吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 612-619.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240304
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
白屈菜碱对小鼠肺癌细胞皮下移植瘤生长和血管生成的抑制作用及其机制
- 1.延边大学分子药物研究中心, 吉林 延吉133002
2.延边大学医学院口腔医学系, 吉林 延吉 133002
Inhibitory effect of leucovorin on growth and angiogenesis of subcutaneous transplanted tumors in mouse lung cancer cells and its mechanism
- 1.Center for Molecular Drug Research,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
2.Department of Dentistry,School of Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
摘要:
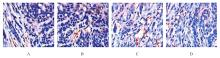
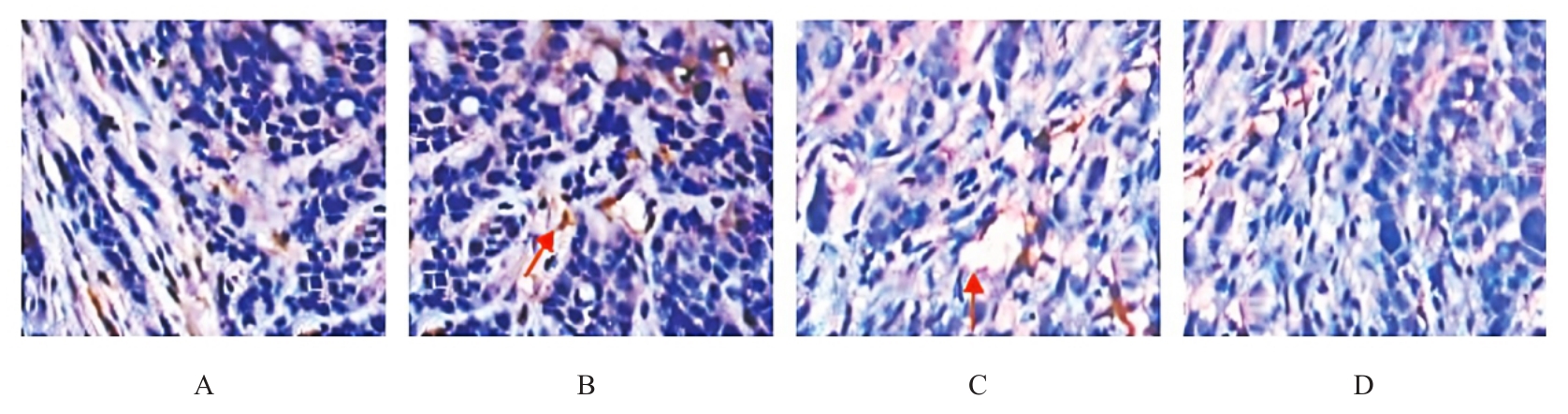
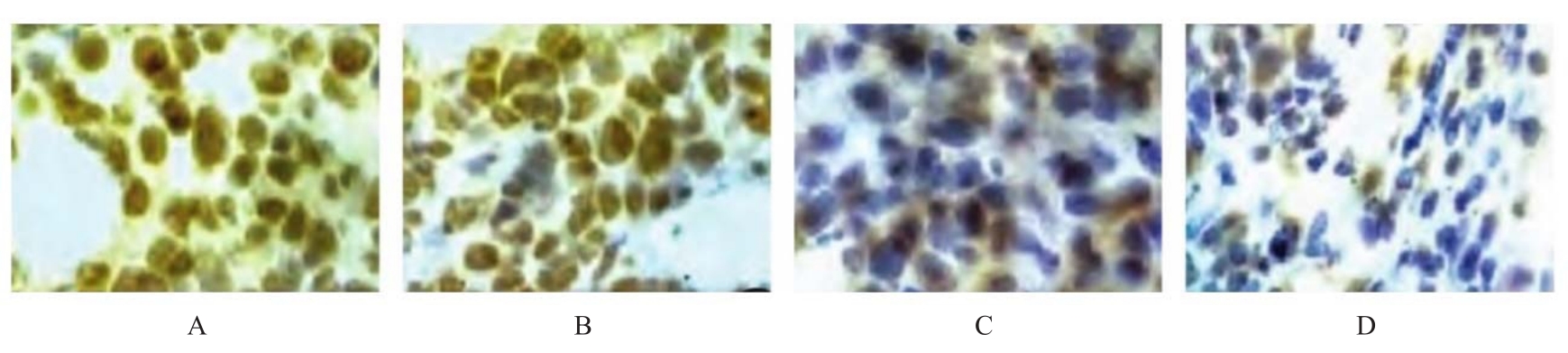
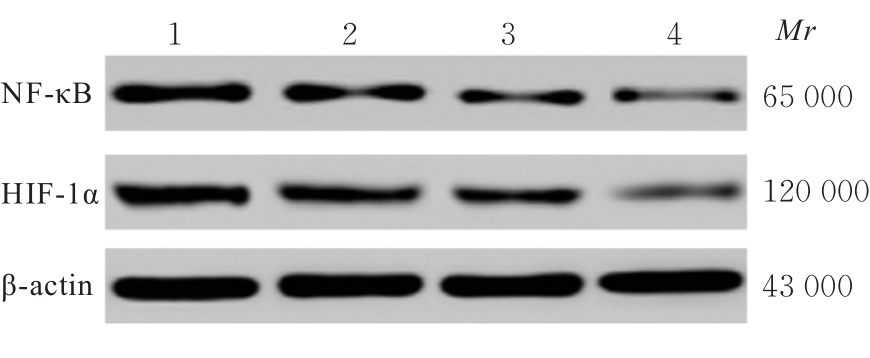
目的 探讨白屈菜碱对肺癌移植瘤小鼠肿瘤生长和血管生成的影响,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 选取32只健康C57BL/6小鼠,制备Lewis肺癌移植瘤小鼠模型。将小鼠随机分为模型组(0.9% 氯化钠)、低剂量白屈菜碱组(25 mg·kg-1白屈菜碱)、高剂量白屈菜碱组(50 mg·kg-1白屈菜碱)和阳性对照组(60 mg·kg-1环磷酰胺),每组8只。称量各组小鼠移植瘤质量并计算抑瘤率,计算各组小鼠胸腺指数和脾脏指数,采用酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)法检测各组小鼠血清中白细胞介素2(IL-2)、γ干扰素(INF-γ)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)水平,免疫组织化学法检测各组小鼠肿瘤组织中血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)蛋白表达情况并计算微血管密度(MVD)及VEGF蛋白表达评分,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠肿瘤组织中核因子κB(NF-κB)和缺氧诱导因子1α(HIF-1α)蛋白表达水平。 结果 与模型组比较,低和高剂量白屈菜碱组及阳性对照组小鼠移植瘤质量均降低(P<0.05);与低剂量白屈菜碱组比较,高剂量白屈菜碱组和阳性对照组小鼠移植瘤质量均降低(P<0.05),抑瘤率均升高(P<0.05);与高剂量白屈菜碱组比较,阳性对照组小鼠移植瘤质量均降低(P<0.05),抑瘤率升高(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,低和高剂量白屈菜碱组及阳性对照组小鼠脾脏指数和胸腺指数均升高(P<0.05);与低剂量白屈菜碱组比较,高剂量白屈菜碱组和阳性对照组小鼠脾脏指数及胸腺指数均升高(P<0.05);与高剂量白屈菜碱组比较,阳性对照组小鼠脾脏指数和胸腺指数均升高(P<0.05)。ELISA法,与模型组比较,低和高剂量白屈菜碱组及阳性对照组小鼠血清中IL-2、INF-γ和TNF-α水平均升高(P<0.05);与低剂量白屈菜碱组比较,高剂量白屈菜碱组和阳性对照组小鼠血清中IL-2、INF-γ和TNF-α水平均升高(P<0.05);与高剂量白屈菜碱组比较,阳性对照组小鼠血清中IL-2、INF-γ和TNF-α水平均升高(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,低和高剂量白屈菜碱组及阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织MVD降低(P<0.05);与低剂量白屈菜碱组比较,高剂量白屈菜碱组和阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织MVD降低(P<0.05);与高剂量白屈菜碱组比较,阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织中MVD降低(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,低和高剂量白屈菜碱组及阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织中VEGF蛋白表达量减少;与低剂量白屈菜碱组比较,高剂量白屈菜碱组和阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织中VEGF蛋白表达量减少;与高剂量白屈菜碱组比较,阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织中VEGF蛋白表达量减少;模型组、低剂量白屈菜碱组、高剂量白屈菜碱组和阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织VEGF蛋白表达评分比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。Western blotting法,与模型组比较,低和高剂量白屈菜碱组及阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织中NF-κB和HIF-1α蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05);与低剂量白屈菜碱组比较,高剂量白屈菜碱组和阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织中NF-κB和HIF-1α蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05);与高剂量白屈菜碱组比较,阳性对照组小鼠肿瘤组织中NF-κB和HIF-1α蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 白屈菜碱能够抑制Lewis肺癌移植瘤小鼠肿瘤组织生长、保护免疫器官和抑制肿瘤血管生成,可能通过靶向NF-κB/HIF-1α信号通路和下调NF-κB及HIF-1α蛋白表达水平发挥治疗作用。
中图分类号:
- R392