吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 53-58.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210107
姜黄素对高胆固醇血症模型大鼠脑微循环障碍的改善作用及其机制
李红芳1,杨绍2,曹莫寒3,袁丽丽4,李晓琎4,史才兴4,王茁桠3,亚白柳5( )
)
- 1.济宁医学院附属医院神经内科,山东 济宁 272029
2.济宁医学院中西医结合学院,山东 济宁 272067
3.济宁医学院基础医学院,山东 济宁 272067
4.济宁医学院基础医学院组织学与胚胎学 教研室,山东 济宁 272067
5.济宁医学院基础医学院生理学教研室,山东 济宁 272067
Improvement effect of curcumin on cerebral microcirculation disorder in hypercholesterolemia model rats and its mechanism
Hongfang LI1,Shao YANG2,Mohan CAO3,Lili YUAN4,Xiaojin LI4,Caixing SHI4,Zhuoya WANG3,Bailiu YA5( )
)
- 1.Department of Neurology,Affiliated Hospital,Jining Medical University,Jining 272029,China
2.School of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine,Jining Medical University,Jining 272067,China
3.School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jining Medical University,Jining 272067,China
4.Department of Histology and Embryology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jining Medical University,Jining 272067,China
5.Department of Physiology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jining Medical University,Jining 272067,China
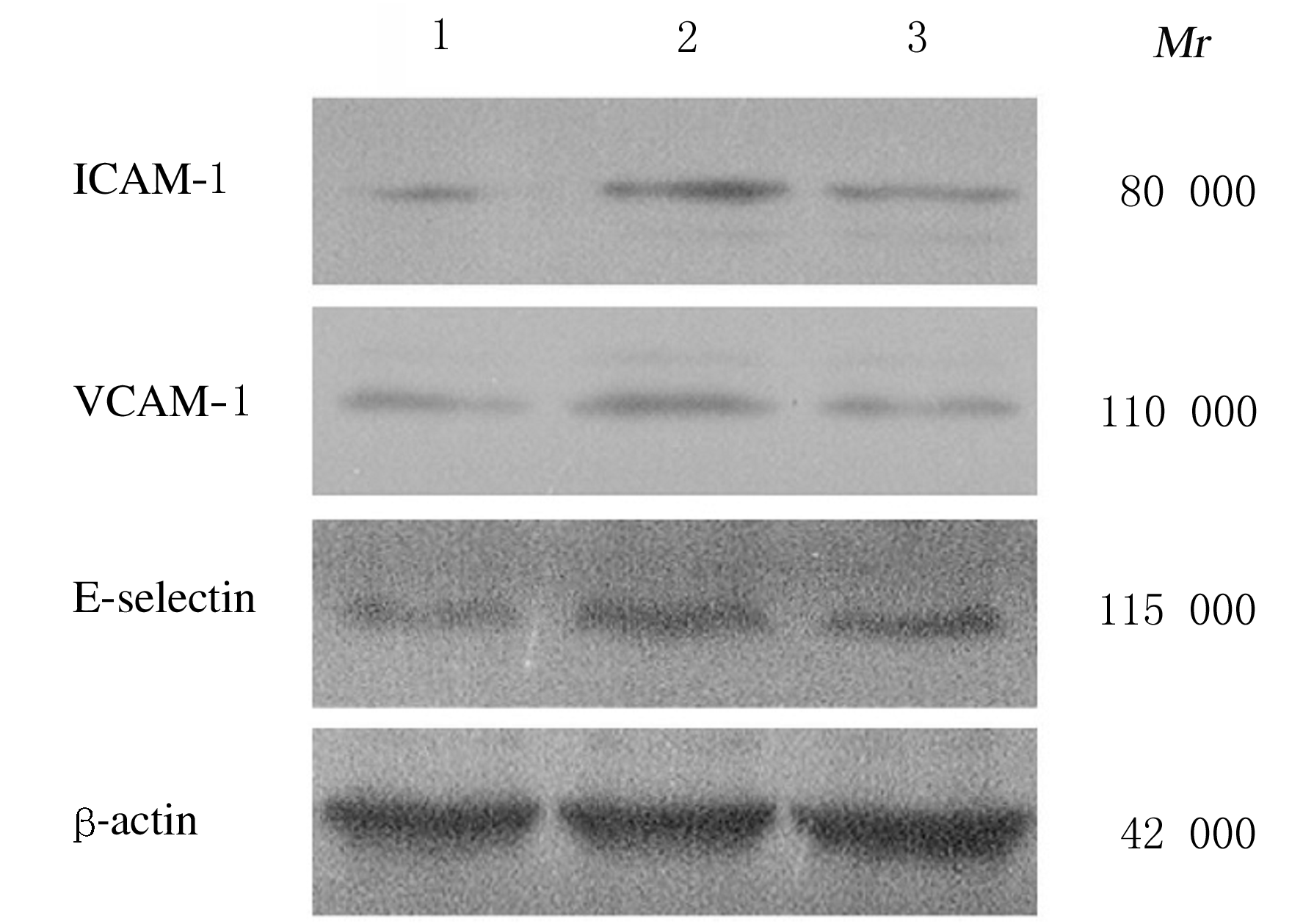
摘要: 探讨姜黄素对高胆固醇饮食致高胆固醇血症模型大鼠脑微循环氧化应激和炎症状态的影响,阐明其作用机制。 30只SD大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组和姜黄素组,每组10只。对照组大鼠每日给予普通饲料,其余2组大鼠每日给予高胆固醇饲料,连续喂饲28 d。造模同时灌胃给药,姜黄素组大鼠给予姜黄素200 mg·kg-1·d-1,对照组和模型组大鼠给予等量1%羧甲基纤维素钠溶液,每日1次。连续给药28 d后,取大鼠血清,采用酶法检测各项血脂水平。提取大鼠脑微血管,采用黄嘌呤氧化酶法检测大鼠脑微血管组织中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,硫代巴比妥酸法测定丙二醛(MDA)水平,Western blotting法检测大鼠脑微血管内皮细胞中细胞间黏附因子1(ICAM-1)、血管间黏附因子1(VCAM-1)和E-选择素(E-selectin)蛋白表达水平。 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠血清中总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)水平明显升高(P<0.01),高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)明显降低(P<0.01),大鼠脑微血管组织中SOD活性明显降低(P<0.01)、MDA水平明显升高(P<0.05),大鼠脑微血管内皮细胞中ICAM-1、VCAM-1和E-selectin蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05 或 P<0.01);与模型组比较,姜黄素组大鼠血清中TC、TG和LDL-C水平明显降低(P<0.05), HDL-C水平明显升高(P<0.05),大鼠脑微血管组织中SOD活性明显升高(P<0.05)、MDA水平明显降低(P<0.05),大鼠脑微血管内皮细胞中ICAM-1、VCAM-1和E-selectin蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。 姜黄素可以通过改善高胆固醇血症模型大鼠的血脂状况,增加脑微血管抗氧化酶能力,减低氧化应激损伤,减少脑微循环内皮细胞中黏附因子表达,进而改善脑微循环障碍。
中图分类号:
- R285.5