吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 620-627.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240305
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
高磷诱导下肢血管平滑肌细胞成骨分化关键差异表达基因筛选及验证
倪英群1,2,3( ),杨矛1,杨迪1,郭呈林1,朱文君4,俞雅琴4,卢芹4,骆金芝4,吴春琴4,方朝晖1,2,3
),杨矛1,杨迪1,郭呈林1,朱文君4,俞雅琴4,卢芹4,骆金芝4,吴春琴4,方朝晖1,2,3
- 1.安徽中医药大学第一附属医院内分泌科,安徽 合肥 230031
2.安徽省中医药科学院中医药防治糖尿病研究所,安徽 合肥 230031
3.安徽中医药大学新安医学教育部重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230038
4.安徽中医药大学研究生院,安徽 合肥 230038
Screening of key differentially expressed genes involved in osteogenic differentiation of lower limb vascular smooth muscle cells and validation
Yingqun NI1,2,3( ),Mao YANG1,Di YANG1,Chenglin GUO1,Wenjun ZHU4,Yaqin YU4,Qin LU4,Jinzhi LUO4,Chunqin WU4,Zhaohui FANG1,2,3
),Mao YANG1,Di YANG1,Chenglin GUO1,Wenjun ZHU4,Yaqin YU4,Qin LU4,Jinzhi LUO4,Chunqin WU4,Zhaohui FANG1,2,3
- 1.Department of Endocrinology,First Affiliated Hospital,Anhui University of Chinese Medicine,Hefei 230031,China
2.Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes,Anhui Academy of Chinese Medicine,Hefei 230031,China
3.Key Laboratory of Xin An Medicine,Ministry of Education,Anhui University of Chinese Medicine,Hefei 230038,China
4.Graduate School,Anhui University of Chinese Medicine,Hefei 230038,China
摘要:
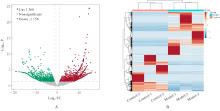
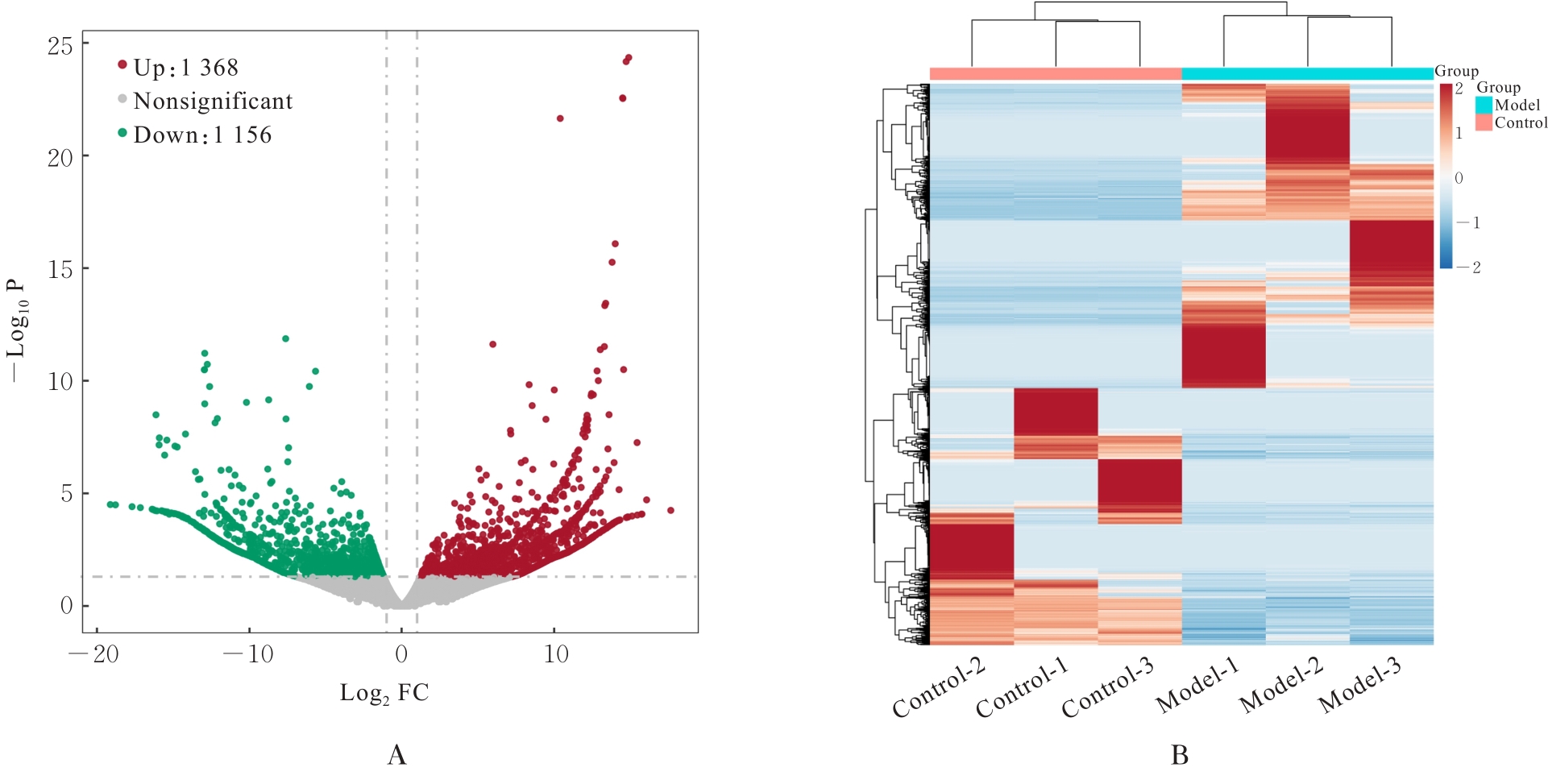
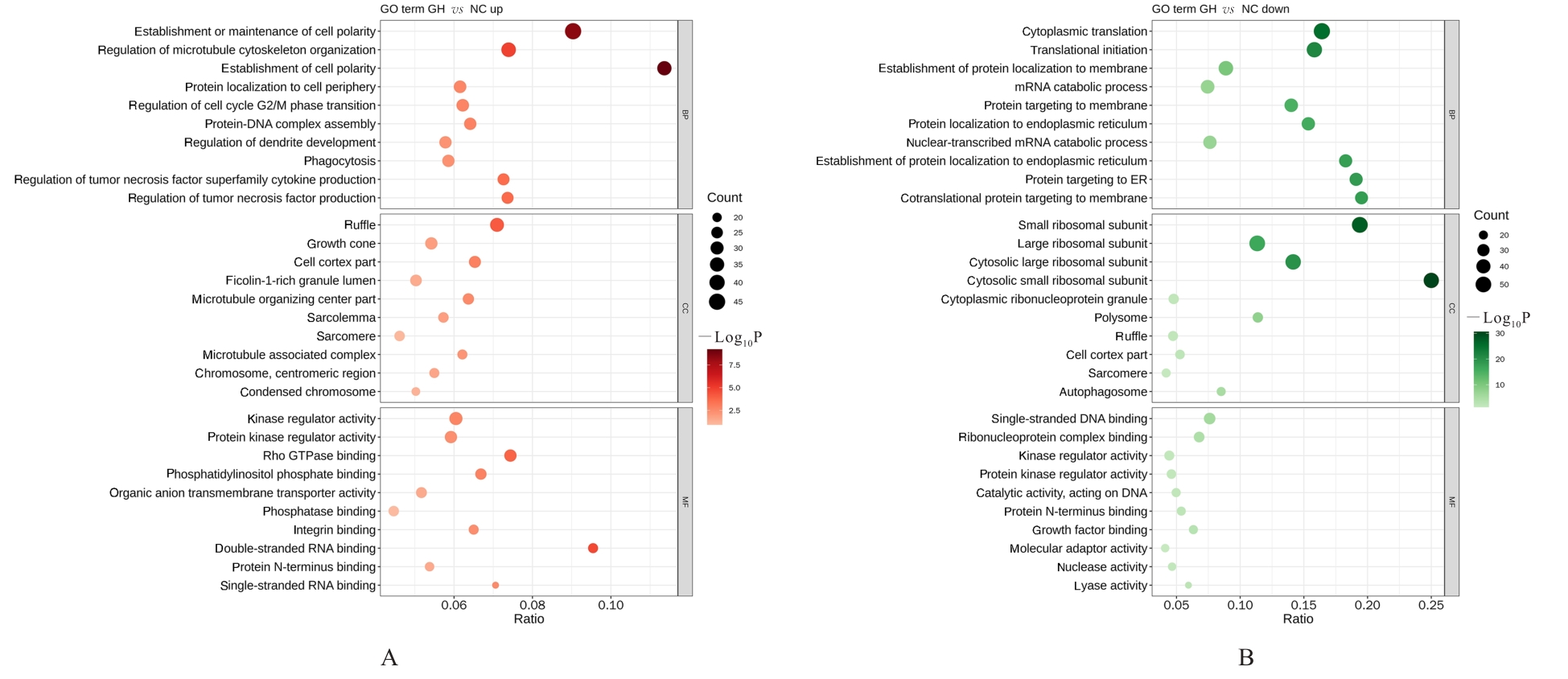
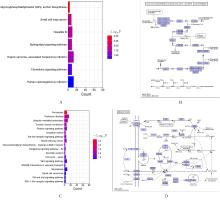
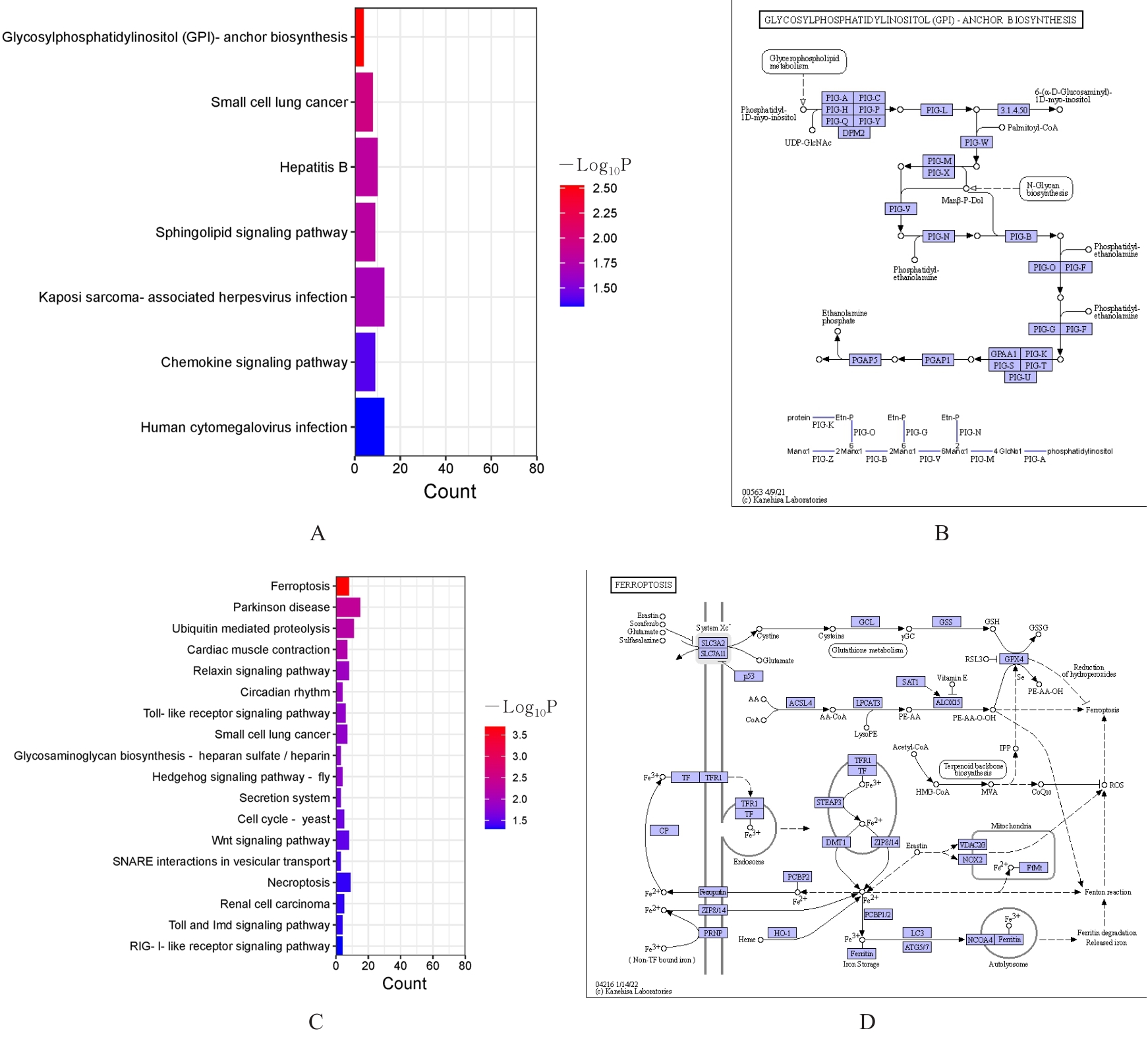
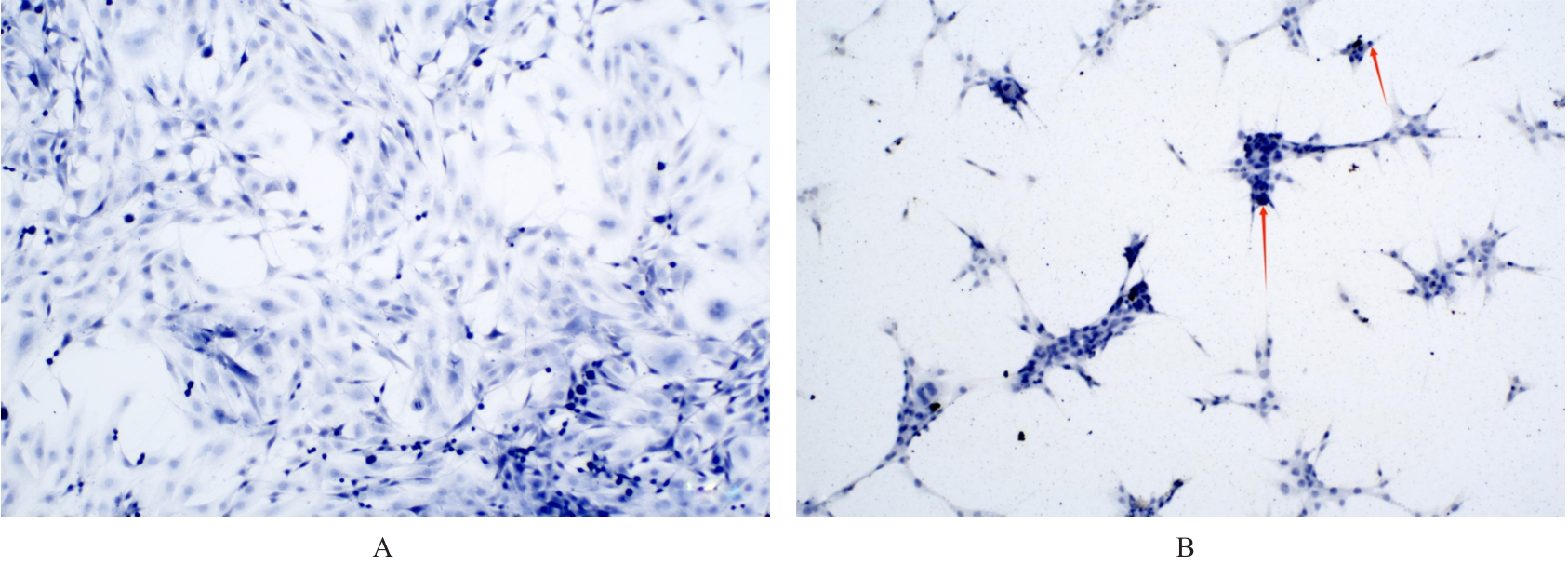
目的 采用mRNA高通量测序技术筛选高磷诱导下肢血管平滑肌细胞(VSMCs)钙化差异表达基因(DEGs),分析VSMCs钙化的关键基因及信号通路。 方法 将人VSMCs分为对照组和模型组,模型组细胞中加入高磷培养基,对照组细胞采用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基于相同条件下培养。调整2组稳定转染VSMCs的状态,培养12 d,倒置显微镜下观察细胞形态表现并拍照。采用Hisat2软件筛选DEGs,采用Stringtie软件从生物过程(BP)、分子功能(MF)和细胞成分(CC)3个方面进行基因本体论(GO)功能和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)信号通路富集分析。Von Kossa染色法观察各组细胞钙化情况,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测2组细胞中碱性磷酸酶(ALP)、骨形态发生蛋白2(BMP2)、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)、肿瘤蛋白53(Tp53)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4(GPX4)、铁蛋白轻链1(Ftl1)和糖基磷脂酰肌醇特异性磷脂酶D1(GPLD1)mRNA表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组共2 524个DEGs,其中1 368个DEGs表达上调,1 156个DEGs表达下调;2组细胞DEGs聚类分离明显。GO功能和KEGG信号通路富集分析表达上调的DEGs主要参与微管细胞骨架组织的调节、细胞极性、蛋白质定位和细胞周期调控等BP,构建细胞膜部分、微管组织、染色体和着丝粒区等CC,发挥与磷脂酰肌醇磷酸盐、Rho鸟苷酸三磷酸酶(GTPase)蛋白结合、参与跨膜转运和调节蛋白激酶活性等MF;表达下调的DEGs主要参与细胞质翻译、蛋白质膜定位、mRNA代谢和蛋白质内质网定位等BP,构建核糖体亚单位、细胞膜和自噬体等CC,发挥与单链DNA、核糖核蛋白复合物、生长因子结合、调节蛋白激酶活性和催化作用等MF。差异表达上调的基因富集7条信号通路,其中最为显著的是糖基磷脂酰肌醇(GPI)锚定的生物合成;差异表达下调的基因富集18条信号通路,其中最为显著的是铁死亡。RT-qPCR法,与对照组比较,模型组细胞中GPX4、Ftl1和Tp53 mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),GPLD1 mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);与对照组比较,模型组细胞中α-SMA mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),ALP和BMP2 mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。 结论 钙化的VSMCs与正常细胞存在DEGs,铁死亡和GPI锚定的生物合成信号途径是高磷诱导下肢VSMCs钙化的关键信号通路,主要由GPX4、Ftl1、Tp53和GPLD1共同介导完成。
中图分类号:
- Q254