吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 120-127.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240115
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
鹿茸多肽对骨质疏松模型大鼠的改善作用及对SIRT1/FOXO1信号通路的影响
迟雪婷1,黄晓巍1,2,陈芳园1,周高峰1,王晋冀1,律广富3,林喆1( ),龚庆4(
),龚庆4( )
)
- 1.长春中医药大学药学院临床药学与中药药理教研室,吉林 长春 130117
2.长春中医药大学东北亚中医药研究院基础研究所,吉林 长春 130117
3.长春中医药大学 吉林省人参科学研究院中药药理组,吉林 长春 130117
4.长春中医药大学附属医院骨科中心,吉林 长春 130021
Improvement effect of velvet antler polypeptide in osteoporosis model rats and its effect on SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling pathway
Xueting CHI1,Xiaowei HUANG1,2,Fangyuan CHEN1,Gaofeng ZHOU1,Jinji WANG1,Guangfu LYU3,Zhe LIN1( ),Qing GONG4(
),Qing GONG4( )
)
- 1.Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology of Chinese Medicine,School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Basic Research Institute,Northeast Asia Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
3.Department of Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Jilin Ginseng Academy,Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
4.Orthopedic Center,Affiliated Hospital,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
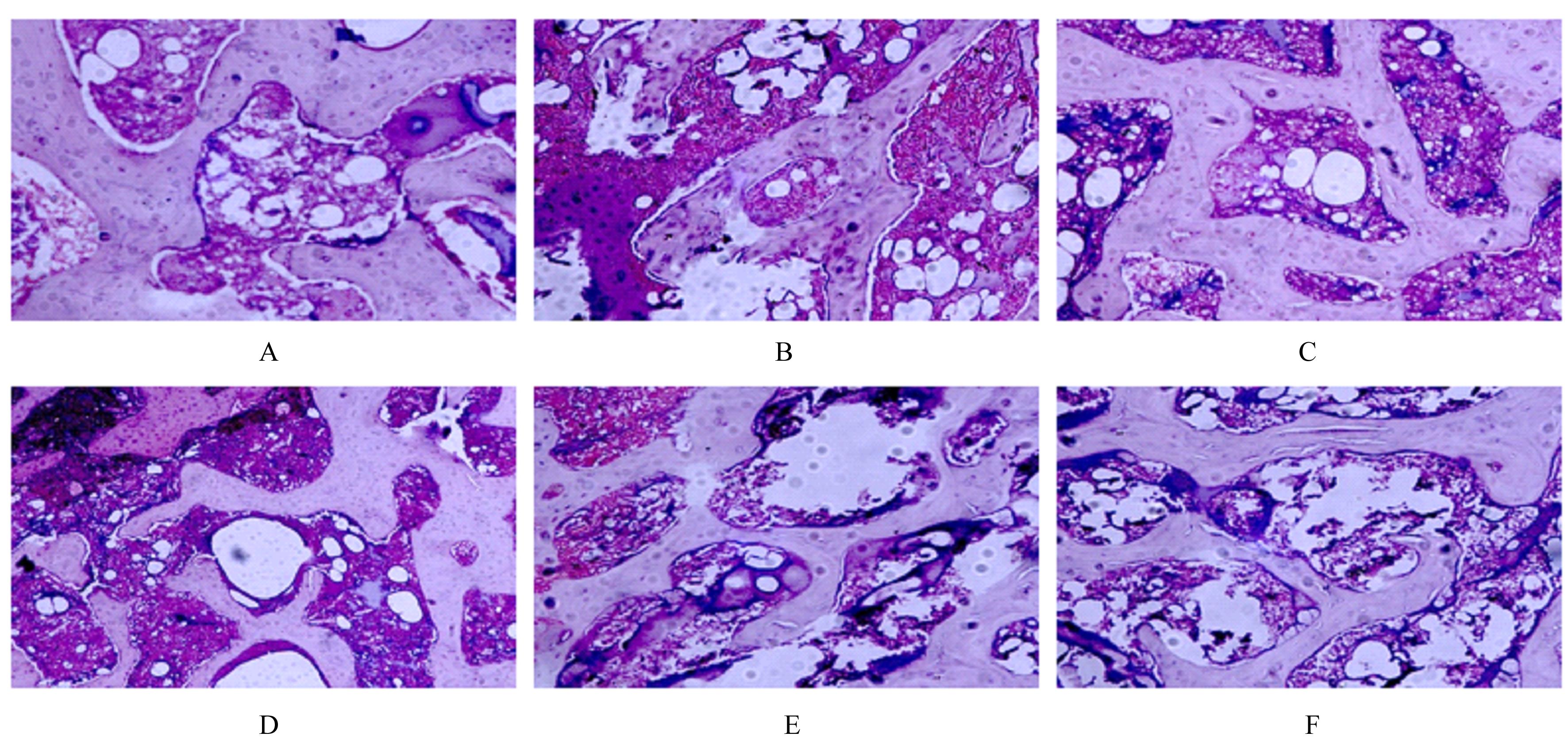
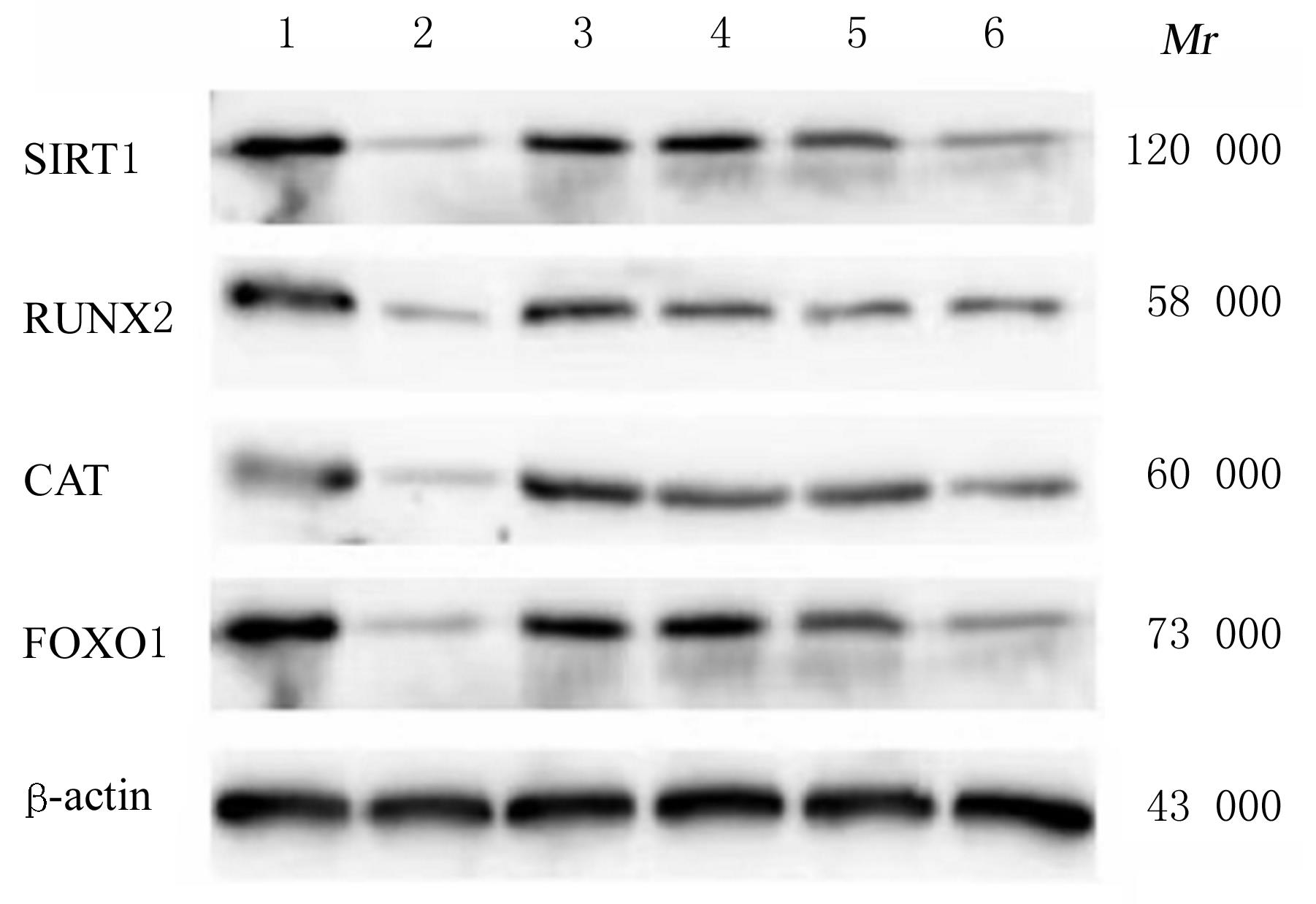
目的 探讨鹿茸多肽(VAP)对骨质疏松(OP)模型大鼠的保护作用,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 60只12周龄SD大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、阳性药组(1 mg·kg-1·d-1阿仑膦酸钠灌胃)、低剂量(100 mg·kg-1·d-1)VAP组、中剂量(200 mg·kg-1·d-1)VAP组和高剂量(300 mg·kg-1·d-1)VAP组,每组10只。除对照组外,其余各组大鼠肌肉注射地塞米松(2 mg·kg-1)复制OP大鼠模型,对照组大鼠肌肉注射等体积生理盐水,每周2次,连续11周。双能X射线骨密度仪检测各组大鼠股骨骨密度(BMD),酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组大鼠血清中血钙(Ca2+)、血磷(P)、骨保护素(OPG)、碱性磷酸酶(ALP)和骨钙素(OCN)水平,生化法检测各组大鼠血清中丙二醛(MDA)水平和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,HE染色观察各组大鼠骨组织病理形态表现,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠骨组织中沉默信息调节因子1(SIRT1)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、Runt相关转录因子2(RUNX2)和叉头框蛋白O1(FOXO1)蛋白表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠股骨BMD明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,阳性药组、中剂量VAP组和高剂量VAP组大鼠股骨BMD明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠血清中Ca2+、P和OPG水平及SOD活性明显降低(P<0.05),ALP、OCN和MDA水平明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低剂量VAP大鼠血清中OPG水平明显升高(P<0.05),阳性药组、中剂量VAP组和高剂量VAP组大鼠血清中Ca2+、P和OPG水平及SOD活性明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),阳性药组和各剂量VAP组大鼠血清中ALP、OCN和MDA水平明显降低(P<0.05或 P<0.01)。HE染色,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠骨组织中骨细胞数量减少且排列混乱,骨小梁纤细,出现大片断裂,髓腔扩大;与模型组比较,阳性药组、中剂量VAP组和高剂量VAP组大鼠骨组织中骨小梁粗壮,排列紧密。Western blotting法,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠骨组织中SIRT1、CAT、RUNX2和FOXO1蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,阳性药组、中剂量VAP组和高剂量VAP组大鼠骨组织中SIRT1、CAT、RUNX2和FOXO1蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。 结论 VAP对OP模型大鼠具有保护作用,其作用机制可能与介导SIRT1/FOXO1信号通路抗氧化应激作用有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5