吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1432-1437.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240530
• 临床医学 • 上一篇
腹壁寄生性平滑肌瘤并发播散性腹膜平滑肌瘤病1例报告及文献复习
- 1.吉林大学中日联谊医院妇产科, 吉林 长春 130033
2.吉林大学中日联谊医院病理科, 吉林 长春 130033
Parasitic leiomyoma of abdominal wall complicated with disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis : A case report and literature review
Jinping ZHANG1,Lingling TONG1,Lu GAO1,Hongjing CHENG2,Minjia SHENG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,China-Japan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
2.Department of Pathology,China-Japan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
摘要:
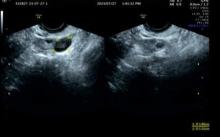
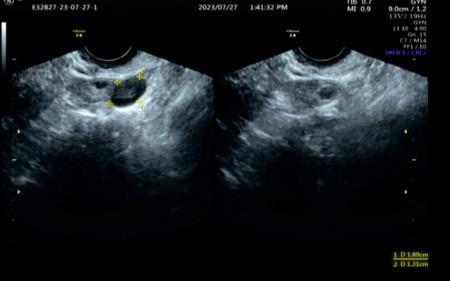
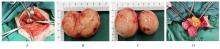
目的 探讨腹腔镜下子宫肌瘤核出术后出现腹壁寄生性平滑肌瘤(PM)并发播散性腹膜平滑肌瘤病(DPL)患者的诊疗经过,以提高对该病的临床认识水平和诊疗水平。 方法 收集1例腹腔镜下子宫肌瘤核出术后出现腹壁PM并发DPL患者的临床资料,分析其发病原因、临床特点、诊断、鉴别诊断和治疗经过,并回顾相关文献。 结果 患者,女性,49岁,因自觉腹部包块1年入院。专科查体,脐左下侧腹壁扪及大小约为6 cm×4 cm包块,活动性欠佳,边界尚清,无压痛;脐下方右侧腹部扪及大小约为7 cm×5 cm包块,活动性尚可,边界清晰,无压痛。妇科彩超,脐孔左下方皮下可探及大小约为6.6 cm×2.7 cm的低回声。脐孔下方腹腔内可探及大小约为7.6 cm×3.3 cm的低回声。浅表局部彩超,左下腹腹直肌内可见大小约为5.79 cm×2.55 cm×4.74 cm低回声,边缘光滑,较浅处距皮约1.97 cm,较深处距皮约4.73 cm,深方及浅方未穿破腹直肌外膜,深方紧邻腹膜。诊断为子宫肌瘤、腹部肿物和子宫肌瘤核出术后。择期在静吸复合全麻下行开腹子宫平滑肌瘤核出术、腹壁平滑肌瘤切除术和腹膜平滑肌瘤切除术,手术过程顺利,患者术后恢复良好,顺利出院。 结论 PM和DPL无典型临床特点,需借助影像学检查等辅助诊断,手术探查为主要治疗手段,多为良性,有恶性转化可能,患者术后需进一步随访。
中图分类号:
- R711.74





 成人患者颧牙槽嵴区骨质特征分析及其临床意义
成人患者颧牙槽嵴区骨质特征分析及其临床意义