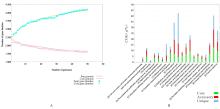
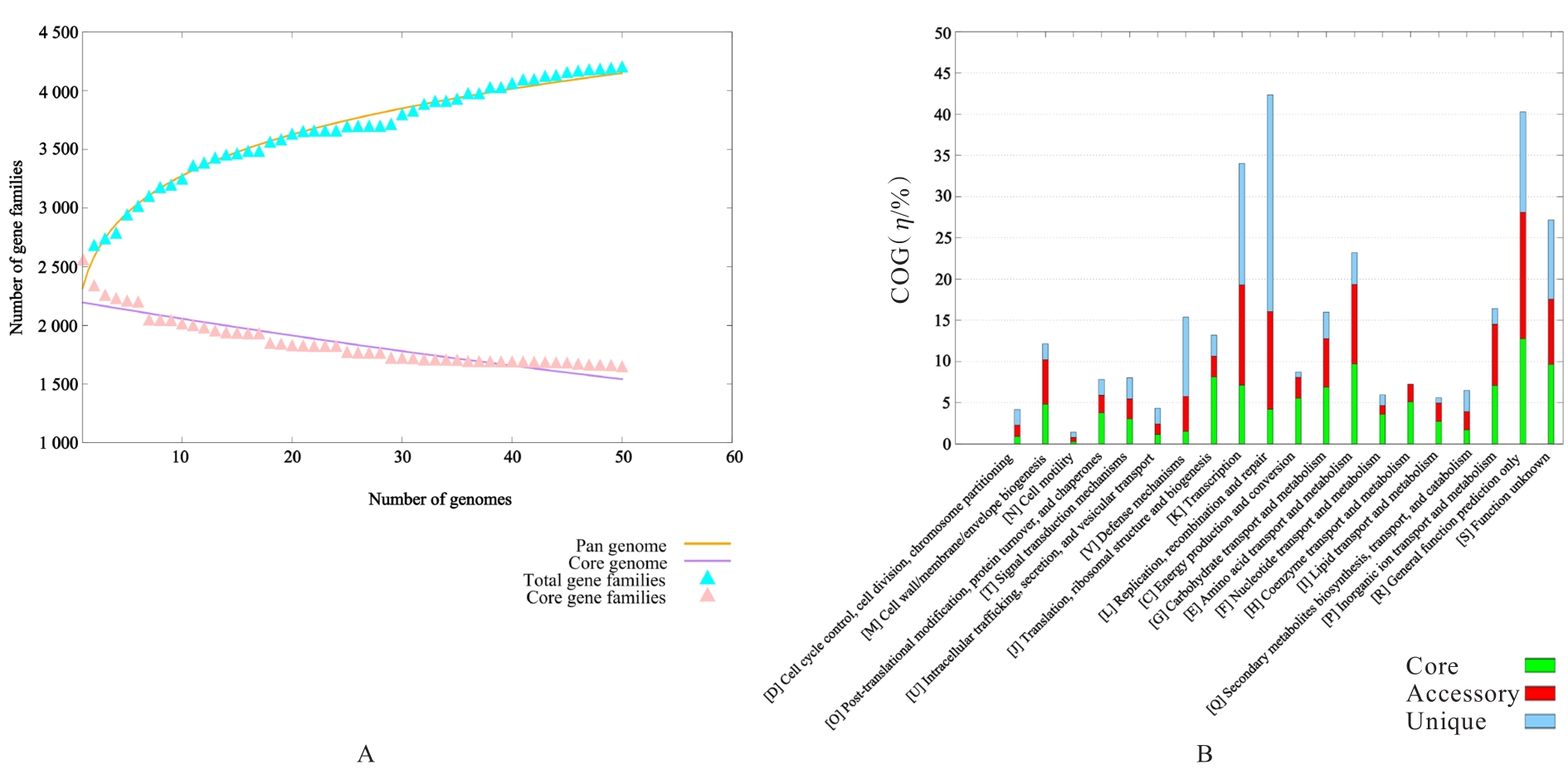
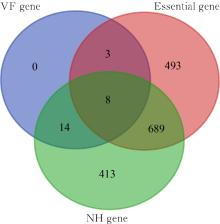
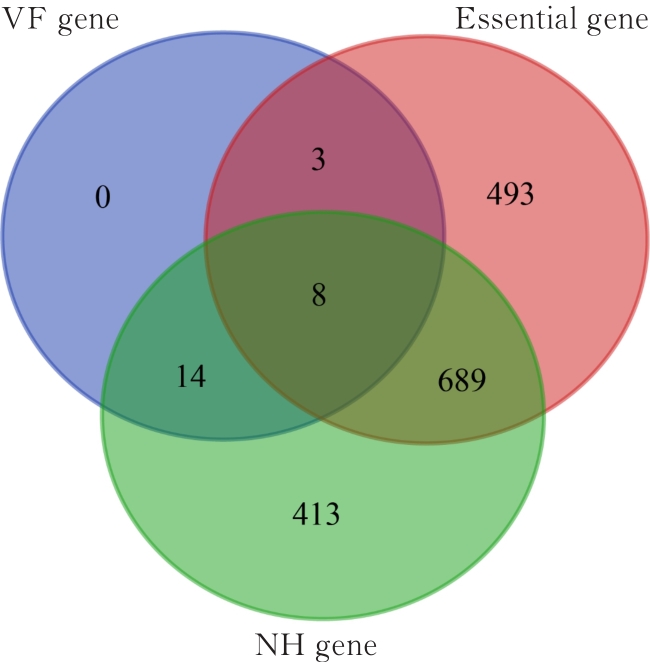
| 1 |
CHEUNG G Y C, BAE J S, OTTO M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Virulence, 2021, 12(1): 547-569.
|
| 2 |
刘东宁, 杨明锡, 刘歆婵, 等. 锌掺杂碳点联合蓝光照射对金黄色葡萄球菌生长及其生物膜形成的抑制作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(3): 515-522, 674.
|
| 3 |
QIN P, LU H W, DU H L, et al. Pan-genome analysis of 33 genetically diverse rice accessions reveals hidden genomic variations[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(13): 3542-3558.e16.
|
| 4 |
CAPUTO A, FOURNIER P E, RAOULT D. Genome and pan-genome analysis to classify emerging bacteria[J]. Biol Direct, 2019, 14(1): 5.
|
| 5 |
IRFAN M, TARIQ M, BASHARAT Z, et al. Genomic analysis of Chryseobacterium indologenes and conformational dynamics of the selected DD-peptidase[J]. Res Microbiol, 2023, 174(1/2): 103990.
|
| 6 |
BASHARAT Z, AKHTAR U, KHAN K, et al. Differential analysis of Orientia tsutsugamushi genomes for therapeutic target identification and possible intervention through natural product inhibitor screening[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2022, 141: 105165.
|
| 7 |
ALI A, KHATOON A, MIRZA T, et al. Intensification in genetic information and acquisition of resistant genes in genome of Acinetobacter baumannii: a pan-genomic analysis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 2022: 3186343.
|
| 8 |
YIP S H, SHAM P C, WANG J W. Evaluation of tools for highly variable gene discovery from single-cell RNA-seq data[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2019, 20(4): 1583-1589.
|
| 9 |
LIU B, ZHENG D D, ZHOU S Y, et al. VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(D1): D912-D917.
|
| 10 |
RASHIDI S, FARAJI S N, MAMAGHANI A J, et al. Bioinformatics analysis for the purpose of designing a novel multi-epitope DNA vaccine against Leishmania major[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 18119.
|
| 11 |
RAHMAN N, MUHAMMAD I, NAYAB G E, et al. In-silico subtractive proteomic analysis approach for therapeutic targets in MDR salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar typhi str. CT18[J]. Curr Top Med Chem, 2019, 19(29): 2708-2717.
|
| 12 |
SILVA M A, NASCIMENTO JÚNIOR J C D, THOMAZ D V, et al. Comparative homology of Pleurotus ostreatus laccase enzyme: Swiss model or Modeller?[J]. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2023, 41(18): 8927-8940.
|
| 13 |
LIU W B, OU P Y, TIAN F Y, et al. Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus compounds from Streptomyces parvus based on Pan-genome and subtractive proteomics[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1218176.
|
| 14 |
KARAKKADPARAMBIL SANKARAN S, NAIR A S. Molecular dynamics and docking studies on potentially active natural phytochemicals for targeting SARS-CoV-2 main protease[J]. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2023, 41(14): 6459-6475.
|
| 15 |
IBRAHIM A A, EL-HOUSSEINY G S, ABOSHANAB K M, et al. Paromomycin production from Streptomyces rimosus NRRL 2455: statistical optimization and new synergistic antibiotic combinations against multidrug resistant pathogens[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2019, 19(1): 18.
|
| 16 |
HARTZEN S H, FRIMODT-MØLLER N, THOMSEN V F. The antibacterial activity of a siderophore. 2. The influence of deferoxamine alone and combined with ascorbic acid on the activity of antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus [J]. APMIS, 1991, 99(10): 879-886.
|
| 17 |
CUI K Y, YANG W F, LIU Z Y, et al. Chenodeoxycholic acid-amikacin combination enhances eradication of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2023, 11(1): e0243022.
|
| 18 |
MARHAUG G, BRATLID D, MOE P J. Effect of methotrexate on phagocytosis and killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human granulocytes[J]. Scand J Infect Dis, 1980, 12(1): 61-65.
|
| 19 |
HU Y, WU Y F, JIANG C P, et al. Investigative on the molecular mechanism of licorice flavonoids anti-melanoma by network pharmacology, 3D/2D-QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Front Chem, 2022, 10: 843970.
|
| 20 |
LOPATKIN A J, BENING S C, MANSON A L, et al. Clinically relevant mutations in core metabolic genes confer antibiotic resistance[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6531): eaba0862.
|
| 21 |
DE BACKER M D, VAN DIJCK P. Progress in functional genomics approaches to antifungal drug target discovery[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2003, 11(10): 470-478.
|
| 22 |
SHARMA D, SHARMA A, SINGH B, et al. Pan-proteome profiling of emerging and re-emerging zoonotic pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi for getting insight into microbial pathogenesis[J]. Microb Pathog, 2021, 158: 105103.
|
| 23 |
RIDA T, AHMAD S, ULLAH A, et al. Pan-genome analysis of oral bacterial pathogens to predict a potential novel multi-epitopes vaccine candidate[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(14): 8408.
|
| 24 |
BAKHEET T M, DOIG A J. Properties and identification of human protein drug targets[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(4): 451-457.
|
| 25 |
BHATTACHARYA M, HOTA A, KAR A, et al. In silico structural and functional modelling of Antifreeze protein (AFP) sequences of Ocean pout (Zoarces americanus, Bloch & Schneider 1801)[J]. J Genet Eng Biotechnol, 2018, 16(2): 721-730.
|
| 26 |
KHAN K, BASHARAT Z, JALAL K, et al. Identification of therapeutic targets in an emerging gastrointestinal pathogen Campylobacter ureolyticus and possible intervention through natural products[J]. Antibiotics, 2022, 11(5): 680.
|
| 27 |
WANDERLEY K, SOUSA D, SILVA G, et al. Tyrosine kinase self-phosphorylation controls exopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus strain Pal5[J]. Life, 2021, 11(11): 1231.
|
| 28 |
FERREIRA A S, LEITÃO J H, SOUSA S A, et al. Functional analysis of Burkholderia cepacia genes bceD and bceF, encoding a phosphotyrosine phosphatase and a tyrosine autokinase, respectively: role in exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and biofilm formation[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2007, 73(2): 524-534.
|
| 29 |
PELLETIER A, FRETON C, GALLAY C, et al. The tyrosine-autokinase UbK is required for proper cell growth and cell morphology of Streptococcus pneumoniae [J]. Front Microbiol, 2019, 10: 1942.
|
| 30 |
耿 月, 朱晓玥, 周小华, 等. 五氟苯基柱HPLC-PAD法测定硫酸巴龙霉素含量及有关物质[J]. 中国药学杂志, 2022, 57(16): 1380-1386.
|
| 31 |
赖思含, 刘俊彤, 谭璐瑩, 等. 西洋参茎叶三醇组皂苷抗缺血性脑卒中作用机制的网络药理学和分子对接分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023, 49(4): 913-922.
|
| 32 |
LIU W B, LI E T, LIU L Y, et al. Antifungal activity of compounds from Gordonia sp. WA8-44 isolated from the gut of Periplaneta americana and molecular docking studies[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(7): e17777.
|
 )
)
 )
)