吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 85-95.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250111
积雪草酸通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路对脂多糖诱导大鼠海马神经元损伤的改善作用
- 锦州医科大学基础医学院药理学教研室,辽宁 锦州 121000
Improvement effect of asiatic acid on damage of lipopolysaccharide-induced hippocampum neuron in rats through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
Yanyan BAI,Yutong ZHOU,Haijuan SUI,Zhuo LIU( )
)
- Department of Pharmacology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
摘要:
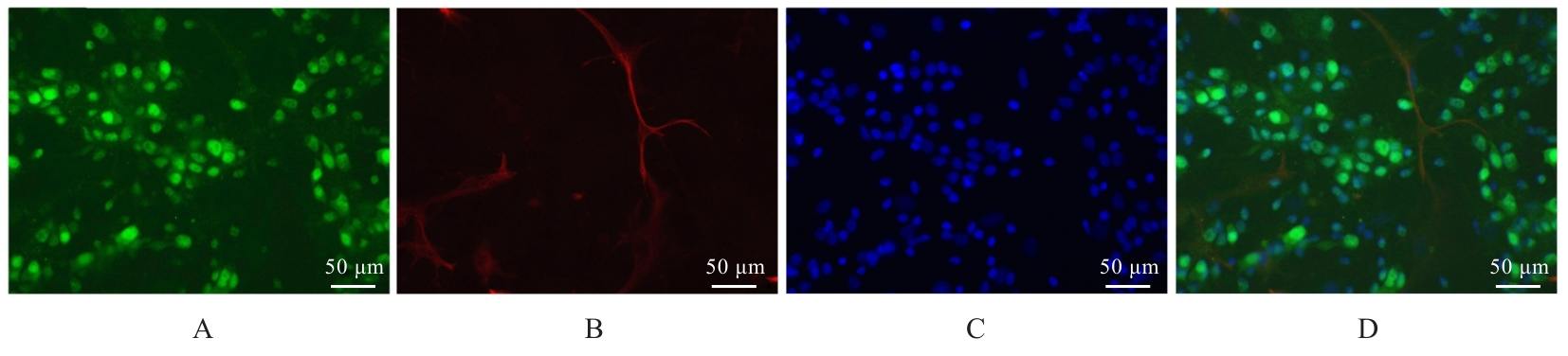
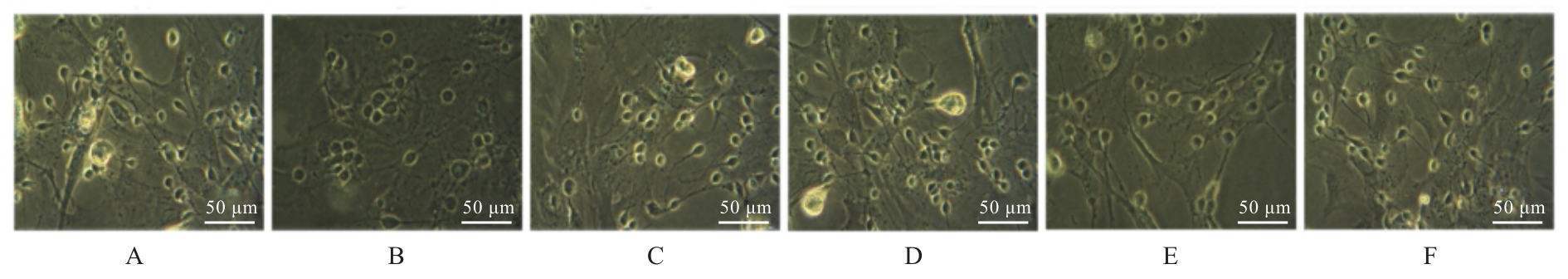
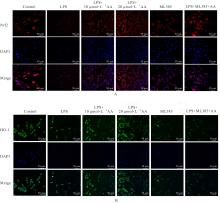
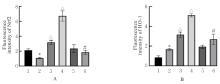
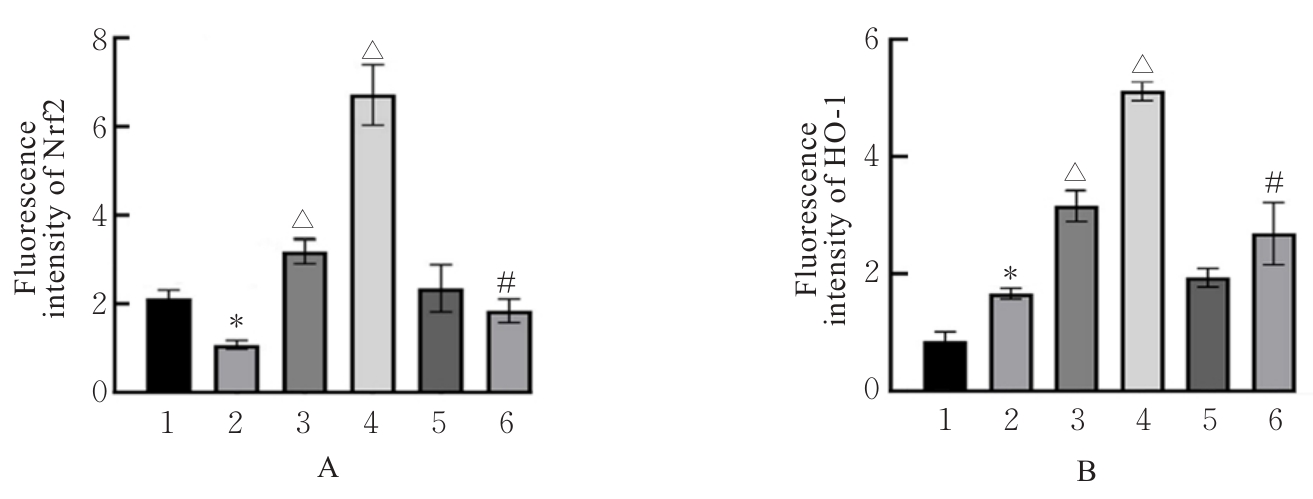
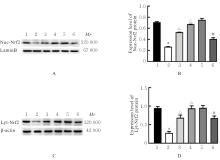
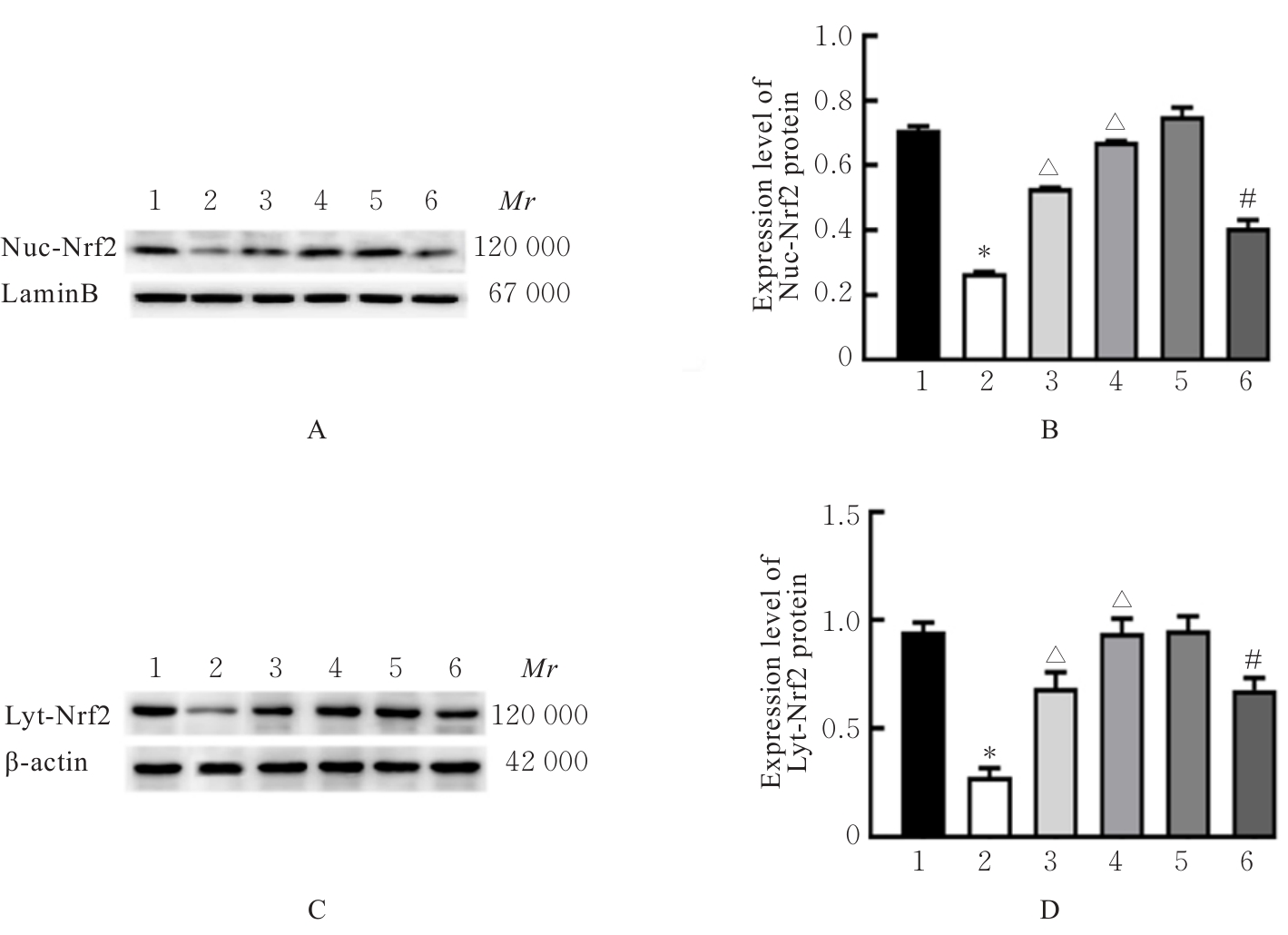
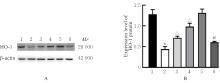
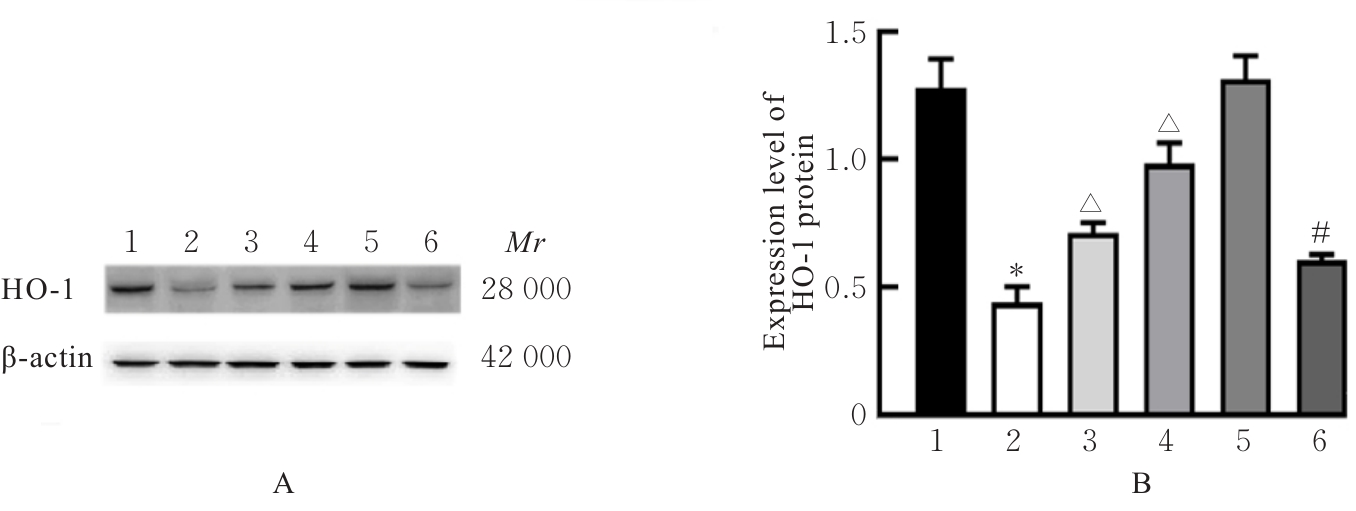
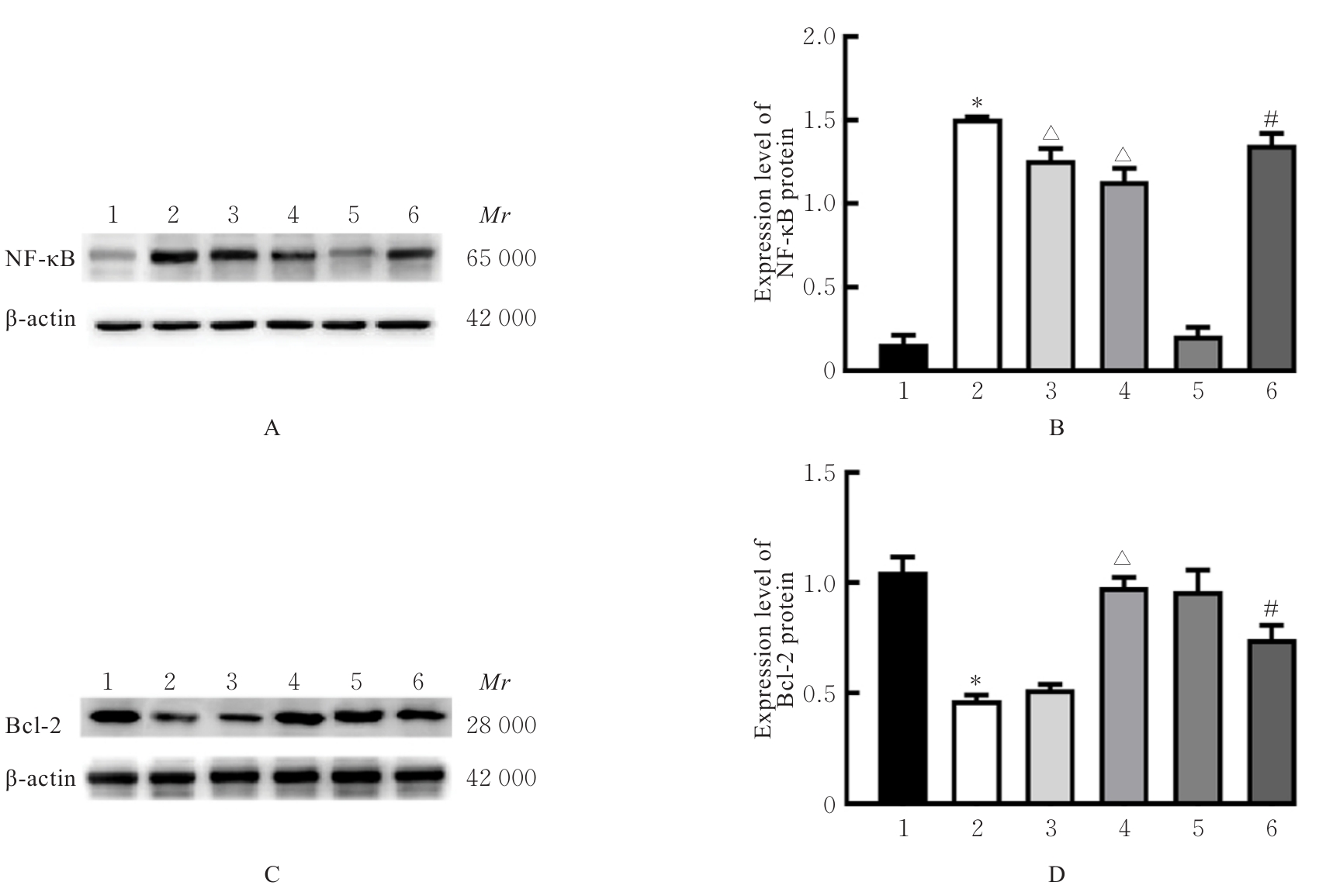
目的 探讨积雪草酸(AA)对脂多糖(LPS)诱导大鼠原代海马神经元炎症和氧化应激损伤的作用,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 原代培养大鼠海马神经元(免疫荧光染色法鉴定细胞纯度)分为对照组、LPS组(10 mg·L-1 LPS)、LPS+AA组(10 mg·L-1 LPS+10、20和40 μmol·L-1 AA)、AA组(20 μmol·L-1 AA)、ML385组[10 μmol·L-1核因子E2相关因子2(Nrf2)抑制剂]和LPS+ML385+AA组(10 mg·L-1 LPS+10 μmol·L-1 ML385+20 μmol·L-1 AA);给药处理后,噻唑蓝(MTT)法检测各组大鼠海马神经元的存活率,乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)试剂盒检测各组大鼠海马神经元LDH漏出率,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒检测各组大鼠海马神经元上清液中炎症因子[白细胞介素(IL)-1β和肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)-α]水平以及各组大鼠海马神经元中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性和丙二醛(MDA)水平,Griess法测定各组大鼠海马神经元上清液中一氧化氮(NO)水平,免疫荧光法检测各组大鼠海马神经元中Nrf2和血红素氧合酶1(HO-1)蛋白表达情况;Western blotting法检测各组大鼠海马神经元中Nrf2、HO-1、核因子κB(NF-κB)和B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)蛋白表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,LPS组大鼠海马神经元中的海马神经元存活率、SOD活性和Bcl-2表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),LDH漏出率、IL-1β和TNF-α水平、MDA水平、NO水平以及NF-κB蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01),Nrf2和HO-1的荧光强度明显减弱,Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01);与LPS组比较,LPS+10 μmol?L-1 AA组和LPS+20 μmol?L-1 AA组大鼠海马神经元存活率、SOD活性和Bcl-2表达水平明显升高(P<0.01),LDH漏出率、IL-1β和TNF-α水平、MDA水平、NO水平以及NF-κB蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),Nrf2和HO-1的荧光强度明显升高(P<0.01),Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);与LPS+20 μmol?L-1 AA组比较,LPS+ML385+AA组海马神经元中Nrf2和HO-1荧光强度明显减弱(P<0.01),细胞核和细胞质中Nrf2、细胞中HO-1和Bcl-2蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),NF-κB蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。 结论 AA可改善LPS诱导的原代培养大鼠海马神经元炎症和氧化应激损伤,其机制可能与激活Nrf2/HO-1信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R742