吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1512-1518.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240604
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
大黄酚对H2O2诱导EA.hy926细胞凋亡的改善作用及其机制
- 1.暨南大学粤港澳中枢神经再生研究院神经生物学系,广东 广州 510632
2.南方医科大学珠江医院儿科,广东 广州 510282
3.广东省妇幼保健院儿科,广东 广州 511400
Improvement effect of chrysophanol on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of EA. hy926 cells and its mechanism
Siqi LI1,2,Guangdao CHEN3( ),Qiyi ZENG2(
),Qiyi ZENG2( )
)
- 1.Department of Neurobiology,Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Institute of Central Nervous System Regeneration,Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632,China
2.Department of Pediatrics,Zhujiang Hospital,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510282,China
3.Department of Pediatrics,Women and Children’s Hospital,Guangdong Province,Guangzhou 511400,China
摘要:
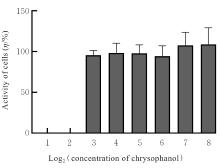
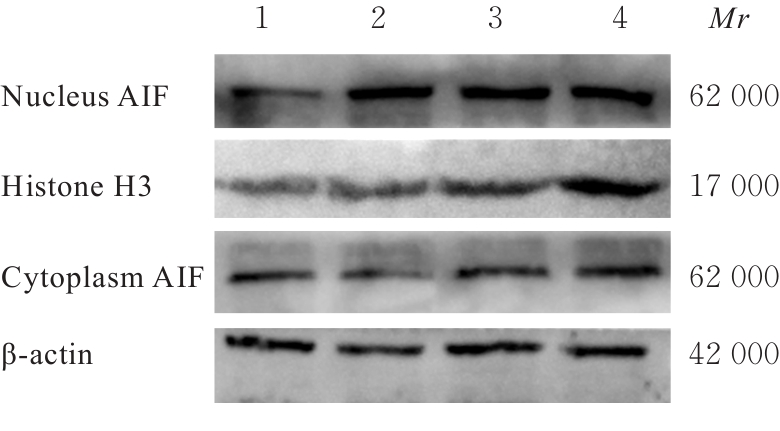
目的 探讨大黄酚对过氧化氢(H2O2)诱导EA.hy926细胞氧化损伤的作用,并阐明其对支气管肺发育不良(BPD)的治疗作用及其相关机制。 方法 分别采用25、50、100、200、400、800和1 600 μmol·L-1 H2O2及0、8、16、32、64、128和256 μmol·L-1大黄酚诱导EA.hy926细胞,CCK-8法检测不同浓度H2O2和大黄酚处理后EA.hy926细胞活性。将细胞分为对照组、模型组(200 μmol·L-1 H2O2)、低剂量大黄酚组(8 μmol·L-1大黄酚和200 μmol·L-1 H2O2)和高剂量大黄酚组(256 μmol·L-1大黄酚和200 μmol·L-1 H2O2)。Western blotting法检测各组细胞质和细胞核中凋亡诱导因子(AIF)蛋白表达水平,免疫荧光法检测各组细胞AIF核转位情况,试剂盒检测各组细胞中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性和丙二醛(MDA)、含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白酶(Caspase)-8及Caspase-9水平。 结果 不同浓度H2O2作用下,EA.hy926细胞呈倒置S形细胞活性曲线,细胞活性良好,半数抑制浓度(IC50)为261.52 μmol·L-1,采用200 μmol·L-1 H2O2干预24 h诱导建立细胞模型。随着大黄酚药物浓度升高,EA.hy926细胞活性无明显变化(P>0.05),采用8和256 μmol·L-1大黄酚进行细胞干预。Western blotting法检测,与对照组比较,模型组细胞核中AIF蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),细胞质中AIF蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低和高剂量大黄酚组细胞核中AIF蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05),细胞质中AIF蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。免疫荧光法检测,对照组细胞AIF定位于细胞核内较少;与对照组比较,模型组细胞AIF核转位阳性值明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低和高剂量大黄酚组细胞AIF核转位阳性值均明显降低(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,模型组细胞中SOD活性明显降低(P<0.05),MDA水平明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,低和高剂量大黄酚组细胞中SOD活性均明显升高(P<0.05),MDA水平均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);各组细胞中Caspase-8和Caspase-9水平比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 大黄酚通过抑制氧化应激和AIF核转位改善H2O2诱导的EA.hy926细胞凋亡,有助于治疗BPD。
中图分类号:
- R725.6