吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1130-1136.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240428
低血压预测指数在机器人辅助腹腔镜膀胱切除术患者血流动力学管理中应用1例报告及文献复习
- 1.吉林大学中日联谊医院麻醉科,吉林 长春 130033
2.吉林省长春市绿园区人民医院麻醉科,吉林 长春 130062
Application of hypotension prediction index in intraoperative hemodynamic management of robot-assisted laparoscopic cystectomy:A case report and literature review
Wenqing RUAN1,Zerun FU1,Yi HUANG1,Longyun LI1,Yao SUN2,Kai LI1( )
)
- 1.Department of Anesthesiology,China-Japan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
2.Department of Anesthesiology,People’s Hospital,Lyuyuan District,Changchun City,Jilin Province,Changchun 130062,China
摘要:
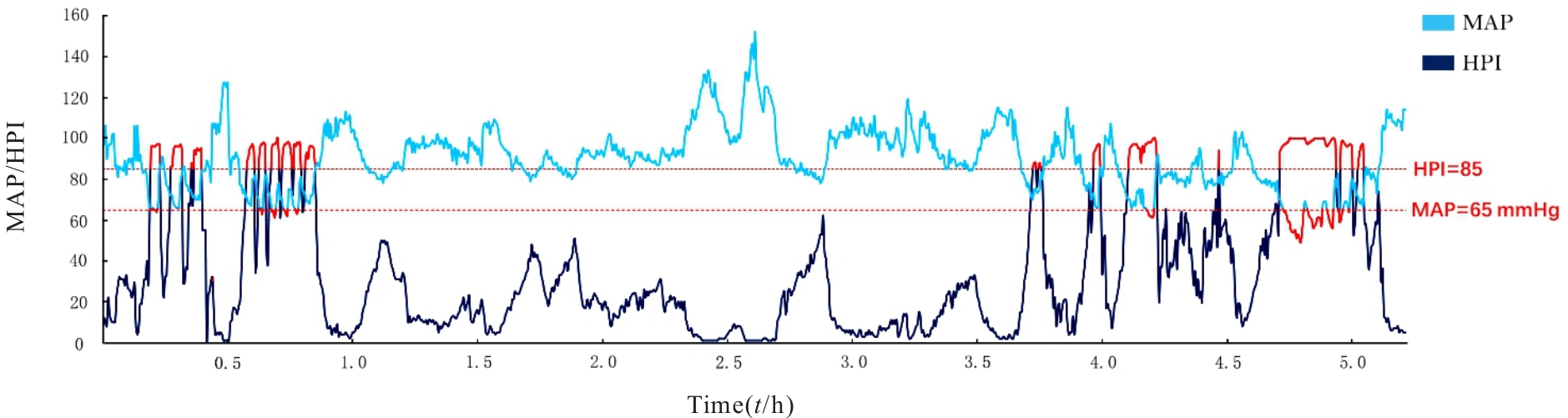
目的 分析在机器人辅助腹腔镜膀胱切除术患者应用低血压预测指数(HPI)进行术中血流动力学管理的经过,为同类型大手术的麻醉监测和血流动力学管理提供参考。 方法 回顾性分析1例采用HPI进行术中血流动力学管理的接受机器人辅助腹腔镜膀胱切除术患者的临床资料、术中血流动力学资料、血管活性药物用法用量和临床效果,并结合相关文献进行分析。 结果 患者,女性,72岁,因肉眼血尿5个月伴尿痛3个月入院。膀胱镜检查,膀胱三角区右侧可见7 cm×7 cm×5 cm肿物,近膀胱颈可见大小约4 cm×3 cm×3 cm肿物。正电子发射/计算机断层扫描(PET/CT)检查,膀胱右后壁增厚伴高代谢,初步诊断为膀胱恶性肿瘤。进行麻醉前评估后拟行机器人辅助腹腔镜膀胱切除术。患者入室后常规监测,同时采用搭载HPI软件的监护仪指导术中血流动力学管理。常规麻醉诱导后,使用可视喉镜进行气管插管。患者术中共发生低血压事件(IOH)6次,平均动脉压(MAP)<65 mmHg累计时间为13.7 min,占麻醉时长的4.4%,MAP<65 mmHg时间加权平均数为0.28 mmHg。HPI≥85的时间范围与MAP<65 mmHg大致重叠且包含后者。146个HPI≥85的时间点,68.5%(100/146)MAP>65 mmHg;47个MAP<65 mmHg的时间点,97.9%(46/47)均出现HPI≥85。患者术后第1天超敏肌钙蛋白I<0.01 μg·L-1,未发生围术期不良事件,第8天顺利出院。 结论 HPI可及时并准确地预警机器人辅助腹腔镜膀胱切除术患者IOH的发生。术中使用基于HPI的低血压纠正策略可将患者MAP<65 mmHg的时间加权平均数维持在较低水平。
中图分类号:
- R614.2