吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 1117-1123.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200602
芦丁对肝细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用及其机制
- 延边大学基础医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,吉林 延吉 133002
Protective effect of rutin on oxidative stress injury of HepG2 cells and its mechanism
Fangduo JIN,Tian ZHANG,Zhao ZHANG,Xuezhe YIN,Jishu QUAN( )
)
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
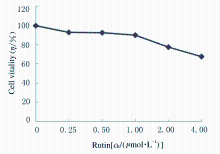
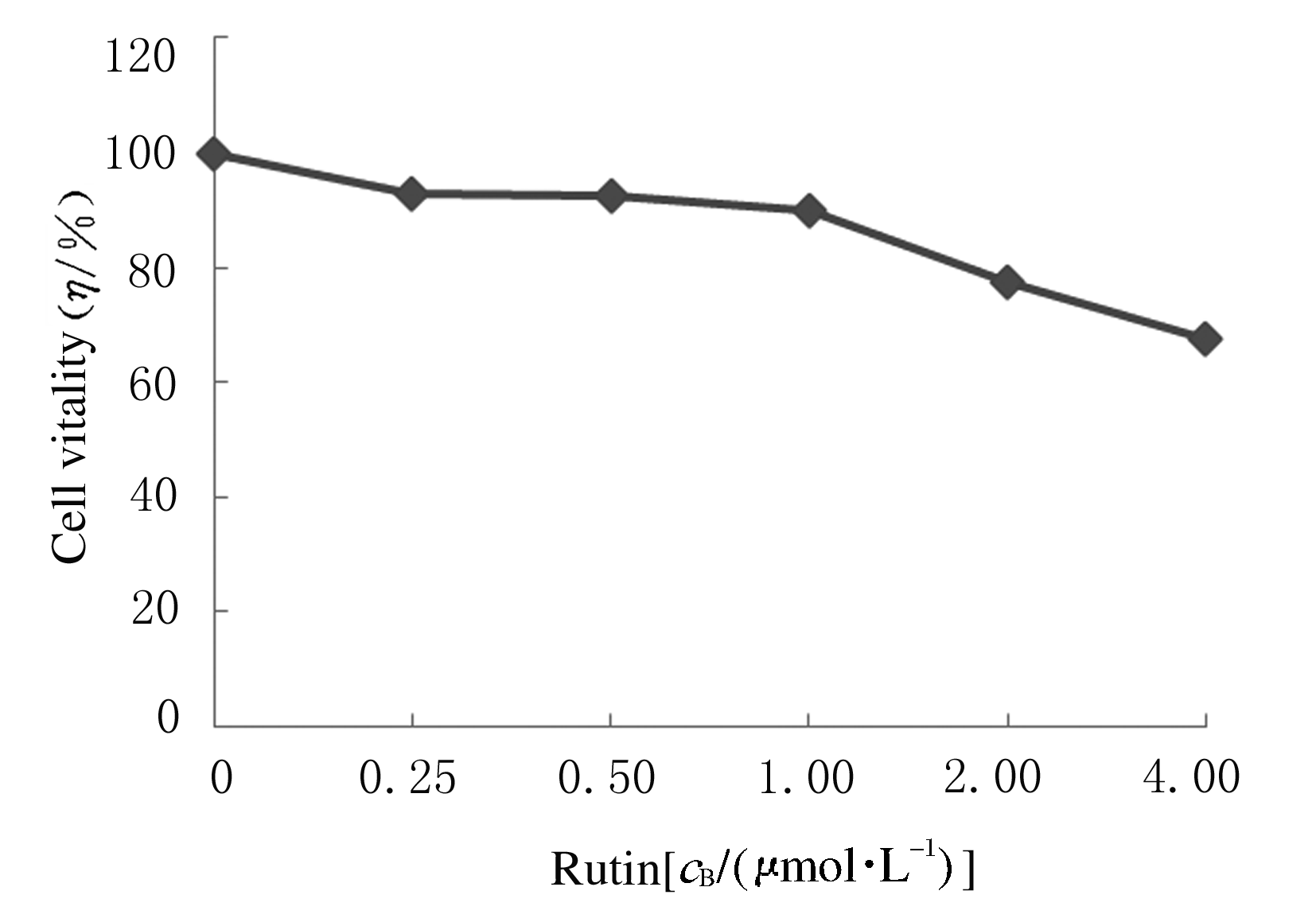
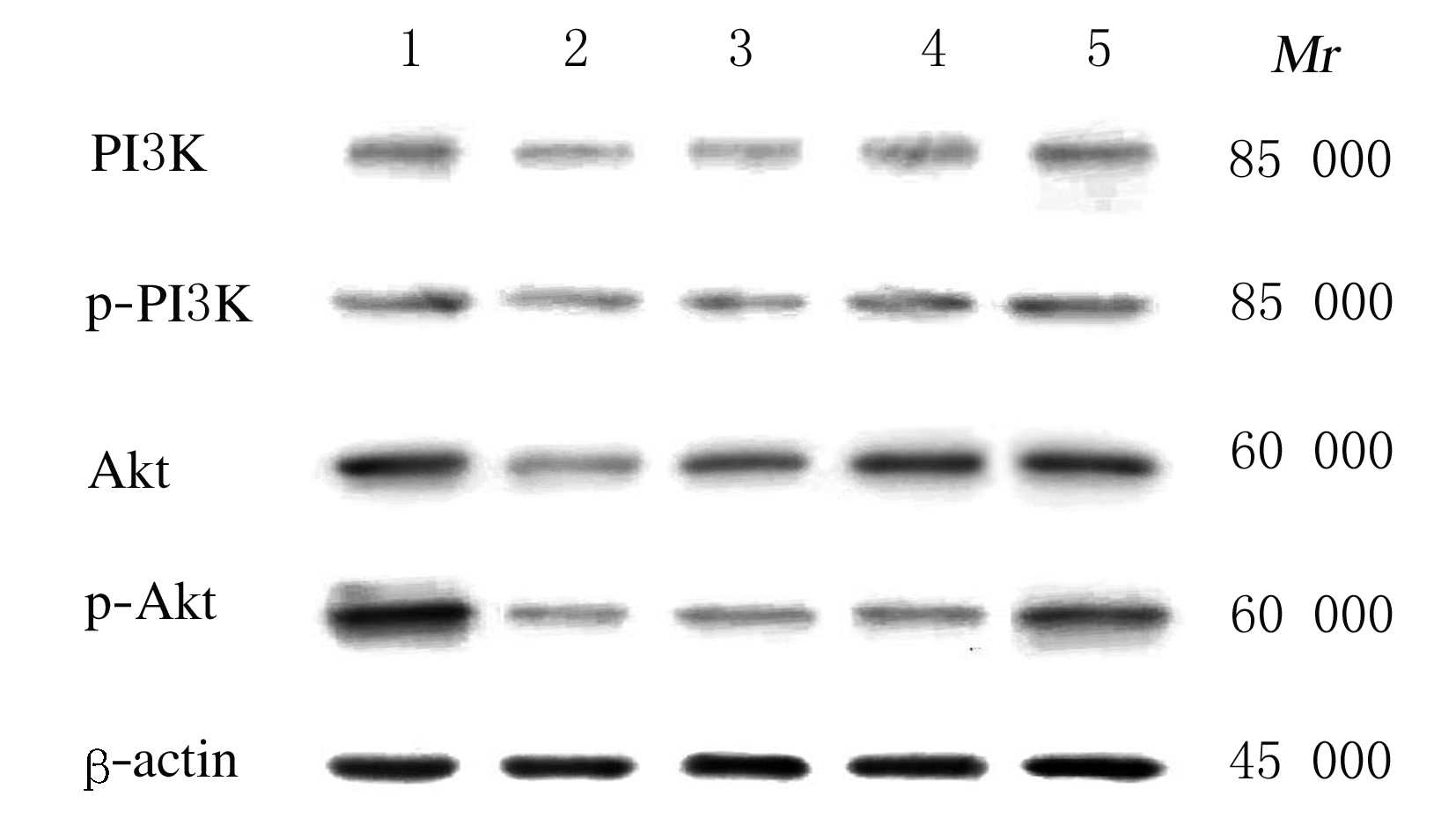
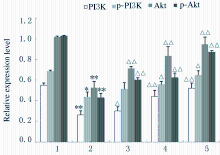
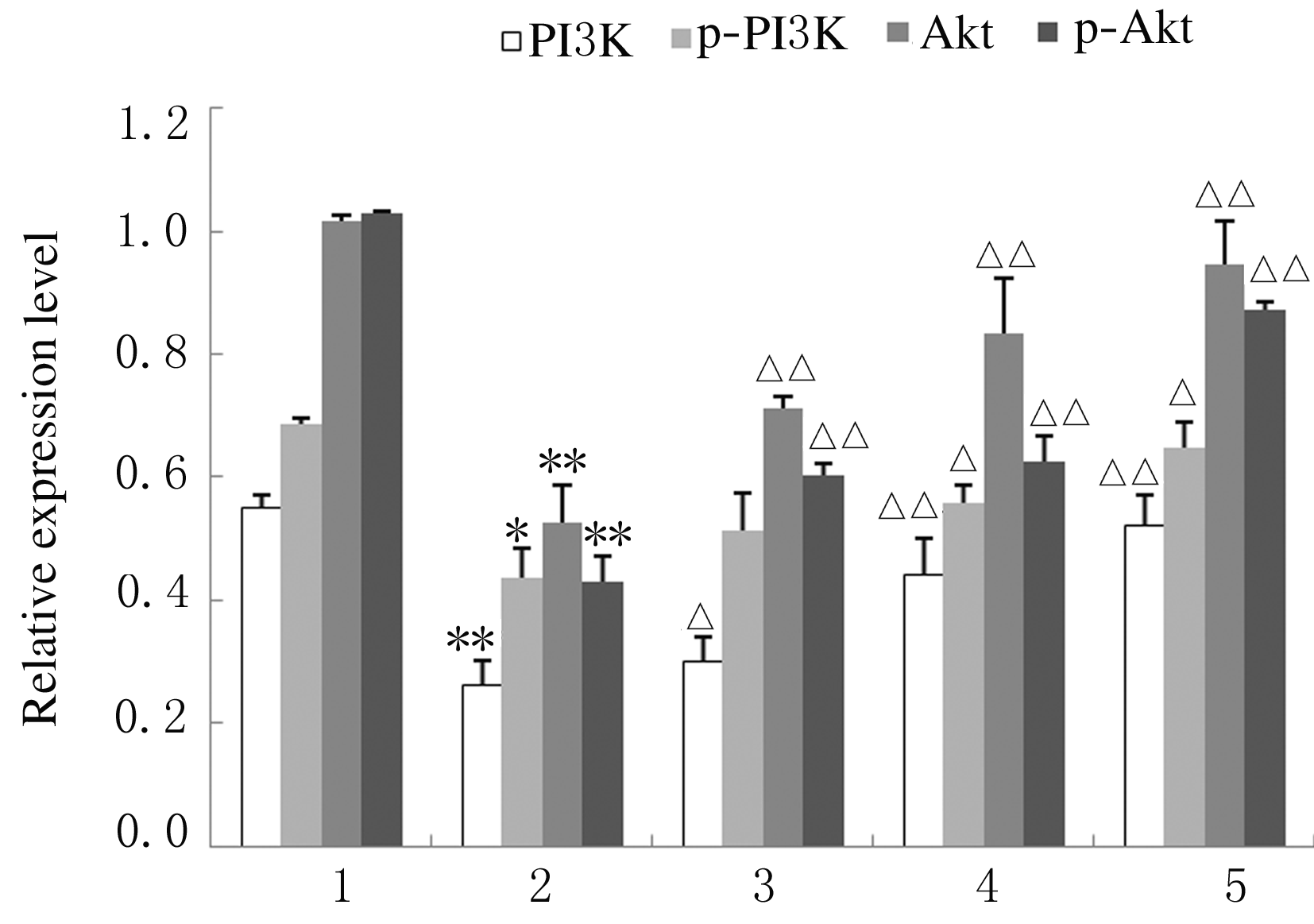
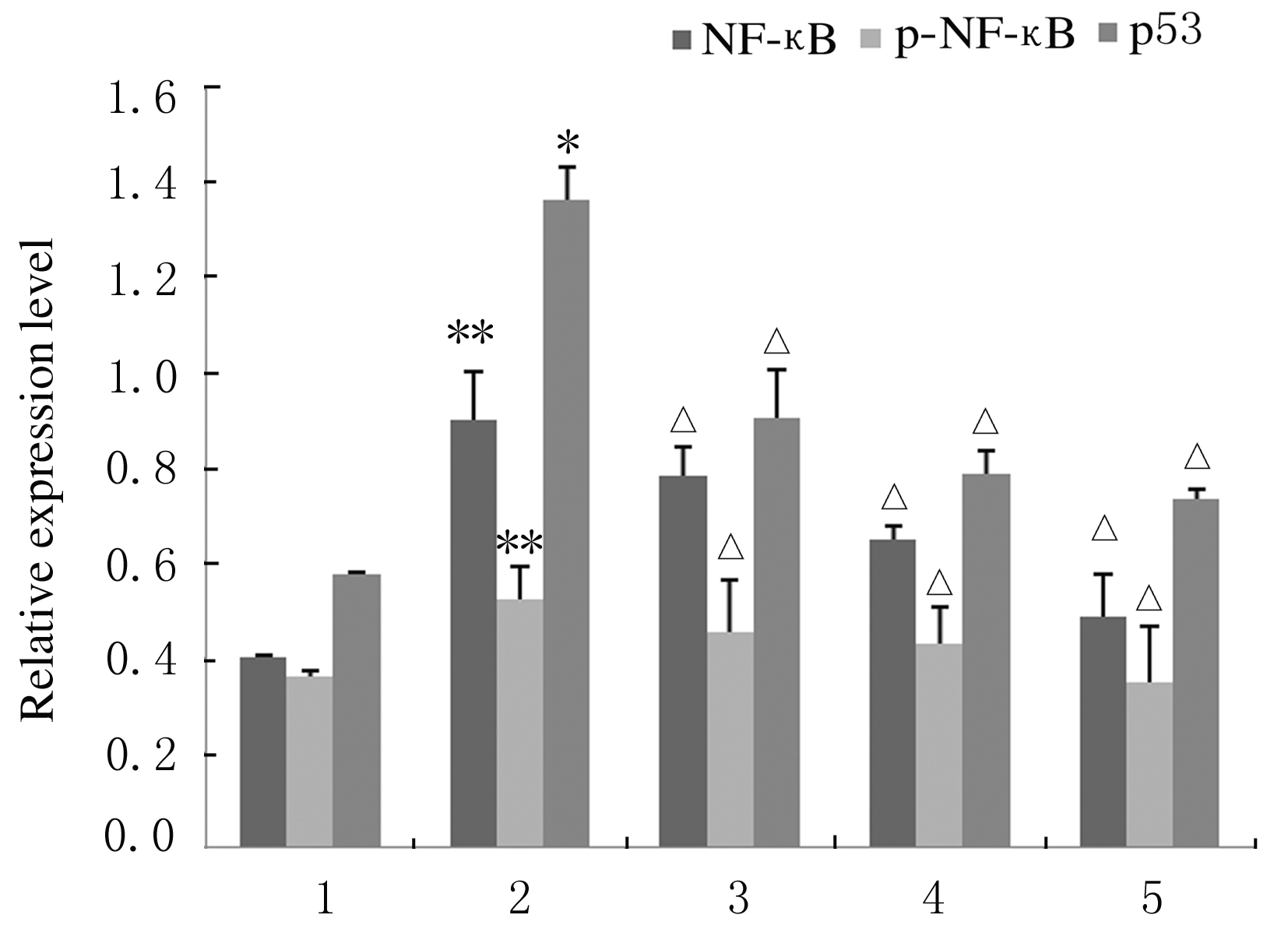
摘要: 探讨芦丁对肝癌HepG2细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用,并阐明其作用机制。 培养人肝癌HepG2细胞,取处于对数生长期的HepG2细胞分为对照组、叔丁基过氧化氢(TBHP)组(给予400 μmol·L-1TBHP)和0.25、0.50、1.00 μmolL-1芦丁组(给予0.25、0.50和1.00 μmol·L-1芦丁+400 μmol·L-1 TBHP)。采用四甲基偶氮唑盐(MTT)法检测各组HepG2细胞活性和各组肝癌HepG2细胞存活率,比色法检测各组肝癌HepG2细胞中丙二醛(MDA)和还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)水平及超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,采用二氯荧光素乙酰乙酸盐(DCFH-DA)荧光染色法检测各组肝癌HepG2细胞中活性氧(ROS)水平,Western blotting法检测各组肝癌HepG2细胞中磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(PI3K)、磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(p-PI3K)、蛋白激酶B(Akt)、磷酸化AktB(p-Akt)、核转录因子κB(NF-κB)、磷酸化NF-κB(p-NF-κB)和p53蛋白表达水平。 MTT检测,芦丁摩尔浓度≤1 μmol·L-1时,肝癌HepG2细胞的存活率均>90%,不显示细胞毒性;当芦丁摩尔浓度>1 μmol·L-1时,肝癌HepG2细胞存活率逐渐降低,均<90%,显示细胞毒性。与对照组比较,TBHP组HepG2细胞存活率明显降低(P<0.01);与TBHP组比较,不同浓度芦丁组HepG2细胞存活率明显升高(P<0.01)。比色法检测,与对照组比较,TBHP组肝癌HepG2细胞中MDA水平明显升高(P<0.01),GSH水平和SOD活性明显降低(P<0.01);与TBHP组比较,不同浓度芦丁组肝癌HepG2细胞中MDA水平明显降低(P<0.01),GSH水平和SOD活性明显升高(P<0.01)。DCFH-DA染色,与对照组比较,TBHP组肝癌HepG2细胞中ROS水平明显升高;与TBHP组比较,不同浓度芦丁组肝癌HepG2细胞中ROS水平降低。Western blotting法检测,与对照组比较,TBHP组肝癌HepG2细胞中PI3K、p-PI3K、Akt和p-Akt蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),NF-κB、p-NF-κB和p53蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05);与TBHP组比较,不同浓度芦丁组肝癌HepG2细胞中PI3K、p-PI3K、Akt和p-Akt蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),NF-κB、p-NF-κB和p53蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 芦丁对肝癌HepG2细胞损伤具有保护作用,其机制可能与调控PI3K/Akt和NF-κB两条信号通路有关联。
中图分类号:
- R282.7