| 1 |
PAZ-ARES L, DVORKIN M, CHEN Y, et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN):a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial[J].Lancet,2019, 394(10212):1929-1939.
|
| 2 |
KASMANN L, ABDO R, EZE C, et al. External validation of a survival score for limited-stage small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy[J]. Lung, 2020, 198(1): 201-206.
|
| 3 |
WU Q, XIONG Y T, ZHANG S J, et al. A meta-analysis of the efficacy and toxicity of twice-daily vs. once-daily concurrent chemoradiotherapy for limited-stage small cell Lung Cancer Based on randomized controlled trials[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 1460.
|
| 4 |
HORN L, MANSFIELD A S, SZCZESNA A, et al. First-line atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 379(23): 2220-2229.
|
| 5 |
SHEN X B, WANG Y, SHAN B J, et al. Prognostic significance of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and mean platelet volume (MPV) during etoposide-based first-line treatment in small cell lung cancer patients[J]. 2019, 11: 8965-8975.
|
| 6 |
SACDALAN D B, LUCERO J A, SACDALAN D L. Prognostic utility of baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review and meta-analysis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2018, 11: 955-965.
|
| 7 |
BAGLEY S J, KOTHARI S, AGGARWAL C, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker of outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer [J].Lung Cancer,2017,106: 1-7.
|
| 8 |
BOWEN R C, LITTLE N A B, HARMER J R, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as prognostic indicator in gastrointestinal cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(19): 32171-32189.
|
| 9 |
KANG M H, GO S I, SONG H N, et al. The prognostic impact of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with small-cell lung cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2014, 111(3): 452-460.
|
| 10 |
SAKIN A, SAHIN S, YASAR N, et al. The relation between hemogram parameters and survival in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncol Res Treat, 2019, 42(10): 506-515.
|
| 11 |
PAN Z C, ZHANG L, LIU C, et al. Cisplatin or carboplatin? Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio may serve as a useful factor in small cell lung cancer therapy selection[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(2): 1513-1520.
|
| 12 |
XIE D, MARKS R, ZHANG M, et al. Nomograms predict overall survival for patients with small-cell lung cancer incorporating pretreatment peripheral blood markers[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2015, 10(8): 1213-1220.
|
| 13 |
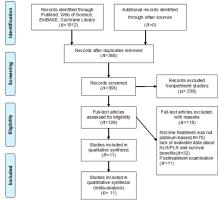
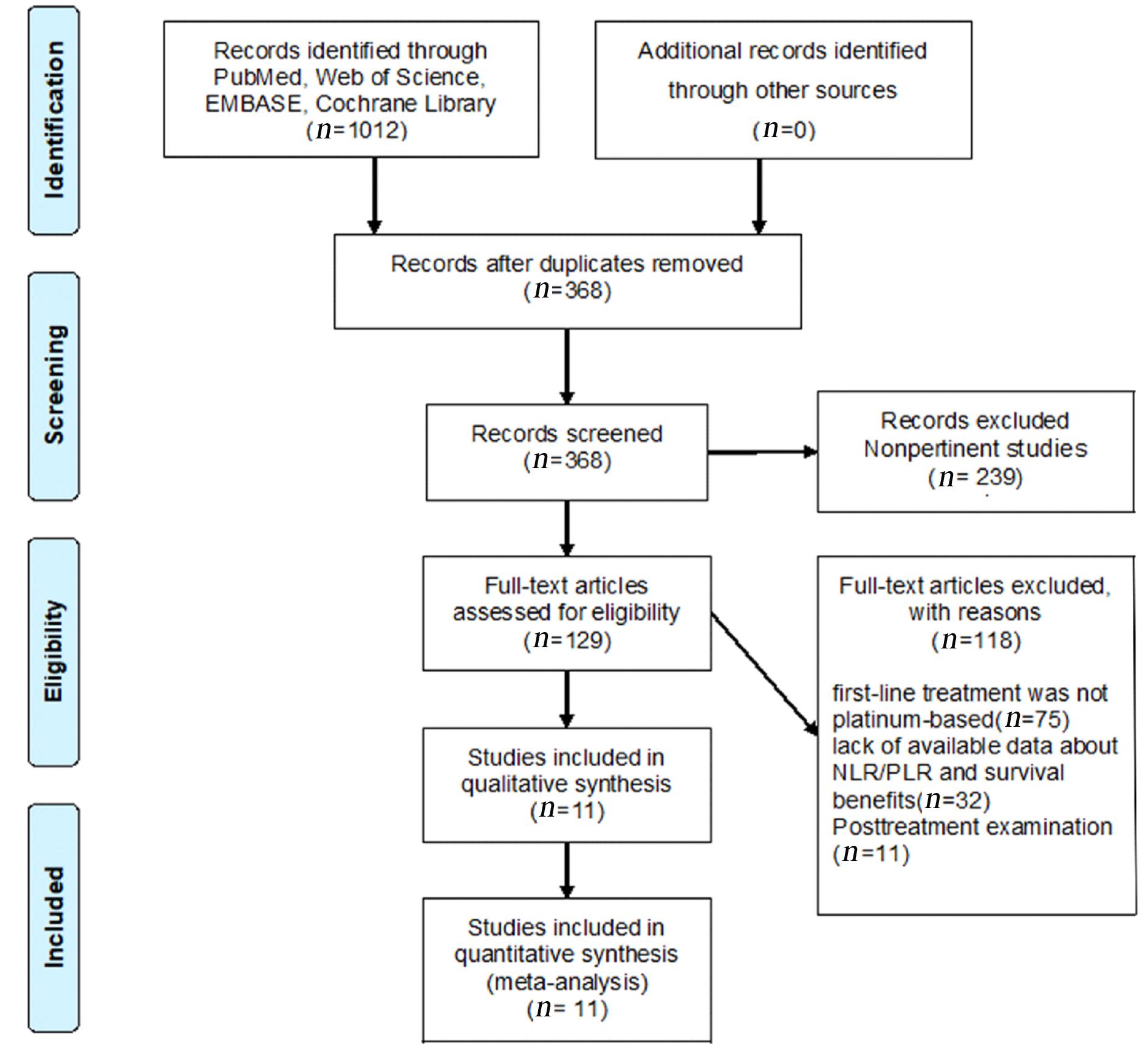
MOHER D, LIBERATI A, TETZLAFF J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 2009, 62(10): 1006-1012.
|
| 14 |
CAO S B, JIN S, SHEN J, et al. Selected patients can benefit more from the management of etoposide and platinum-based chemotherapy and thoracic irradiation-a retrospective analysis of 707 small cell lung cancer patients[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(5): 8657-8669.
|
| 15 |
KASMANN L, BOLM L, SCHILD S E, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts outcome in limited disease small-cell lung cancer [J]. Lung, 2017, 195(2): 217-224.
|
| 16 |
PENG H, LUO X. Prognostic significance of elevated pretreatment systemic inflammatory markers for patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 70.
|
| 17 |
GUO W, LU X, LIU Q, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio for breast cancer patients: an updated meta-analysis of 17079 individuals[J]. Cancer Med, 2019, 8(9): 4135-4148.
|
| 18 |
YANG S S, ZHAO K, DING X, et al. Prognostic significance of hematological markers for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis[J].J Cancer, 2019, 10(11): 2568-2577.
|
| 19 |
WEN Q, MENG X, XIE P, et al. Evaluation of factors associated with platinum-sensitivity status and survival in limited-stage small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(46): 81405-81418.
|
| 20 |
SUZUKI R, LIN S H, WEI X, et al. Prognostic significance of pretreatment total lymphocyte count and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2018, 126(3): 499-505.
|
| 21 |
SUZUKI R, WEI X, ALLEN P K, et al. Prognostic significance of total lymphocyte count, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in Limited-stage Small-cell lung cancer[J]. Clin Lung Cancer, 2019, 20(2): 117-123.
|
| 22 |
SHAO N, CAI Q. High pretreatment neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts recurrence and poor prognosis for combined small cell lung cancer[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2015, 17(10): 772-778.
|
| 23 |
WANG X, JIANG R, LI K. Prognostic significance of pretreatment laboratory parameters in combined small-cell lung cancer[J].Cell Biochem Biophys,2014,69(3): 633-640.
|
| 24 |
HARAM A, BOLAND M R, KELLY M E, et al. The prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in colorectal cancer: a systematic review[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2017, 115(4): 470-479.
|
| 25 |
LUCCA I, JICHLINSKI P, SHARIAT S F, et al. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor for patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder following radical cystectomy: validation and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2016, 2(1): 79-85.
|
| 26 |
YANG T, ZHU J, ZHAO L, et al. Lymphocyte to monocyte ratio and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio are superior inflammation-based predictors of recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2017, 115(6): 718-728.
|
| 27 |
DIEM S, SCHMID S, KRAPF M, et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with nivolumab[J]. Lung Cancer, 2017, 111: 176-181.
|
| 28 |
FERRUCCI P F, ASCIERTO P A, PIGOZZO J,et al. Baseline neutrophils and derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: prognostic relevance in metastatic melanoma patients receiving ipilimumab[J]. Ann Oncol, 2016, 27(4): 732-738.
|
| 29 |
ZHANG Q, QU Y L, LIU H Y, et al. Initial platelet-to-lymphocyte count as prognostic factor in limited-stage small cell lung cancer[J]. Biomark Med, 2019, 13(4): 249-258.
|
| 30 |
ROTONDO R, BERTOLOTTO M, BARISIONE G, et al. Exocytosis of azurophil and arginase 1-containing granules by activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils is required to inhibit T lymphocyte proliferation[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2011, 89(5): 721-727.
|
| 31 |
NIESWANDT B, HAFNER M, ECHTENACHER B, et al. Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is impeded by platelets[J].Cancer Res,1999,59(6):1295-1300.
|
| 32 |
YANG H B, XING M, MA L N, et al. Prognostic significance of neutrophil-lymphocyteratio/platelet-lymphocyteratioin lung cancers: a meta-analysis[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(47):76769-76778.
|
| 33 |
万广财, 孙洪帅, 朱 华, 等. 中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值与接受EGFR-TKIs治疗的非小细胞肺癌患者预后关系的Meta分析[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2020,46(6):1267-1273.
|
 )
)