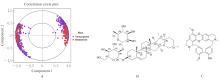
| [1] |
YANG M, TAO L, ZHAO C C, et al. Antifatigue effect of Panax notoginseng leaves fermented with microorganisms: in-vitro and in-vivo evaluation[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 824525.
|
| [2] |
GUO M X, LIU X B, ZHANG W W, et al. Preparation and anti-fatigue effects of Vicatia thibertica polysaccharide [J]. Phcog Mag, 2022, 18(77): 133.
|
| [3] |
KIM J, BEAK S, AHN S, et al. Effects of taurine and ginseng extracts on energy metabolism during exercise and their anti-fatigue properties in mice[J]. Nutr Res Pract, 2022, 16(1): 33-45.
|
| [4] |
HUANG W, HUI H Q, XU J P, et al. Study on the antifatigue effect of compound amino acid capsules[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2022, 2022(1): 6593811.
|
| [5] |
CHEN Y, WANG J J, JING Z H, et al. Anti-fatigue and anti-oxidant effects of curcumin supplementation in exhaustive swimming mice via Nrf2/Keap1 signal pathway[J]. Curr Res Food Sci, 2022, 5: 1148-1157.
|
| [6] |
LIU G Y, YANG X, ZHANG J X, et al. Synthesis, stability and anti-fatigue activity of selenium nanoparticles stabilized by Lycium barbarum polysaccharides [J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 179: 418-428.
|
| [7] |
ZHANG Y H, ZHANG W J, SHEN C H, et al. Anti-fatigue effect of pigeon meat hydrolysate on exercise mice and its underlying mechanism: Related to oxidative stress and energy metabolism[J]. Food Biosci, 2024, 62: 105407.
|
| [8] |
ZHU H K, WANG R Y, HUA H Y, et al. Network pharmacology exploration reveals gut microbiota modulation as a common therapeutic mechanism for anti-fatigue effect treated with maca compounds prescription[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14(8): 1533.
|
| [9] |
LIU C, HUA H Y, ZHU H K, et al. Study of the anti-fatigue properties of macamide, a key component in maca water extract, through foodomics and gut microbial genomics[J]. Food Biosci, 2022, 49: 101876.
|
| [10] |
LIU S L, GENG J N, CHEN W J, et al. Isolation, structure, biological activity and application progress of ginseng polysaccharides from the Araliaceae family[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 276: 133925.
|
| [11] |
LI D, REN J W, ZHANG T, et al. Anti-fatigue effects of small-molecule oligopeptides isolated from Panax quinquefolium L. in mice[J]. Food Funct, 2018, 9(8): 4266-4273.
|
| [12] |
LI K X, LIU W Z, WU C H, et al. The anti-fatigue and sleep-aiding effects vary significantly among different recipes containing Ganoderma lucidum extracts[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(10): e30907.
|
| [13] |
CAI M, ZHU H, XU L, et al. Structure, anti-fatigue activity and regulation on gut microflora in vivo of ethanol-fractional polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 234: 123572.
|
| [14] |
JIA L M, ZHAO F. Evaluation of silymarin extract from Silybum marianum in mice: anti-fatigue activity[J]. Food Sci Hum Wellness, 2022, 11(4): 914-921.
|
| [15] |
YAN K, GAO H Y, LIU X H, et al. Establishment and identification of an animal model of long-term exercise-induced fatigue[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 915937.
|
| [16] |
ZHOU Y P, CAO F L, WU Q, et al. Dietary supplementation of octacosanol improves exercise-induced fatigue and its molecular mechanism[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2021, 69(27): 7603-7618.
|
| [17] |
XIAO R, WEI Y, ZHANG Y P, et al. Trilobatin, a naturally occurring food additive, ameliorates exhaustive exercise-induced fatigue in mice: involvement of Nrf2/ARE/ferroptosis signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 913367.
|
| [18] |
MAO S Y, SUO S K, WANG Y M, et al. Systematical investigation on anti-fatigue function and underlying mechanism of high Fischer ratio oligopeptides from Antarctic krill on exercise-induced fatigue in mice[J]. Mar Drugs, 2024, 22(7): 322.
|
| [19] |
JING Y S, LI M S, LI Y Q, et al. Structural characterization and anti-fatigue mechanism based on the gut-muscle axis of a polysaccharide from Zingiber officinale [J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 283(Pt 1): 137621.
|
| [20] |
DAVIS L A, FOGARTY M J, BROWN A, et al. Structure and function of the mammalian neuromuscular junction[J]. Compr Physiol, 2022, 12(4): 3731-3766.
|
| [21] |
ITO S, KIMURA T, GOMI H. Attribution of sensory prediction error to perception of muscle fatigue[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12: 16708.
|
| [22] |
SHI C, LIANG Z H, LI T, et al. Metabolome and microbiome analyses of the anti-fatigue mechanism of Acanthopanax senticosus leaves[J]. Food Funct, 2024, 15(7): 3791-3809.
|
| [23] |
SHAO J J, QU L L, LIU Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rk3 regulates tryptophan metabolism along the brain-gut axis by targeting tryptophan hydroxylase and remodeling the intestinal microenvironment to alleviate depressive-like behavior in mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2024, 72(13): 7100-7120.
|
| [24] |
XUAN Q W, RUAN Y, CAO C B, et al. Effect of ultrasonic penetration with volatile oil of Olibanum and Chuanxiong Rhizoma on acute knee synovitis induced by sports training: an open-label randomized controlled study[J]. Pain Res Manag, 2022, 2022: 6806565.
|
| [25] |
ALFARO-RODRÍGUEZ A, REYES-LONG S, ROLDAN-VALADEZ E, et al. Association of the serotonin and kynurenine pathways as possible therapeutic targets to modulate pain in patients with fibromyalgia[J]. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 2024, 17(9): 1205.
|
| [26] |
TORNERO-AGUILERA J F, JIMENEZ-MORCILLO J, RUBIO-ZARAPUZ A, et al. Central and peripheral fatigue in physical exercise explained: a narrative review[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(7): 3909.
|
| [27] |
LIN Z D, XU G Y, LU X, et al. Piezo1 exacerbates inflammation-induced cartilaginous endplate degeneration by activating mitochondrial fission via the Ca2+/CaMKII/Drp1 axis[J]. Aging Cell, 2025, 24(4): e14440.
|
| [28] |
李梦佳. 异常应力通过机械门控Piezo1促进软骨细胞Ca2+内流引起颞下颌关节骨关节炎的实验研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2024.
|
 ),王金辉1,3,李涵4,邵丹4
),王金辉1,3,李涵4,邵丹4
 ),Jinhui WANG1,3,Han LI4,Dan SHAO4
),Jinhui WANG1,3,Han LI4,Dan SHAO4