吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 759-769.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240320
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
基于红景天苷对三阴性乳腺癌关键差异基因作用机制的生物信息学和分子对接技术分析
- 1.吉林大学第一医院乳腺外科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学基础医学院药理学系,吉林 长春 130021
3.吉林大学第一医院普通妇一科,吉林 长春 130021
4.吉林大学第一医院 耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科,吉林 长春 130021
Bioinformatics and molecular docking technology analysis on mechanism of salidroside on key differential genes of triple negative breast cancer
Zijia ZHU1,Xia CHEN2,Man CUI3,Jihong WEN3,Ping WANG4,Dong SONG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Breast Surgery, First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
2.Department of Pharmacology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
3.Department of General Gynecology, First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
4.Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
摘要:
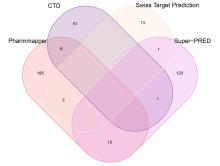
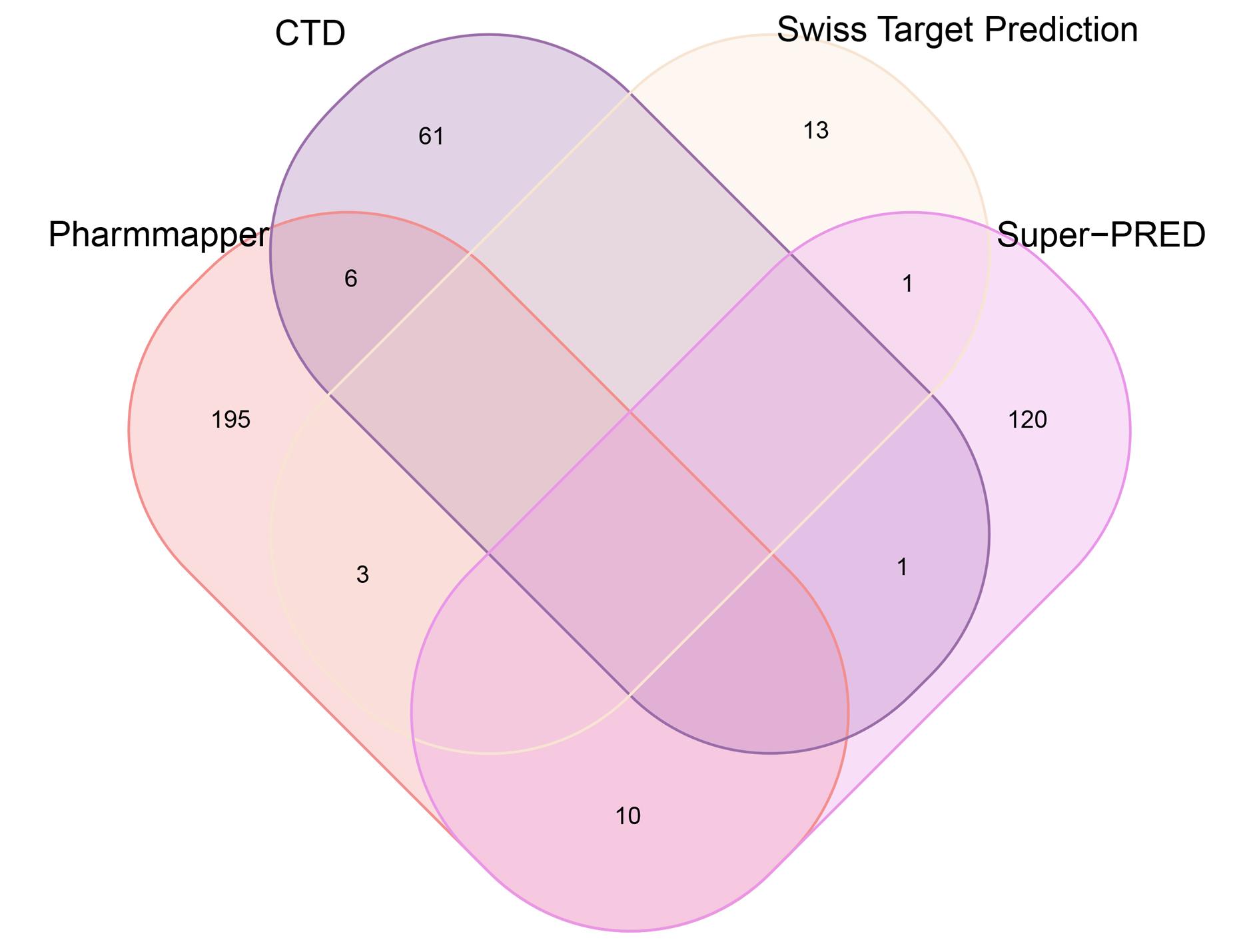
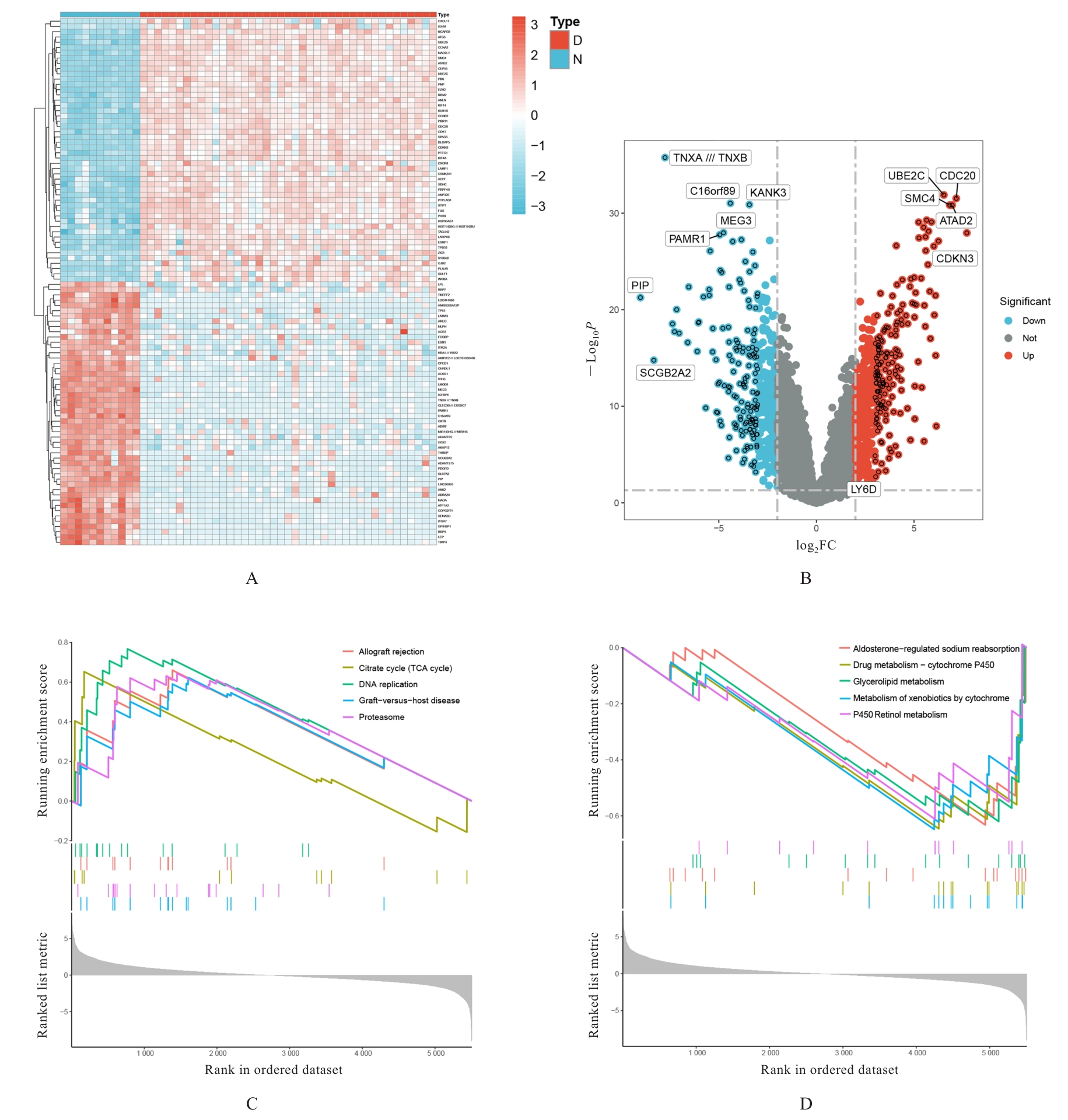
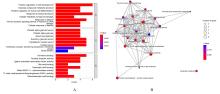
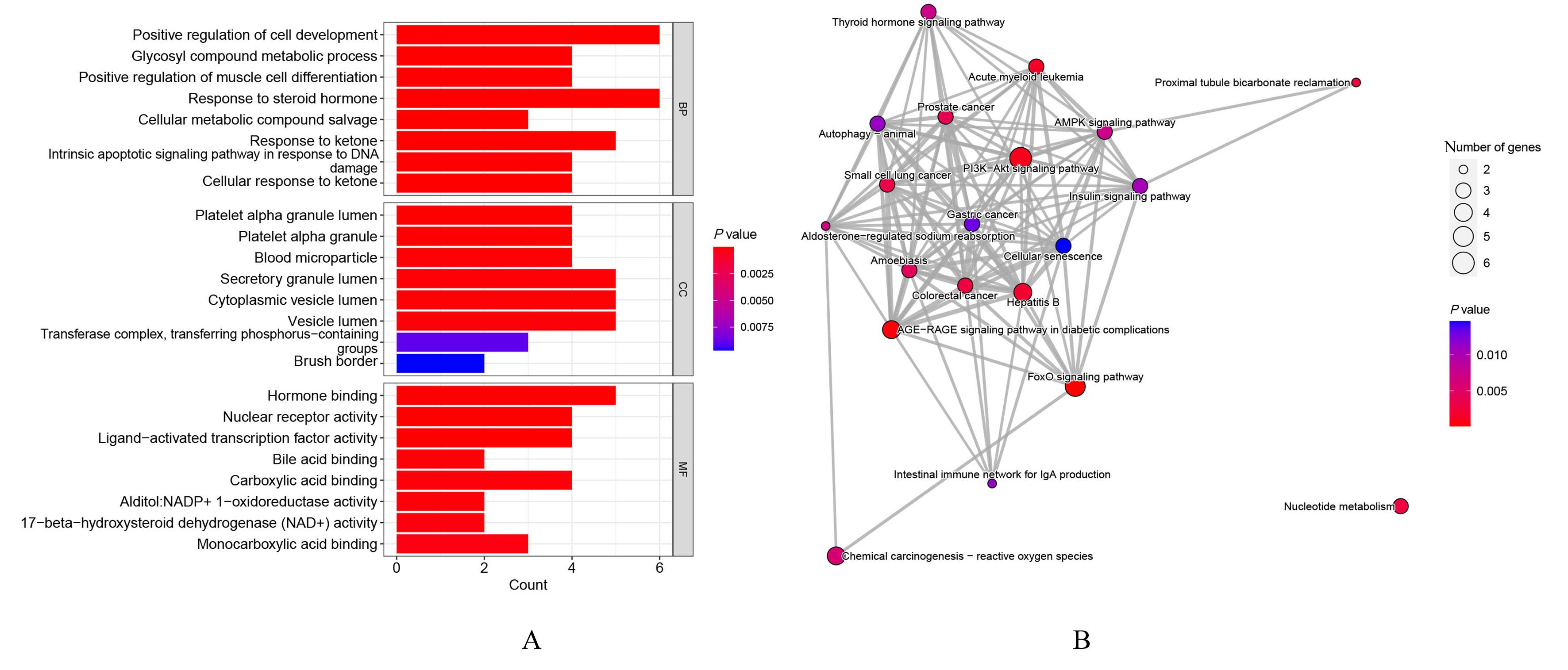
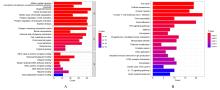
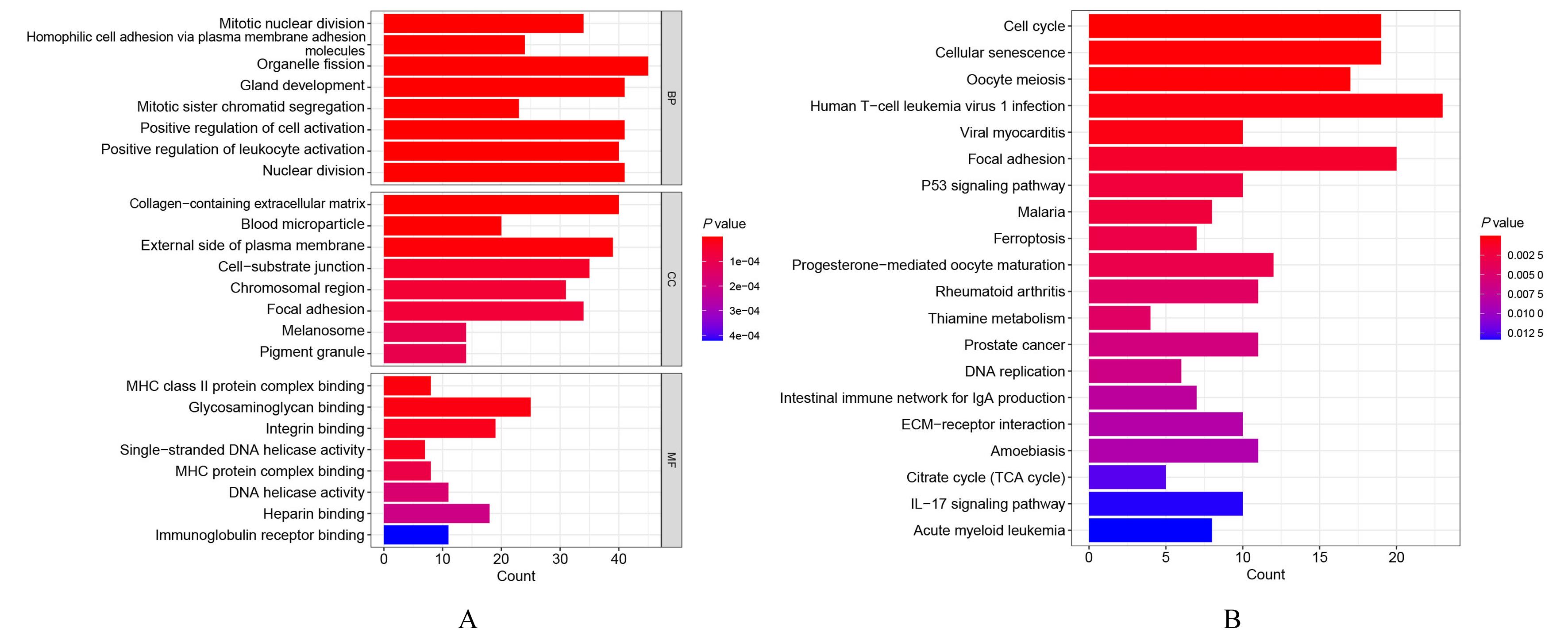
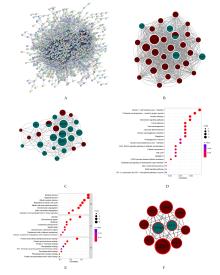
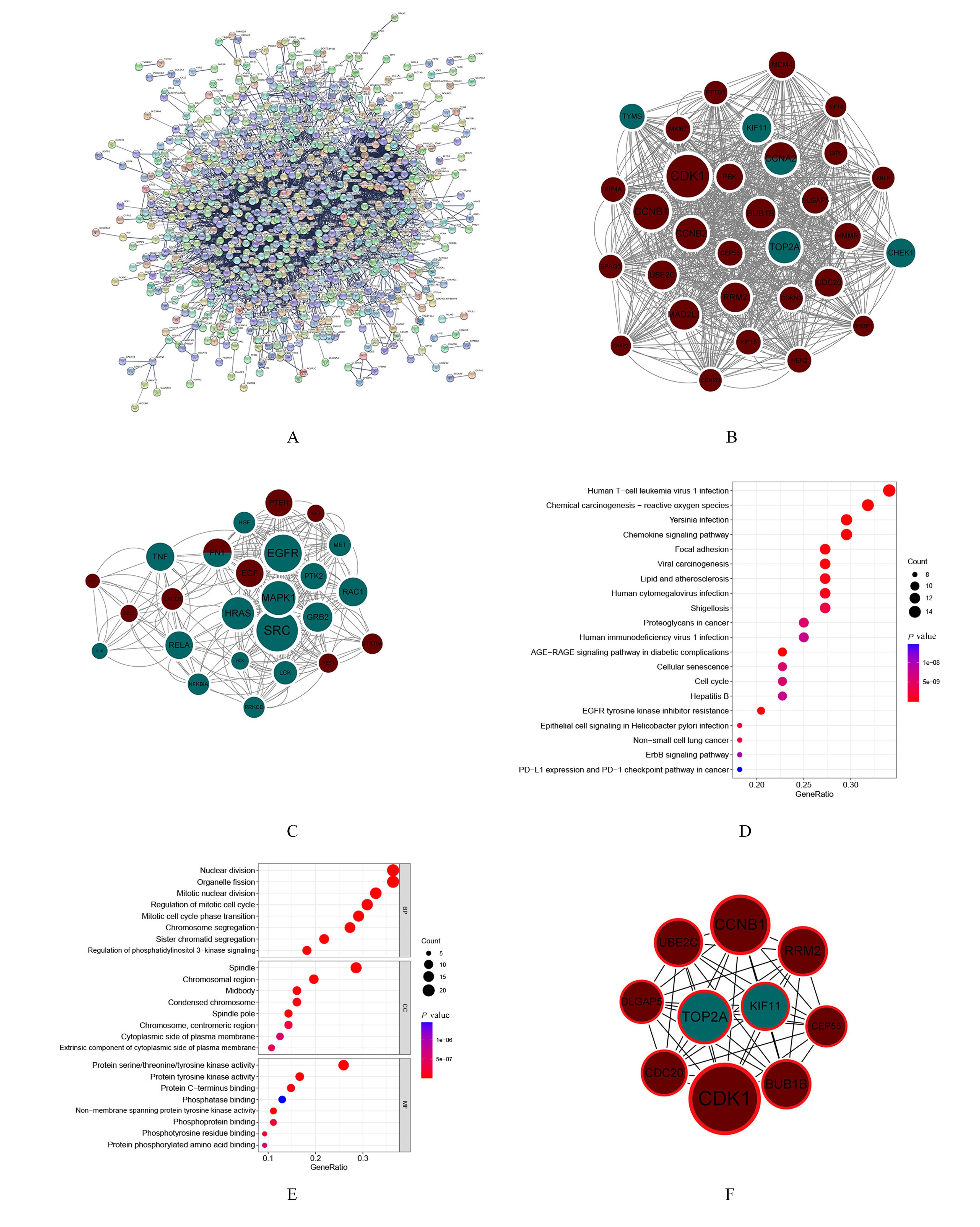
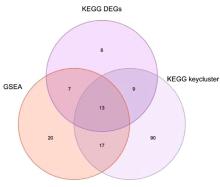
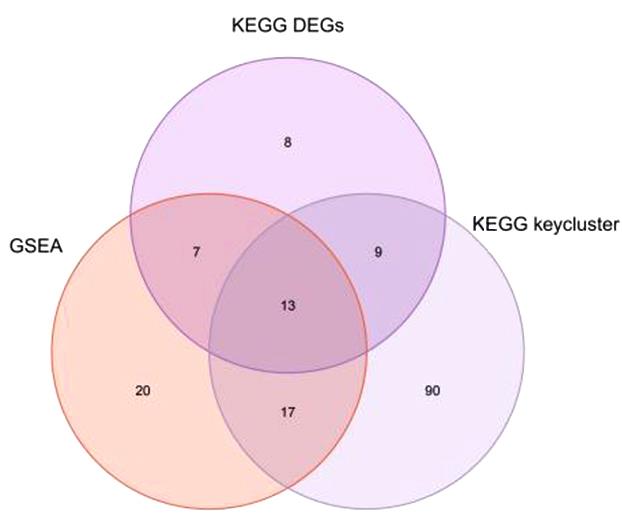
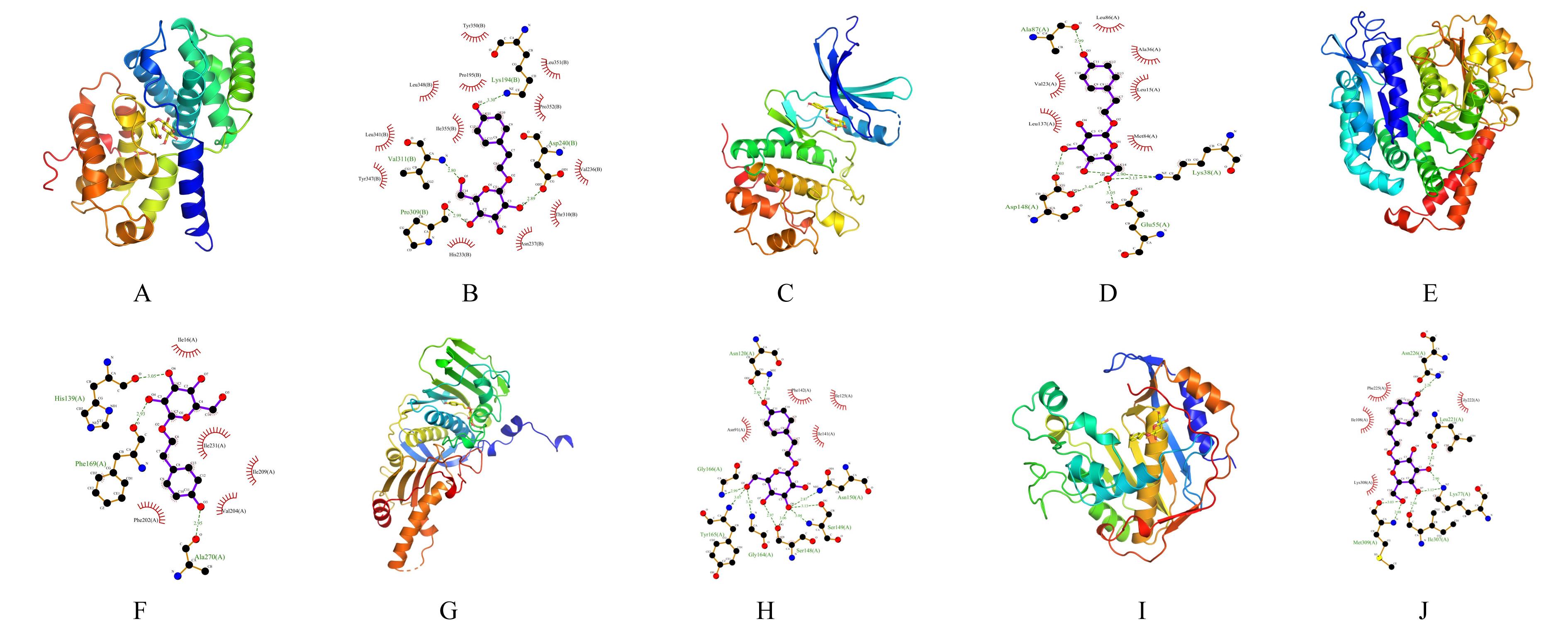
目的 通过生物信息学和网络药理学方法探讨红景天苷治疗三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)的作用机制,阐明其产生治疗作用的主要靶点和信号通路。 方法 通过基因表达综合数据库(GEO)获取数据集 GSE45827,利用R软件包GSEABase进行基因集富集分析(GSEA),采用limma R软件包寻找相邻正常组织和TNBC组织之间的差异表达基因(DEGs),对DEGs进行基因本体论(GO)功能富集分析和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)信号通路富集分析,将DEGs与药物靶点结合,导入基因/蛋白相互作用检索搜查工具String数据库,形成蛋白-蛋白相互作用 (PPI)网络。使用MCODE插件对 PPI网络进行功能模块筛选,对SCORE值排名前2位的关键模块基因再次进行GO功能富集分析和KEGG信号通路富集分析。将2次KEGG富集分析所得通路与转录组数据GSEA富集分析结果取交集,获得红景天苷治疗TNBC的作用通路。使用CytoHubba插件计算出关键模块中最大团中心性(MCC)评分前 10 位的关键节点基因, 即为核心基因。 应用 AutoDock Vina 1.1.2 和PyMOL 2.3.0软件完成分子对接。 结果 KEGG与GSEA富集分析的结果取交集得到13条共同通路,涉及细胞周期、细胞衰老和p53信号通路等。GO功能富集分析结果中所涉及的有丝分裂、核分裂和姐妹染色单体分离等生物学过程与细胞周期有密切关联,与KEGG富集分析结果一致。SCORE值排名第1位的关键模块中包含5个红景天苷药物作用靶点,分别为重组人细胞周期蛋白A2(CCNA2)、细胞周期检查点激酶1(CHEK1)、驱动蛋白家族成员11(KIF11)、DNA拓扑异构酶2(TOP2A)和胸腺嘧啶酸合酶(TYMS),将上述蛋白与红景天苷进行分子对接,结果均表现出很强的结合能力(结合能<-7.0 kcal·mol-1)。 结论 红景天苷的紧密结合靶标位于TNBC的DEGs关键功能模块中,可以与CCNA2蛋白结合产生直接的调控作用,与KIF11、TOPA2、CHEK1和TYMS蛋白结合可针对TNBC的关键节点基因产生间接的调控作用,红景天苷有可能成为TNBC的临床治疗药物。
中图分类号:
- R737.9