吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 689-696.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240313
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
五加生脉饮对小鼠的抗疲劳作用及其机制
- 1.北华大学药学院药物分析教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
2.长春中医药大学健康管理学院 预防医学教研室,吉林 长春 130117
Anti-fatigue effect of Wujia Shengmai Yin in mice and its mechanism
Jianan HAN1,Zhuorui LIU1,Peiyong ZENG1,Shuang JIANG2,Hongyu LI1( )
)
- 1.Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis,School of Pharmacy,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
2.Department of Preventive Medicine,School of Health Management,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
摘要:
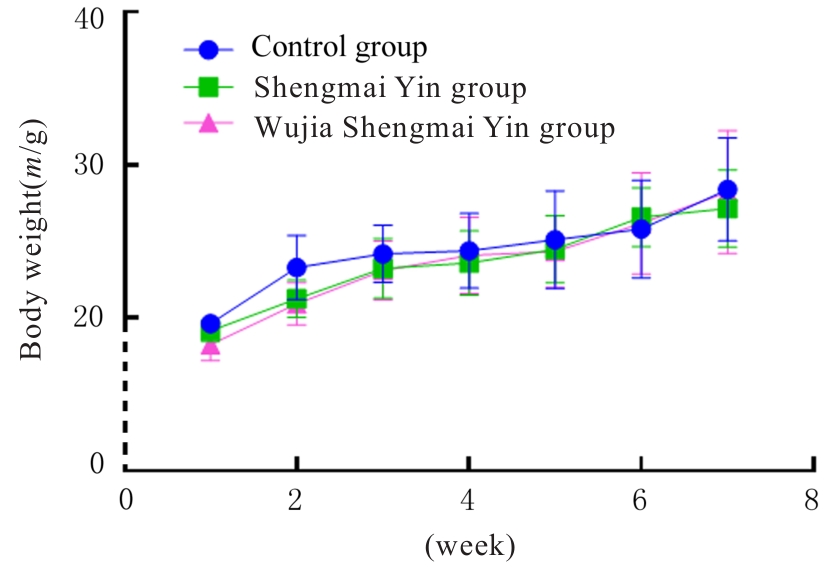
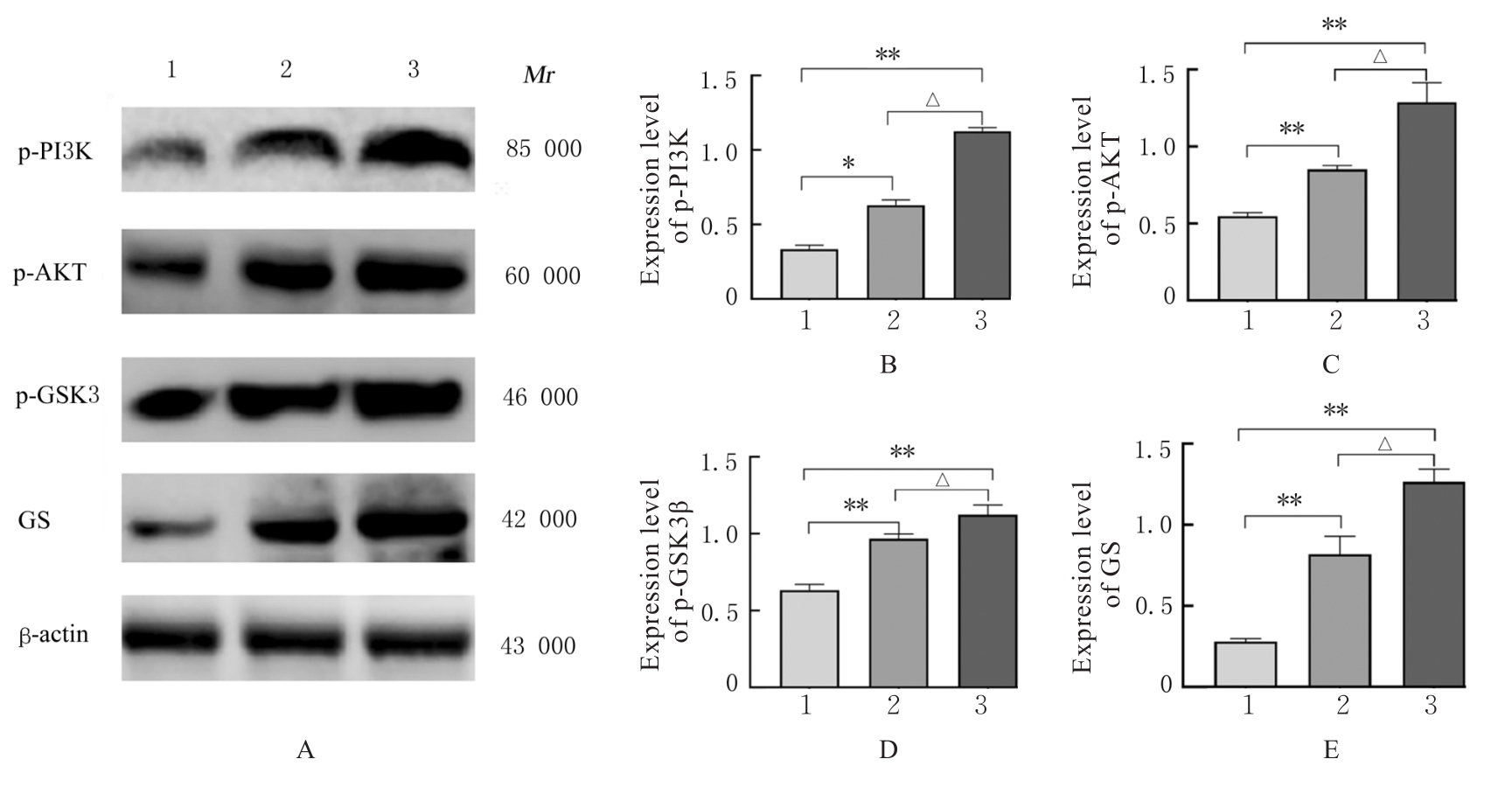
目的 探讨五加生脉饮的抗疲劳作用,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 36只雄性ICR小鼠随机分为对照组(等体积蒸馏水)、生脉饮组(500 mg·kg-1生脉饮)和五加生脉饮组(600 mg·kg-1五加生脉饮)。每隔7 d测定各组小鼠体质量,观察其精神状态。采用疲劳转棒实验和力竭负重游泳实验检测各组小鼠转棒停留时间和力竭游泳时间;试剂盒检测各组小鼠血清中血尿素氮(BUN)和乳酸(LA)水平及乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)活性、肝脏组织中肝糖原(LG)水平、肌肉组织中肌糖原(MG)和丙二醛(MDA)水平及谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性;Western blotting法检测各组小鼠肝脏组织中糖代谢相关蛋白表达水平。 结果 与实验前比较,实验后各组小鼠体质量均呈现增长趋势,但差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。疲劳转棒实验,与对照组比较,五加生脉饮组小鼠转棒停留时间明显增加(P<0.01);力竭负重游泳实验,与对照组比较,生脉饮组和五加生脉饮组小鼠力竭游泳时间均明显增加(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,生脉饮组和五加生脉饮组小鼠血清中BUN水平均明显降低(P<0.01),LDH活性均明显升高(P<0.01);五加生脉饮组LA水平明显降低(P<0.01)。与生脉饮组比较,五加生脉饮组小鼠血清中BUN和LA水平均明显降低(P<0.01),LDH活性明显升高(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,生脉饮组和五加生脉饮组小鼠肝脏组织中LG水平和肌肉组织中MG水平均明显升高(P<0.01);与生脉饮组比较,五加生脉饮组小鼠肝脏组织中LG水平和肌肉组织中MG水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,生脉饮组和五加生脉饮组小鼠肌肉组织中GSH-Px和SOD活性均明显升高(P<0.01),MDA水平明显降低(P<0.01);与生脉饮组比较,五加生脉饮组小鼠肌肉组织中GSH-Px和SOD活性均明显升高(P<0.01),MDA水平明显降低(P<0.01)。Western blotting法,与对照组比较,生脉饮组和五加生脉饮组小鼠肝脏组织中磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(p-PI3K)、磷酸化蛋白激酶B(p-AKT)、磷酸化糖原合成酶激酶3β(p-GSK3β)及糖原合成酶(GS)蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01);与生脉饮组比较,五加生脉饮组小鼠肝脏组织中p-PI3K、p-AKT、p-GSK3β和GS蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。 结论 五加生脉饮可通过激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(AKT)/糖原合成酶激酶3β(GSK3β)信号通路,提高机体抗氧化能力并增加糖原合成,发挥抗疲劳作用。
中图分类号:
- R289.1