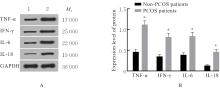
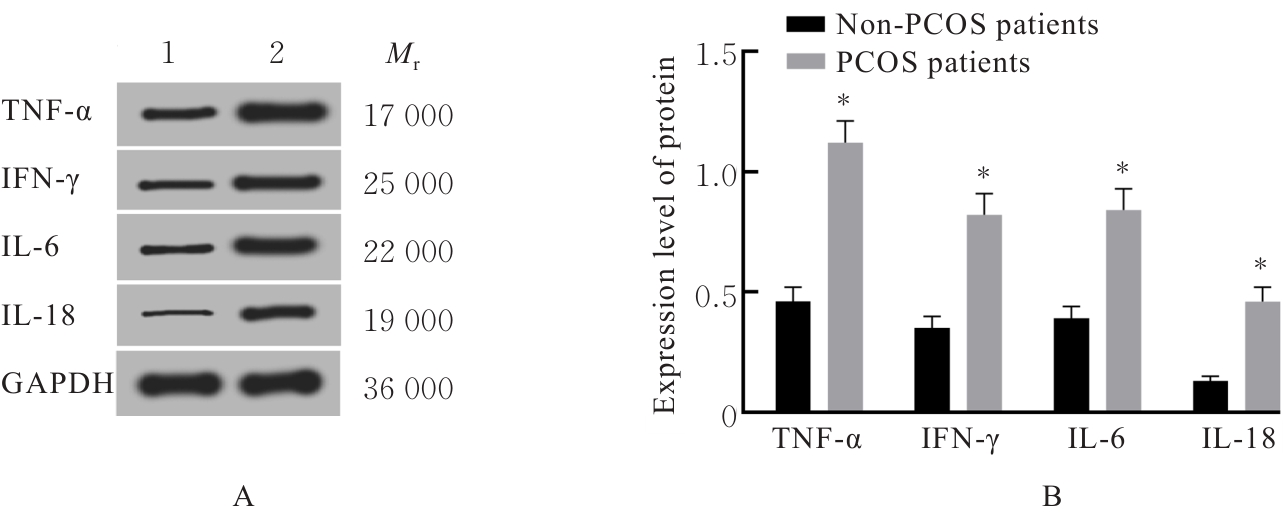
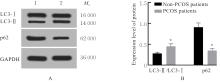
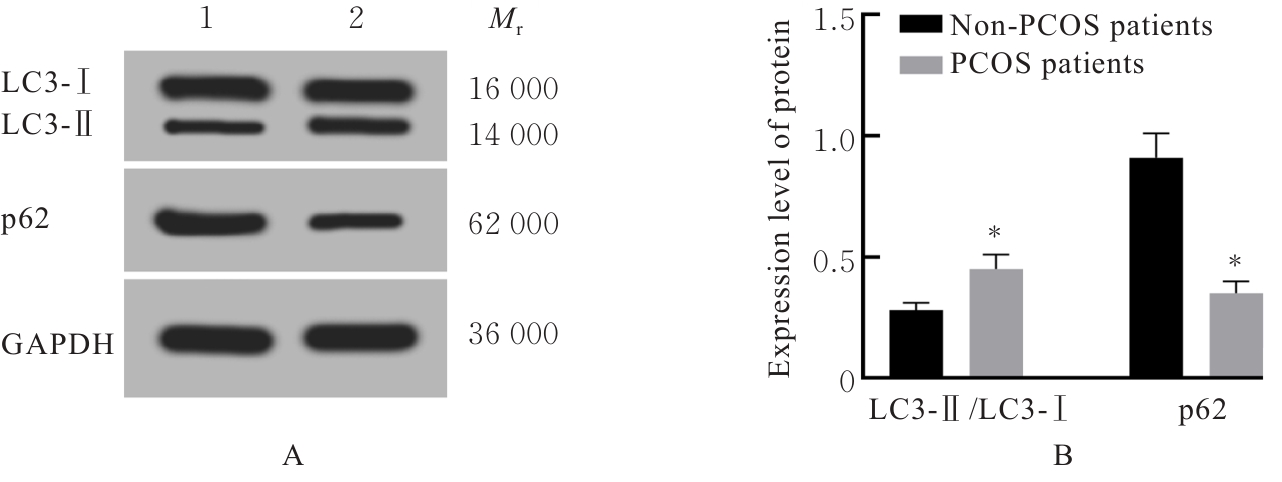
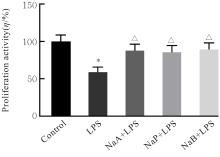
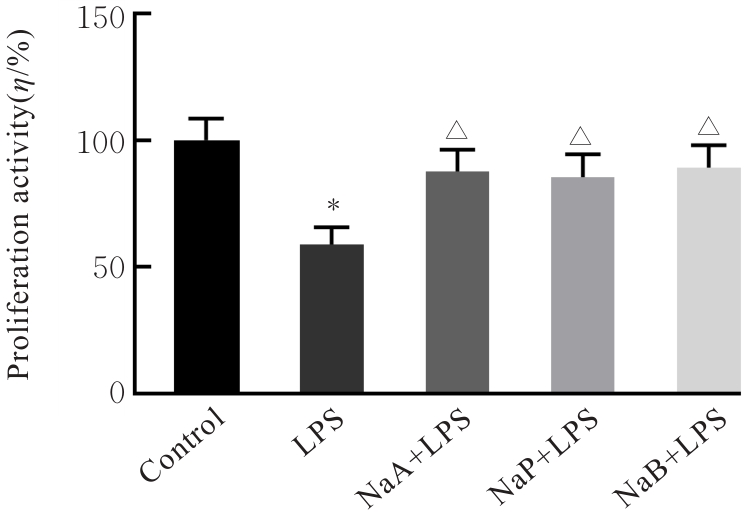
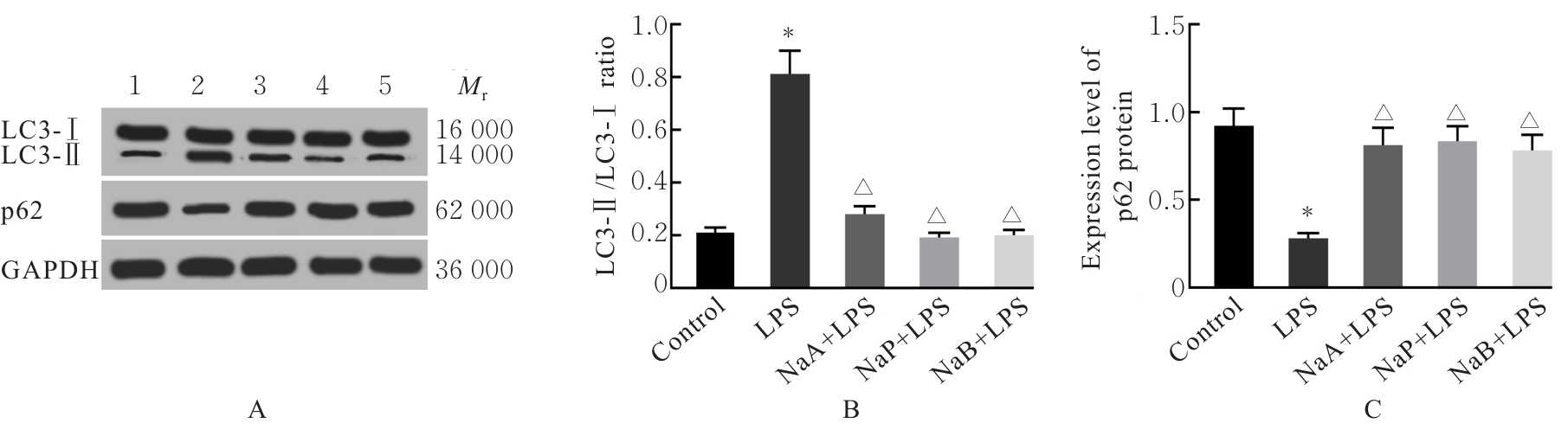
| [1] |
SHRIVASTAVA S, CONIGLIARO R L. Polycystic ovarian syndrome[J]. Med Clin N Am, 2023, 107(2): 227-234.
|
| [2] |
XIE Q, HONG W L, LI Y, et al. Chitosan oligosaccharide improves ovarian granulosa cells inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1086232.
|
| [3] |
朱瑞可, 孙 婧, 史 昊, 等. 血清基础黄体生成素水平对多囊卵巢综合征患者卵泡期长效长方案助孕结局的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2024,59(6): 859-862.
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Q, REN J, WANG F F, et al. Mitochondrial and glucose metabolic dysfunctions in granulosa cells induce impaired oocytes of polycystic ovary syndrome through Sirtuin 3[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 187: 1-16.
|
| [5] |
JOZKOWIAK M, PIOTROWSKA-KEMPISTY H, KOBYLAREK D, et al. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in polycystic ovary syndrome: the relevant role of the theca and granulosa cells in the pathogenesis of the ovarian dysfunction[J]. Cells, 2022, 12(1): 174.
|
| [6] |
BARREA L, MARZULLO P, MUSCOGIURI G, et al. Source and amount of carbohydrate in the diet and inflammation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Nutr Res Rev, 2018, 31(2): 291-301.
|
| [7] |
LIU Y S, LIU H, LI Z T, et al. The release of peripheral immune inflammatory cytokines promote an inflammatory cascade in PCOS patients via altering the follicular microenvironment[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 685724.
|
| [8] |
TONG C, WU Y, ZHANG L L, et al. Insulin resistance, autophagy and apoptosis in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: Association with PI3K signaling pathway[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 1091147.
|
| [9] |
LUO X D, GONG Y Y, CAI L Y, et al. Chemerin regulates autophagy to participate in polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49(11): 3000605211058376.
|
| [10] |
HE J, ZHANG P W, SHEN L Y, et al. Short-chain fatty acids and their association with signalling pathways in inflammation, glucose and lipid metabolism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(17): 6356.
|
| [11] |
王 怡, 杨宏毅, 杨焕焕. 短链脂肪酸在多囊卵巢综合征发生发展中的作用[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2021, 12(4): 163-165.
|
| [12] |
赵元元, 路军涛, 吴小华. 人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体miR-100对多囊卵巢综合征患者颗粒细胞炎症的影响[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2023, 61(5): 51-58.
|
| [13] |
PATEL S. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), an inflammatory, systemic, lifestyle endocrinopathy[J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2018, 182: 27-36.
|
| [14] |
VELEZ L M, SELDIN M, MOTTA A B. Inflammation and reproductive function in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Biol Reprod, 2021, 104(6): 1205-1217.
|
| [15] |
RUDNICKA E, SUCHTA K, GRYMOWICZ M, et al. Chronic low grade inflammation in pathogenesis of PCOS[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(7): 3789.
|
| [16] |
张梦蝶, 张欢欢, 肖成炜. 多囊卵巢综合征患者血清TNF-α改变和糖脂代谢异常关系的临床研究[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2023, 39(7): 1141-1144.
|
| [17] |
PENG Z, SUN Y F, LV X L, et al. Interleukin-6 levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(2): e0148531.
|
| [18] |
LI L S, ZHU J, YE F J, et al. Upregulation of the lncRNA SRLR in polycystic ovary syndrome regulates cell apoptosis and IL-6 expression[J]. Cell Biochem Funct, 2020, 38(7): 880-885.
|
| [19] |
ZHANG H Y, ZHU F F, ZHU Y J, et al. Effects of IL-18 on the proliferation and steroidogenesis of bovine theca cells: Possible roles in the pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25(2): 1128-1139.
|
| [20] |
张丽娜, 王 娟, 姚 雪, 等. IFN-γ在多囊卵巢综合征中的表达及对卵巢颗粒细胞的影响[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版), 2020, 30(6): 480-485.
|
| [21] |
BHARDWAJ J K, PALIWAL A, SARAF P, et al. Role of autophagy in follicular development and maintenance of primordial follicular pool in the ovary[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(2): 1157-1170.
|
| [22] |
ZHAO Y, ZHAO X X, JIANG T Y, et al. A retrospective review on dysregulated autophagy in polycystic ovary syndrome: from pathogenesis to therapeutic strategies[J]. Horm Metab Res, 2024, 56(8): 547-558.
|
| [23] |
POPELKA H, KLIONSKY D J. Structural basis for extremely strong binding affinity of giant ankyrins to LC3/GABARAP and its application in the inhibition of autophagy[J]. Autophagy, 2018, 14(11): 1847-1849.
|
| [24] |
LAMARK T, SVENNING S, JOHANSEN T. Regulation of selective autophagy: the p62/SQSTM1 paradigm[J]. Essays Biochem, 2017, 61(6): 609-624.
|
| [25] |
ZHANG M M, HU R N, HUANG Y J, et al. Present and future: crosstalks between polycystic ovary syndrome and gut metabolites relating to gut microbiota[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 933110.
|
| [26] |
ZHANG J C, SUN Z H, JIANG S M, et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis V9 regulates the secretion of sex hormones in polycystic ovary syndrome patients through the gut-brain axis[J]. mSystems, 2019, 4(2): e00017-19.
|
| [27] |
LIU K L, HE X, HUANG J Y, et al. Short-chain fatty acid-butyric acid ameliorates granulosa cells inflammation through regulating METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of FOSL2 in polycystic ovarian syndrome[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2023, 15(1): 86.
|
| [28] |
OLANIYI K S, BASHIR A M, ARELOEGBE S E, et al. Short chain fatty acid, acetate restores ovarian function in experimentally induced PCOS rat model[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e0272124.
|
| [29] |
ZHANG H L, WANG W, ZHAO J M, et al. Relationship between body composition, insulin resistance, and hormonal profiles in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023, 13: 1085656.
|
| [30] |
BULLETTI C, BULLETTI F M, SCIORIO R, et al. Progesterone: the key factor of the beginning of life[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(22): 14138.
|
| [31] |
FERREIRA S R, MOTTA A B. Uterine function: from normal to polycystic ovarian syndrome alterations[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2018, 25(15): 1792-1804.
|