吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 1169-1176.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200610
电离辐射对小鼠骨髓造血干/祖细胞中CD47表达的影响
- 吉林大学第一医院转化医学研究院 人类疾病动物模型国家地方联合工程实验室,吉林 长春 130062
Effect of ionizing irradiation on expression of CD47 in bone marrow hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in mice
Guangyao XIE,Feng WANG,Ting ZHANG,Yanhou LIU( ),Yongguang YANG(
),Yongguang YANG( )
)
- Academy of Translational Medicine,National-Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Animal Models for Human Diseases,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
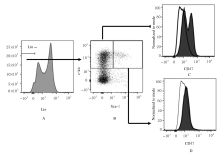
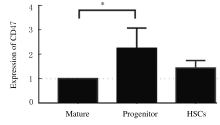
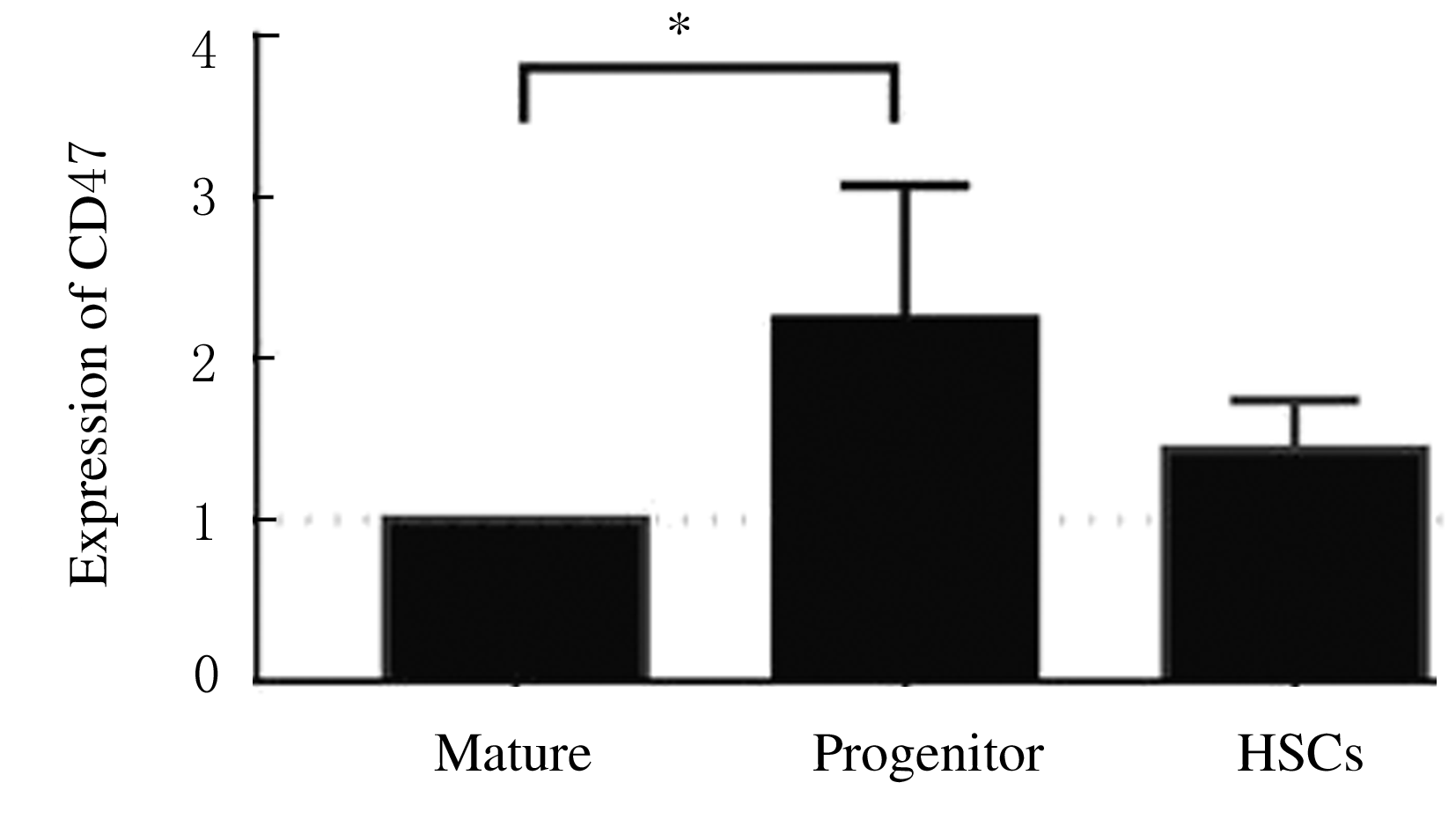
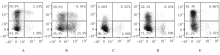
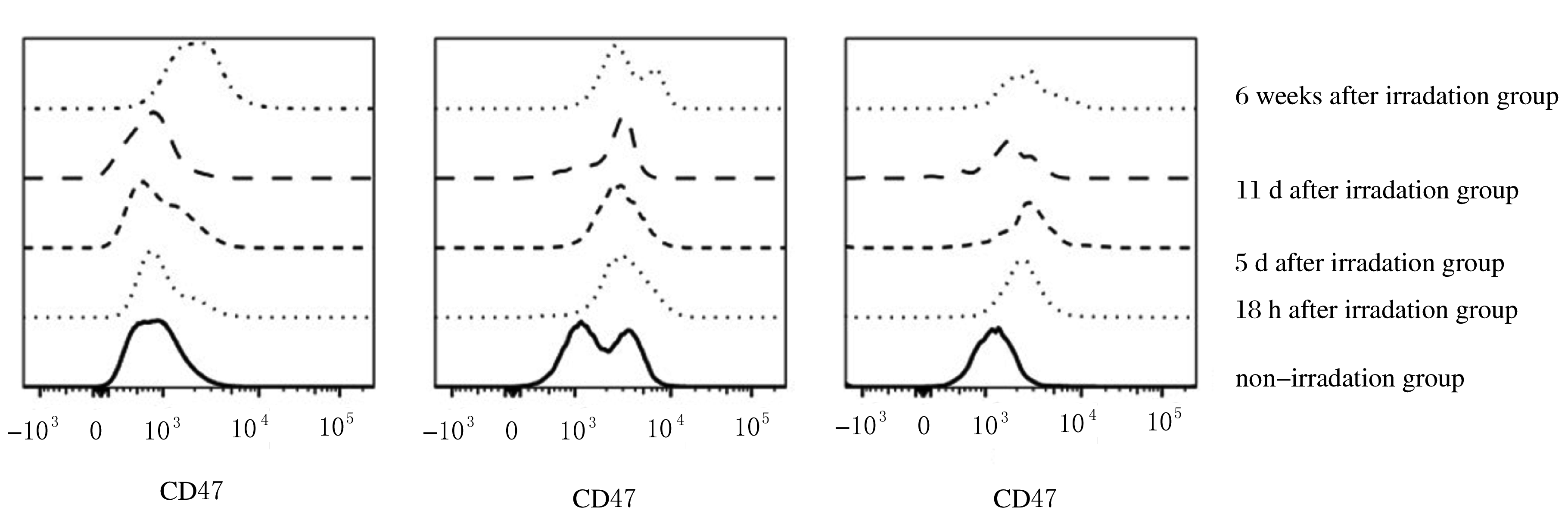
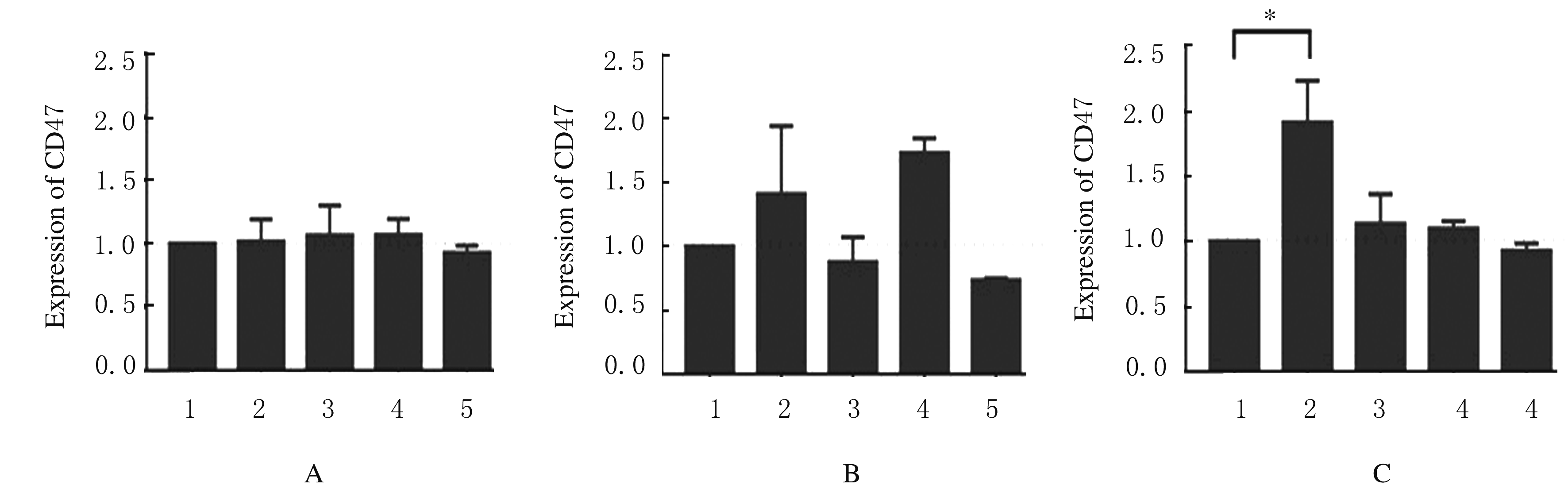
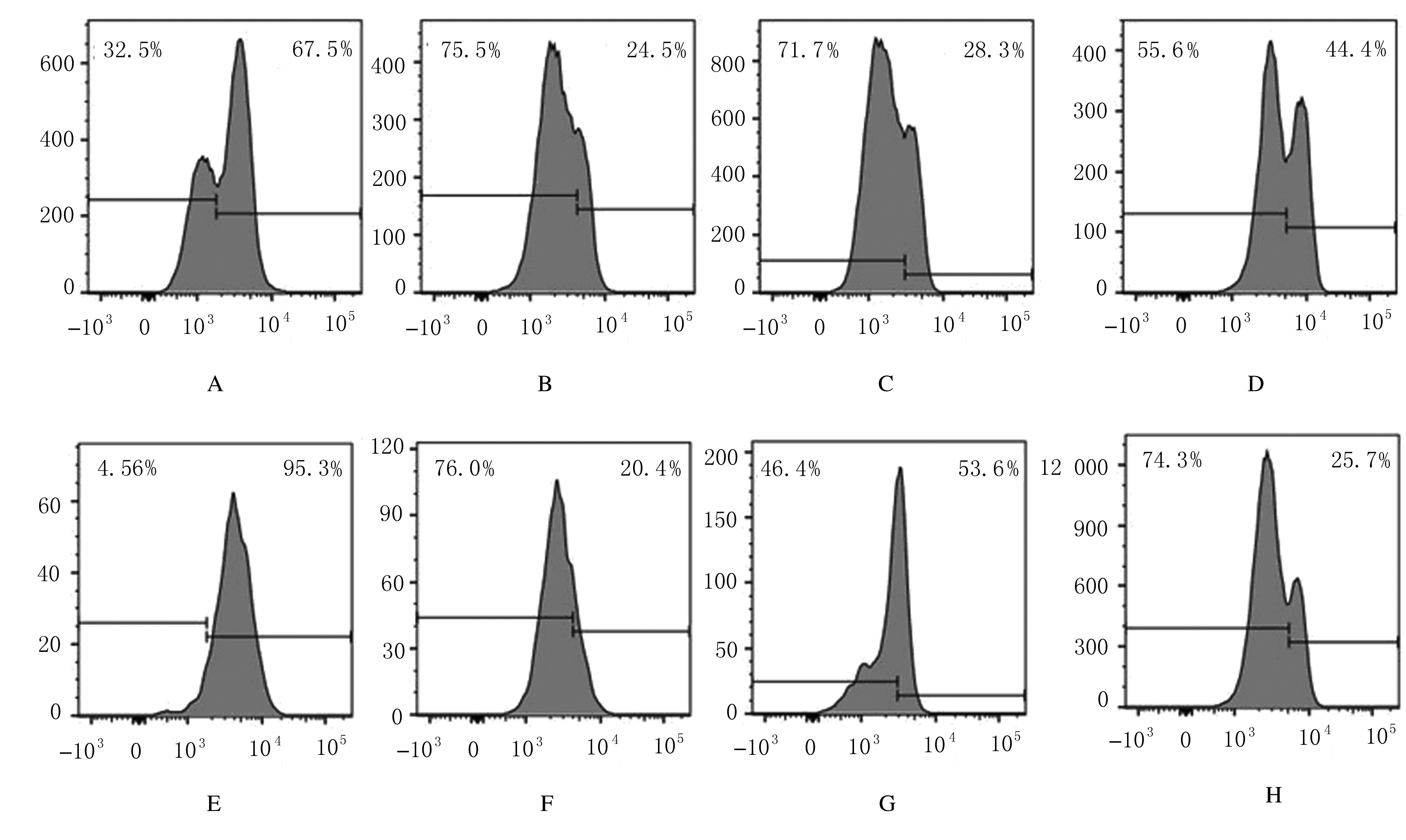
摘要: 探讨X射线全身照射后小鼠骨髓造血干/祖细胞(HSCs/HPCs)损伤和其中CD47表达水平的变化,初步阐明CD47在HSCs/HPCs电离辐射损伤中发挥的作用。 将C57BL/6小鼠分为未照射组和照射组,其中照射组分为照射后18 h组、5 d组、11 d组和6 周组,每组5只。除未照射组小鼠外,其他小鼠均一次性给予3.0或9.0 Gy X射线全身照射。在照射后相应时间点处死小鼠,流式细胞术检测各组小鼠骨髓HSCs与HPCs的百分率。检测照射后各时间点各组小鼠HSCs和HPCs 中CD47表达水平。 未照射组小鼠HSCs中CD47表达水平高于骨髓成熟造血系细胞1倍以上(P<0.01)。X射线照射后18 h、5 d与11 d后,与未照射组比较,照射组小鼠HSCs中 CD47表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);HPCs占lineage-negative(lin-)细胞百分率或占全骨髓细胞百分率降低(P<0.05),照射后6 周HSCs百分率恢复至正常水平。与未照射组比较,照射后18 h HSCs中CD47表达水平差异明显升高(P<0.01),照射后5 d、11 d和6 周组小鼠HSCs中CD47表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);照射后18 h组小鼠HSCs占lin-细胞百分率升高(P<0.01),照射后11 d组小鼠HSCs占全骨髓细胞百分率降低(P<0.01)。照射后18 h组小鼠HPCs中CD47低表达亚群的百分率明显低于CD47高表达亚群(P<0.01)。照射后5 d 组、照射后11 d组和照射组后6周组小鼠HPCs中CD47低表达亚群的百分率与CD47高表达亚群的百分率相近。 全身电离辐射造成了小鼠骨髓组织损伤,在骨髓细胞中HSCs/HPCs百分率降低,其机制可能与照射后HSCs中CD47表达一过性升高有关联。
中图分类号:
- R144.1