吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4): 1034-1039.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230426
• 临床医学 • 上一篇
关节镜治疗膝关节滑膜内膜下血管瘤1例报告及文献复习
- 吉林大学第二医院运动医学关节镜科,吉林 长春 130041
Arthroscopic treatment of subsynovial hemangioma of knee joint: A case report and literature review
Qingshuai WANG,Bo CHEN,Hairui ZHANG,Xiongfeng TANG,Xue GAO,Yingzhi LI( )
)
- Department of Sports Medicine Arthroscopy,Second Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130041,China
摘要:
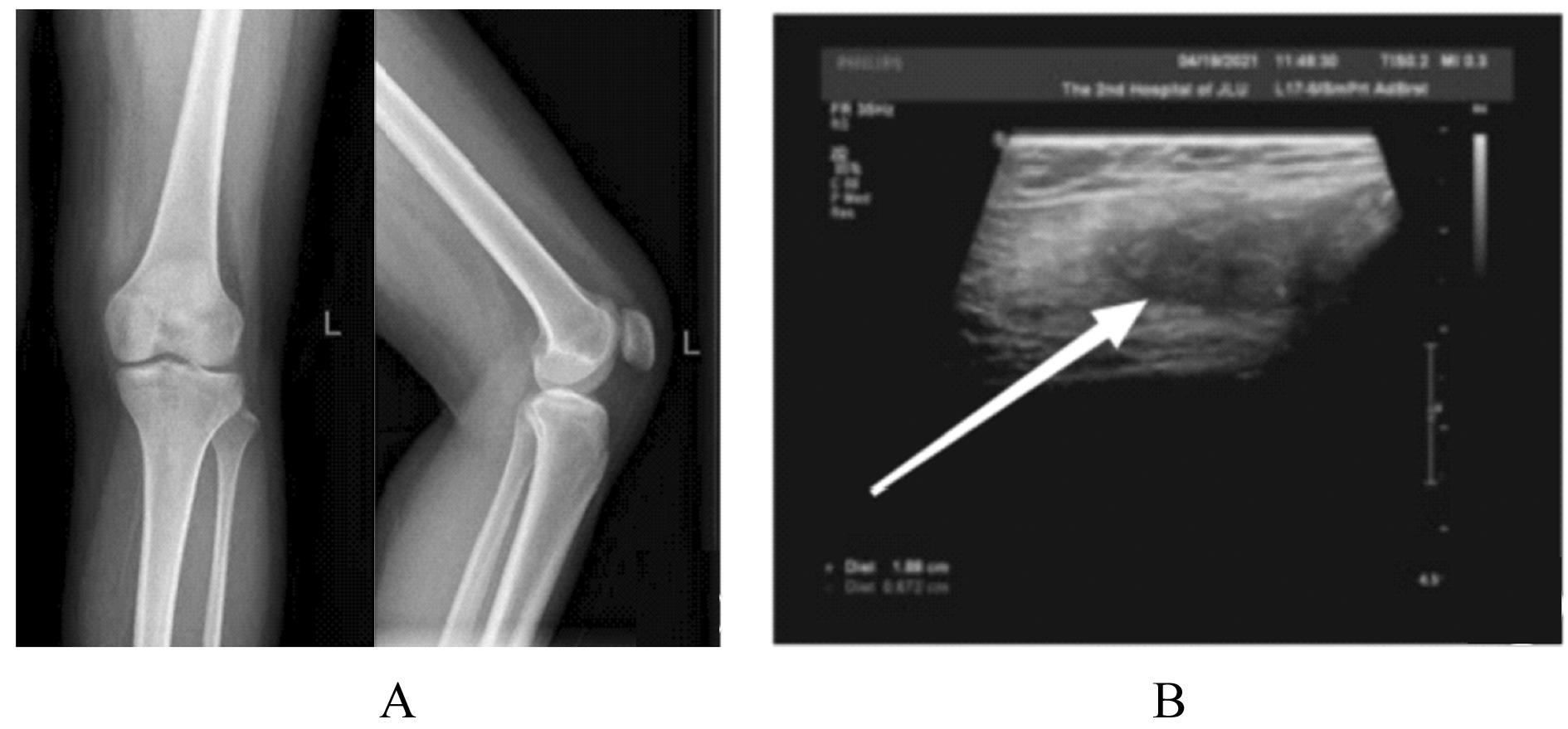
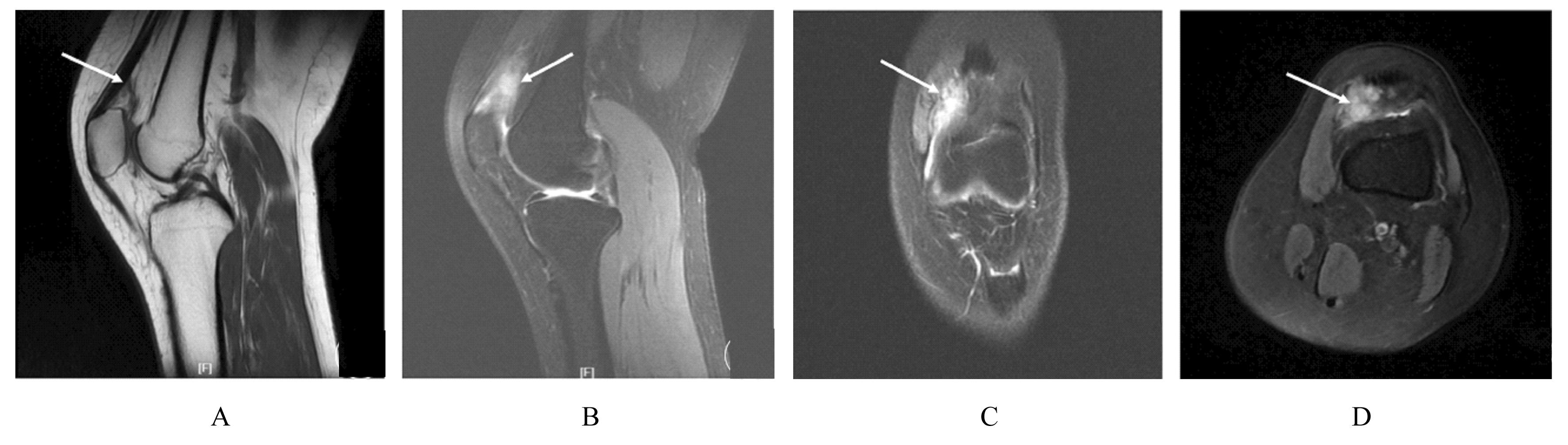
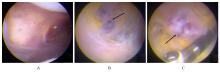
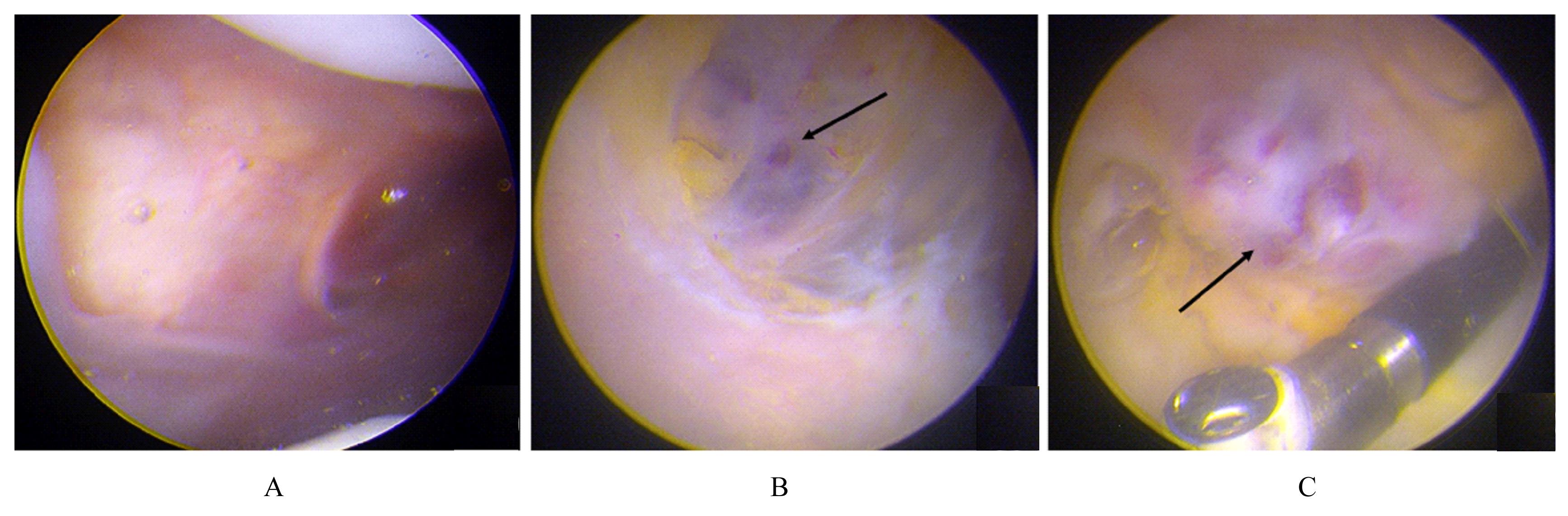
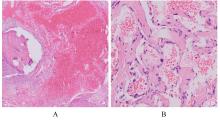
目的 分析1例膝关节滑膜内膜下血管瘤患者的临床表现和诊疗经过,以提高临床医生对该病的认识。 方法 回顾性分析1例膝关节滑膜内膜下血管瘤患者的临床资料、影像学资料、关节镜下表现和病理检查结果,并进行相关文献复习。 结果 患者,女性,22岁,7年内间断性左膝关节疼痛伴肿胀。查体,左膝关节内和外侧间隙压痛明显,左膝关节活动度降低(0°~90°)。超声检查,股内侧肌肌腱深层与滑膜组织间探及低回声光团;磁共振成像(MRI)检查,左膝关节内侧支持带深部靠近髌旁软组织肿胀,表现为T1加权序列上呈稍低信号,T2脂肪抑制序列上呈团片状稍高信号,滑膜组织内见高T2信号,边界欠清晰。初步诊断为左膝关节肿物。行关节镜下左膝关节病损切除术,镜下见内侧髌旁滑膜外观基本正常,清理表面滑膜组织内膜层后见肿物位于滑膜内膜下与关节囊之间,彻底切除肿物并送检,病理检查结果为滑膜内膜下血管瘤,术后患者左膝关节疼痛消失。 结论 膝关节滑膜内膜下血管瘤患者多有外伤病史,表现为不明原因的膝关节疼痛、肿胀和活动受限;结合影像学表现、关节镜和病理检查结果可明确诊断;关节镜手术治疗有助于改善患者预后,且具有损伤小、术后并发症少和恢复快等优势。
中图分类号:
- R686.7