吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 133-138.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210118
妊娠期糖尿病对新生子代大鼠膈肌功能的影响
- 1.河南省郑州市妇幼保健院产科,河南 郑州 450012
2.郑州大学第一附属医院产科,河南 郑州 450000
3.吉林大学第一医院生殖中心,吉林 长春 130021
Effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on diaphragmatic function of newborn offsprings of rats
Ruili ZHANG1,Xiaoqing YANG1,Xiaoge ZHANG2,Huafeng GUO1( ),Jihong ZHU3(
),Jihong ZHU3( )
)
- 1.Department of Obstetrics,Women and Infants Hospital of Zhengzhou,Henan Province,Zhengzhou 450012,China
2.Department of Obstetrics,First Affiliated Hospital,Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450000,China
3.Department of Reproductive Center,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
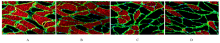
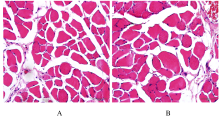
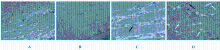
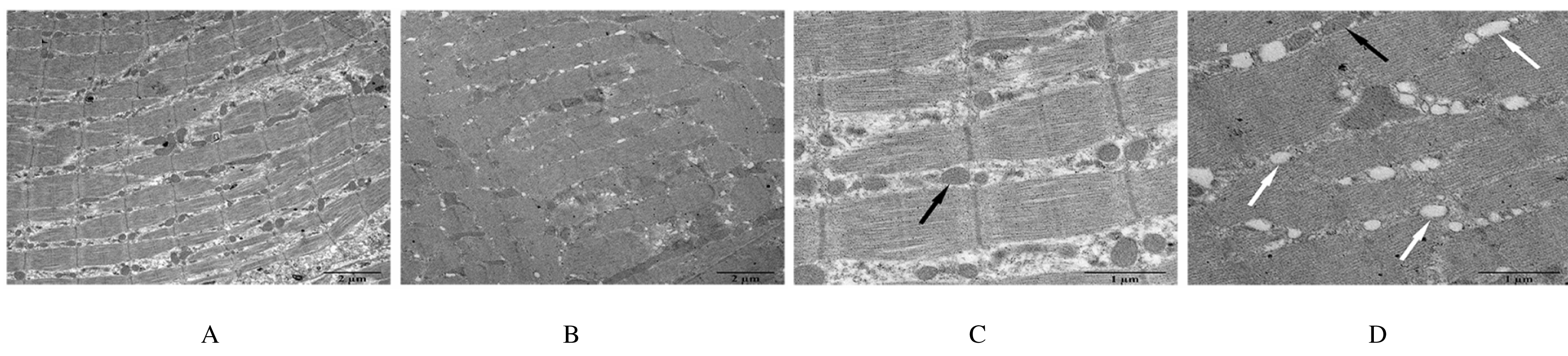
摘要: 探讨妊娠期糖尿病(GDM)对新生子代大鼠膈肌功能和氧化应激水平的影响,阐明其可能作用机制。 44只怀孕的8周龄SD雌性大鼠随机分为正常对照组和GDM模型组。妊娠第1天,GDM组大鼠单次腹腔注射35 mg·kg-1 链脲佐菌素(STZ),建立GDM大鼠模型(建模成功18只);正常对照组大鼠单次腹腔注射相同体积的柠檬酸-柠檬酸钠缓冲液。分娩后,体外检测2组新生子代大鼠的膈肌收缩力,免疫荧光法检测子代大鼠膈肌纤维横截面积,常规HE染色观察子代大鼠膈肌病理形态表现,透射电镜下观察子代大鼠膈肌超微结构,采用试剂盒检测子代大鼠膈肌组织中丙二醛(MDA)和羰基化蛋白水平及超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性。 体外膈肌收缩力检测,与正常对照组比较,GDM组子代大鼠膈肌最大紧张收缩力、最大强直收缩力和不同刺激频率下的膈肌收缩力均明显降低(P<0.05),膈肌疲劳指数明显升高(P<0.05)。免疫荧光法检测,与正常对照组比较,GDM组子代大鼠膈肌组织中Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型膈肌纤维横截面积均明显缩小(P<0.05)。HE染色,2组子代大鼠膈肌纤维结构完整,排列整齐、致密,膈肌细胞无明显肿胀,细胞核染色清晰。透射电镜下观察,正常对照组子代大鼠膈肌纤维排列整齐,明暗带及“Z”线规整且清晰可见,线粒体结构完整,嵴成隔板状,清晰可见;GDM组子代大鼠膈肌纤维明暗带及“Z”线无规则排列或消失,线粒体数量减少,更多线粒体出现凋亡呈空泡化。与正常对照组比较,GDM组子代大鼠膈肌组织中MDA和羰基化蛋白水平均明显升高(P<0.05),SOD和CAT活性明显降低(P<0.05)。 GDM可引起子代大鼠膈肌收缩力降低、纤维横截面积减小和超微结构改变,而氧化应激水平的升高是影响其膈肌功能的原因之一。
中图分类号:
- R714.25