吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (2): 271-276.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220201
• 基础研究 • 下一篇
基于CRISPR/Cas9技术构建LDLR基因敲除的免疫缺陷小鼠模型及其表型分析
- 吉林大学第一医院 器官再造与移植教育部重点实验室,吉林 长春 130061
Construction of LDLR gene knockout immunodeficient mouse model and its phenotypic analysis based on CRISPR/cas9 technology
Zhaowei WANG,Yanan LYU,Zheng HU,Yongguang YANG( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Organ Regeneration & Transplantation of Ministry of Education,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
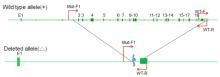
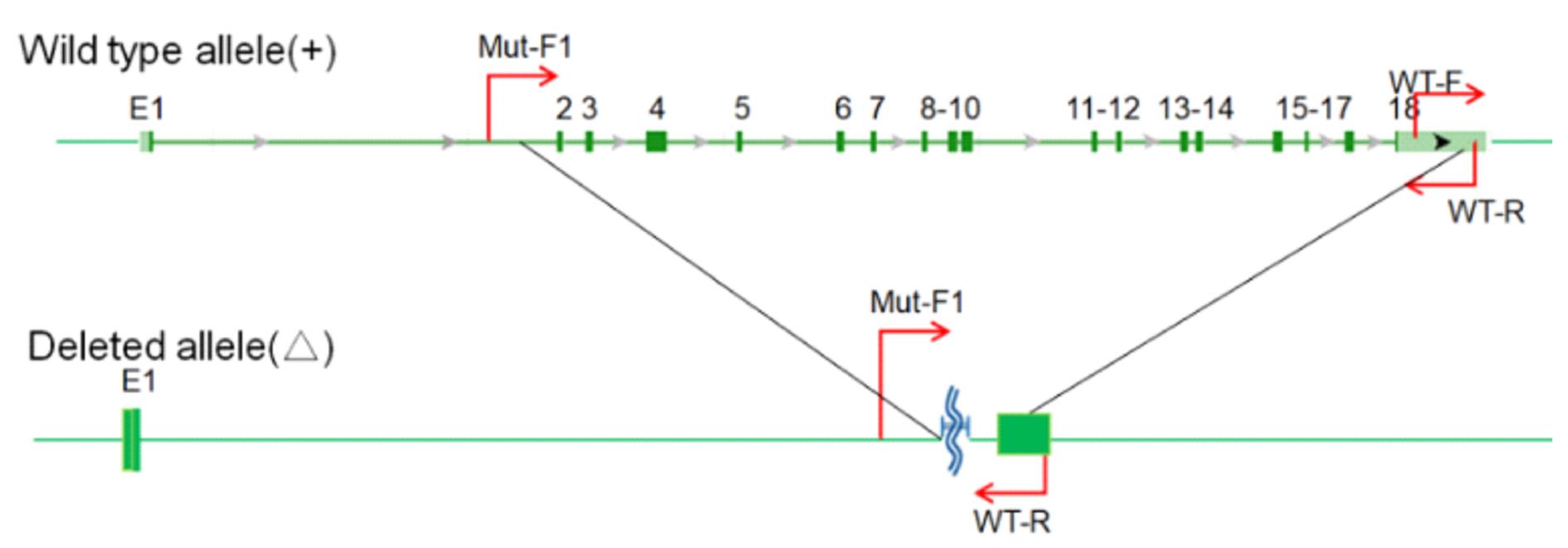
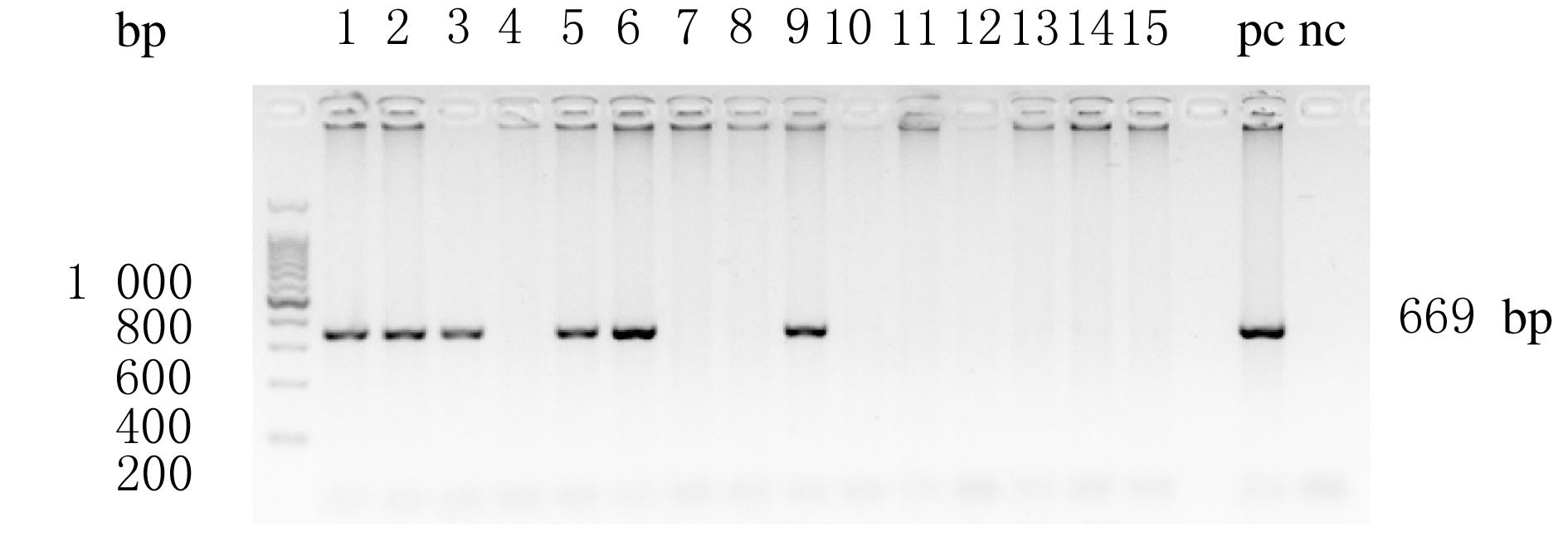
摘要: 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术构建低密度脂蛋白受体(LDLR)基因敲除的免疫缺陷小鼠模型,并对血液胆固醇水平进行分析评价,为构建具有高脂血症的免疫系统人源化小鼠模型提供新方法。 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术,将有效识别LDLR基因外显子2和18的sgRNA/Cas9 mRNA注射到NOD SCID小鼠的受精卵中,通过对新生小鼠基因型鉴定筛选得到基因敲除的F0代阳性(LDLR+/-,Aa)小鼠,再将此小鼠与NOD SCID(LDLR+/+,AA)小鼠繁育,鉴定得到能稳定遗传基因型的F1代(Aa)小鼠。将F1代阳性杂合小鼠与NOD SCID小鼠繁育,获得大量基因序列完全相同的F2代(Aa)小鼠,在F2代间进行大规模繁育,获得的F3代小鼠依据基因型和性别进行分组,分别为雄性AA、雄性Aa、雌性AA和雌性Aa,对体质量进行监测,同时采集外周血进行血液胆固醇水平检测。 通过上述构建方法获得了NOD SCID LDLR+/-(Aa)小鼠,经过8周的体质量检测,Aa杂合子基因型在生长发育过程中并不影响小鼠体质量,雌性Aa的胆固醇水平为(100.80±4.42)mg·dL-1,雄性Aa的胆固醇水平为(120.56±11.16)mg·dL-1,与阴性对照(基因型为AA的小鼠)比较,胆固醇水平明显升高(P<0.05);雌性AA的胆固醇水平为(60.78±2.11)mg·dL-1,雄性AA的胆固醇水平为(75.43±10.06)mg·dL-1,两者比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 在不影响小鼠体质量的前提下,通过CRISPR/Cas9技术在NOD SCID 背景下成功构建出了胆固醇水平自发升高的小鼠模型。
中图分类号:
- Q78