吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1227-1234.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240505
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
液体复苏抑制血管组织铁死亡对爆炸损伤并发失血性休克大鼠血管细胞结构损伤的减轻作用
彭小勇1,朱娱1,张双博2,朱英国2,李涛1,刘良明1,王建民2,杨光明2( )
)
- 1.陆军军医大学大坪医院野战外科研究部战伤休克与输血研究室,创伤、烧伤与复合伤国家重点实验室,重庆 400042
2.陆军军医大学大坪医院野战外科研究部武器杀伤生物效应评估实验室,创伤、烧伤与复合伤国家重点实验室,重庆 400042
Alleviative effect of fluid resuscitation on damage of structure injury of vascular cells after blast injury complicated with hemorrhagic shock in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis of vascular tissue
Xiaoyong PENG1,Yu ZHU1,Shuangbo ZHANG2,Yingguo ZHU2,Tao LI1,Liangming LIU1,Jianmin WANG2,Guangming YANG2( )
)
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Trauma,Burns and Combined Injury,Department of Shock and Transfusion,Research Institute of Surgery,Daping Hospital,Army Medical University,Chongqing 400042,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Trauma,Burns and Combined Injury,Department of Weapon Bioeffect Assessment,Research Institute of Surgery,Daping Hospital,Army Medical University,Chongqing 400042,China
摘要:
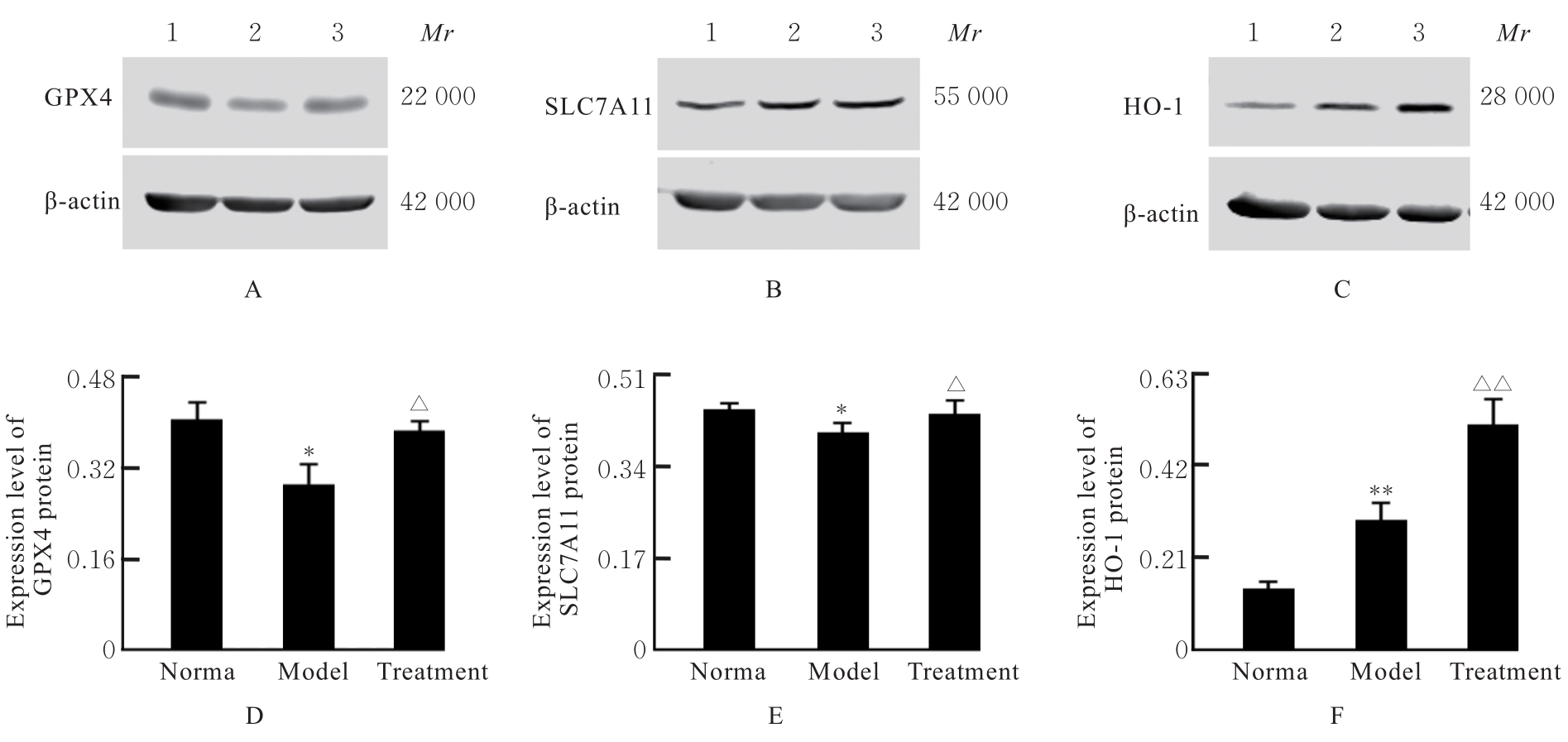
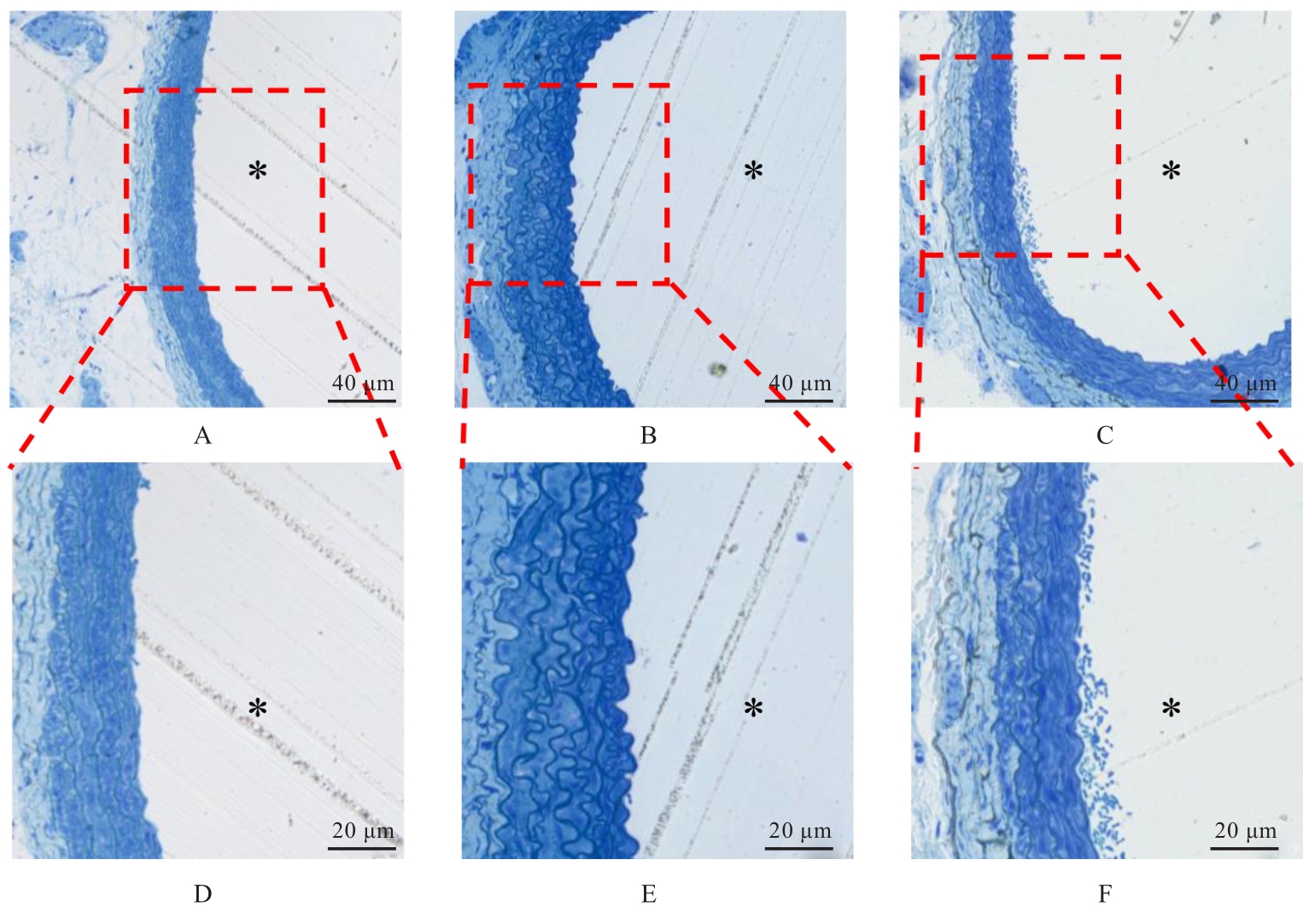
目的 探讨液体复苏对爆炸损伤并发失血性休克大鼠血管铁死亡发生情况和血管细胞结构的影响,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 取54只健康成年SD大鼠,随机分为正常组、爆炸损伤并发失血性休克(模型)组和液体复苏(治疗)组,每组18只,每组随机取10只大鼠观察存活情况,另8只大鼠用于检测其他指标。观察各组大鼠平均存活时间(ST)、24 h及72 h存活情况,观察各组大鼠血压(BP)、心率(HR)和呼吸频率(RR),检测各组大鼠血清中血肌酐(Scr)、血尿素氮(BUN)、乳酸(LAC)、血糖(GLU)、铁离子、谷胱甘肽(GSH)和丙二醛(MDA)水平及天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)和乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)活性,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠肠系膜上动脉组织中铁死亡标志蛋白谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4(GPX4)、溶质载体家族7成员11(SLC7A11)和铁代谢调节蛋白血红素加氧酶1(HO-1)蛋白表达水平,观察各组大鼠肠系膜上动脉组织病理形态表现。 结果 正常组大鼠全部存活72 h,模型组大鼠最长ST不超过9 h。与模型组比较,治疗组大鼠的ST和24 h存活率(SR)明显升高(P<0.05)。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠BP、HR和RR均明显降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,治疗组大鼠的BP、HR和RR明显升高(P<0.05)。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠血清中AST和ALT活性及Scr和BUN水平明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,治疗组大鼠血清中LAC和GLU水平明显降低(P<0.01)。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠血清铁离子浓度、GSH水平、MDA水平和LDH活性明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,治疗组大鼠血清铁离子浓度和LDH活性明显降低(P<0.01)。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠肠系膜上动脉组织中GPX4和SLC7A11蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,治疗组大鼠肠系膜上动脉组织中GPX4和SLC7A11表达水平明显升高(P<0.05)。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠肠系膜上动脉组织中HO-1蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,治疗组大鼠肠系膜上动脉组织中HO-1蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01)。显微病理,模型组大鼠肠系膜上动脉各层细胞排列紊乱,明显肿胀,厚度明显增加;治疗组大鼠肠系膜上动脉组织病理变化减轻。超微病理,正常组大鼠血管内皮细胞结构完整,内皮细胞下基质无肿胀;模型组大鼠血管内皮细胞膜破坏,细胞质溶解破碎,且内皮细胞下基质明显肿胀;治疗组大鼠血管内皮细胞肿胀减轻。 结论 爆炸损伤并发失血性休克大鼠血管组织发生铁死亡,液体复苏能够通过抑制血管组织铁死亡减轻血管细胞结构损伤。
中图分类号:
- R136.37