吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1009-1015.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240415
甲磺酸阿帕替尼联合放疗对肝癌HepG2细胞的体外协同增敏作用
- 吉林省肿瘤医院放疗一科,吉林 长春 130012
Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro
Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO( )
)
- Department of Radiation Oncology,Tumor Hospital,Jilin Province,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
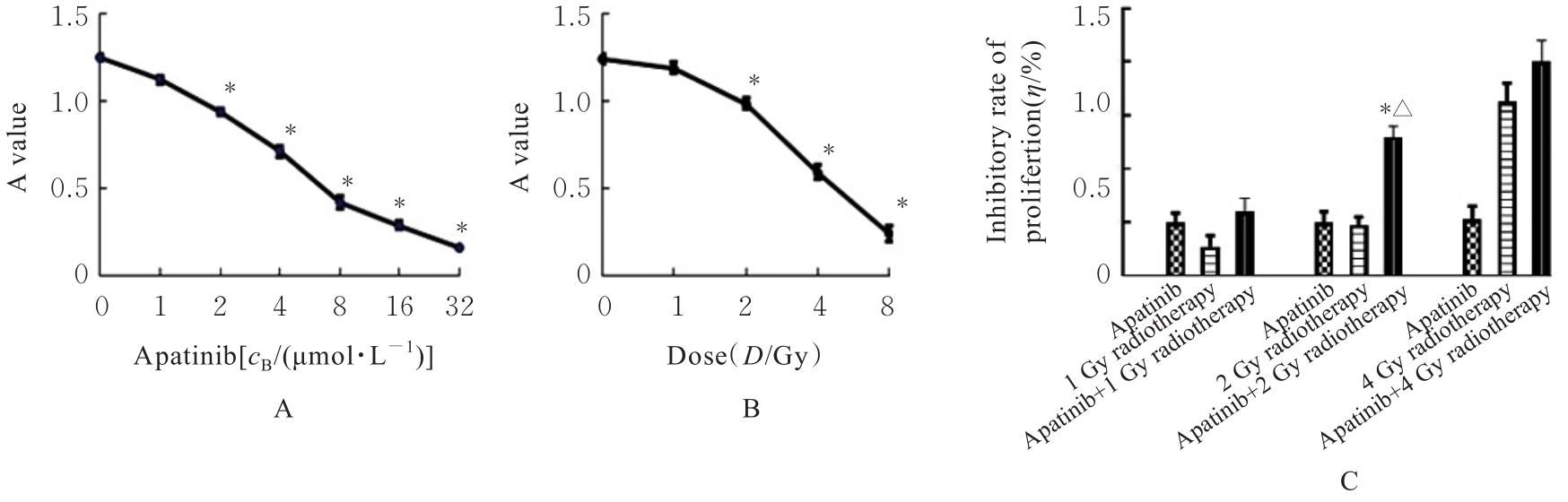
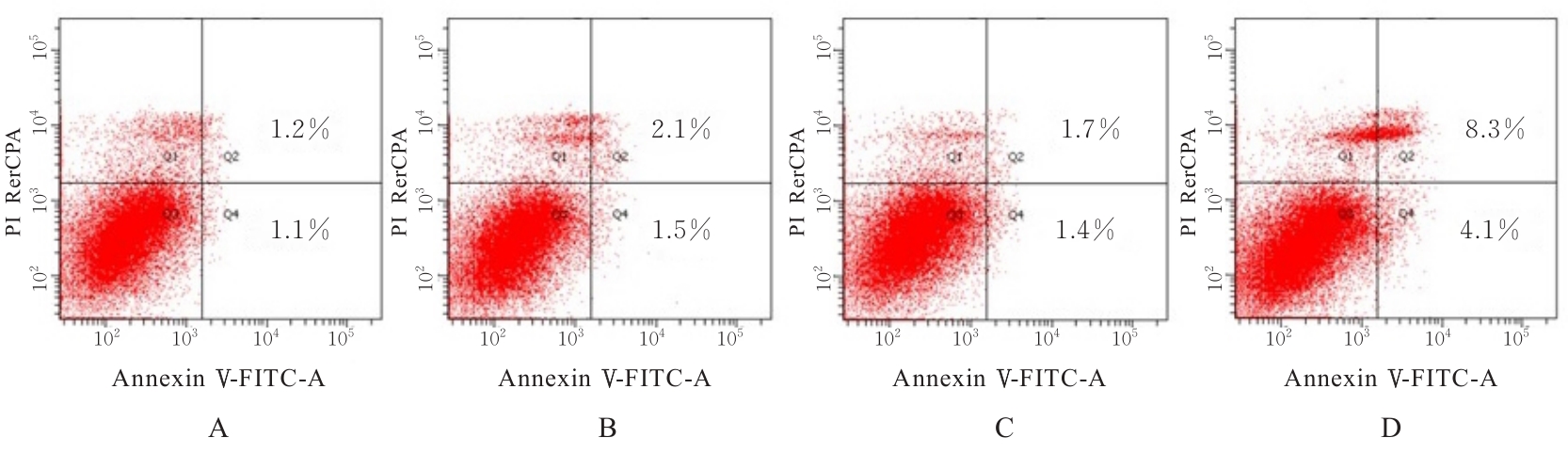
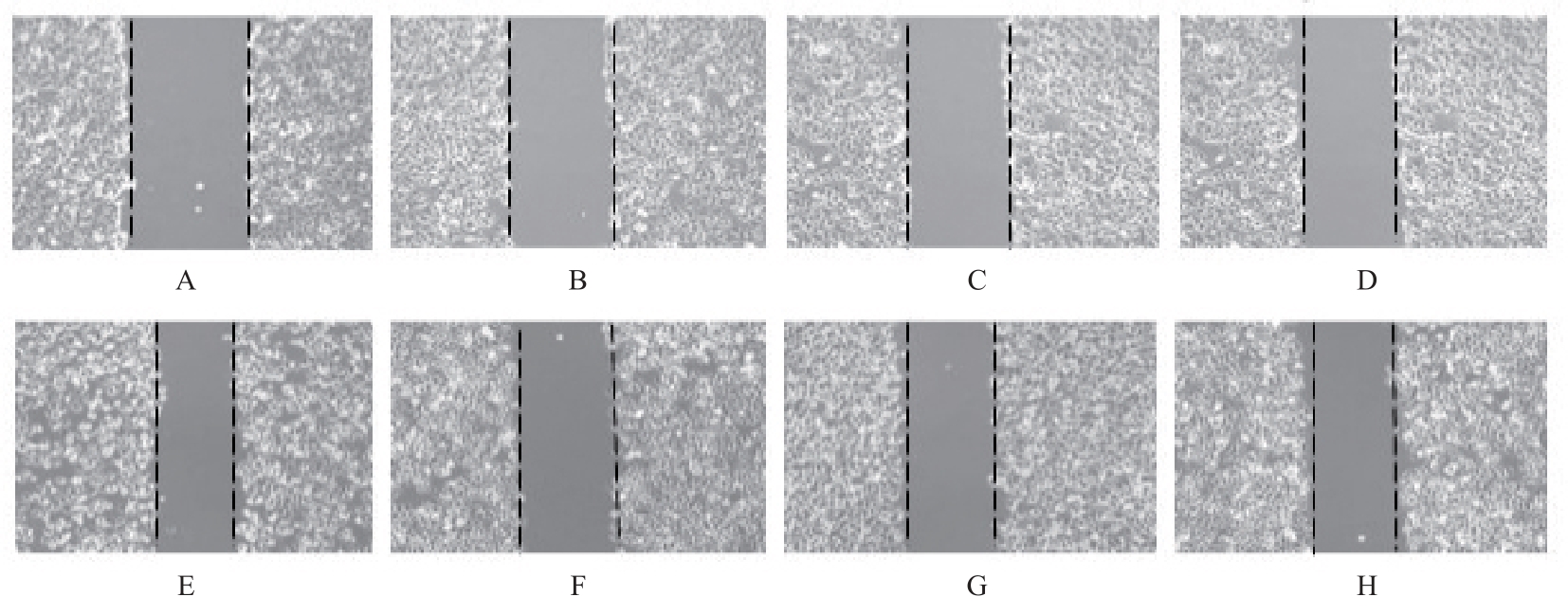
目的 探讨甲磺酸阿帕替尼(阿帕替尼)联合放射治疗(放疗)对肝癌HepG2细胞的体外协同抑制作用,阐明其相关抗肿瘤机制。 方法 体外培养肝癌HepG2细胞,以不同浓度阿帕替尼和(或)不同剂量X射线处理后,采用MTT法检测各组细胞活性,计算各组细胞增殖抑制率和阿帕替尼20%抑制浓度(IC20),并确定后续实验的X射线照射剂量。HepG2细胞分为阿帕替尼组、放疗组和阿帕替尼+放疗组(联合组),流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡率,细胞划痕实验检测各组细胞迁移率,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组细胞培养上清中血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)水平。 结果 MTT法检测,阿帕替尼的IC20为1.32 μmol·L-1,以此作为后续实验阿帕替尼作用浓度,确定2 Gy为后续实验X射线照射剂量。与对照组比较,阿帕替尼组和放疗组细胞凋亡率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),联合组细胞凋亡率升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,阿帕替尼组、放疗组和联合组细胞迁移率降低(P<0.05);与阿帕替尼组和放疗组比较,联合组细胞迁移率降低(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,阿帕替尼组和联合组细胞培养上清中VEGF水平降低(P<0.05);与阿帕替尼和放疗组比较,联合组细胞培养上清中VEGF水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 阿帕替尼联合放疗在体外可明显抑制肝癌HepG2细胞增殖和迁移,并诱导细胞凋亡,其作用可能与抑制细胞VEGF分泌有关。
中图分类号:
- R735.7