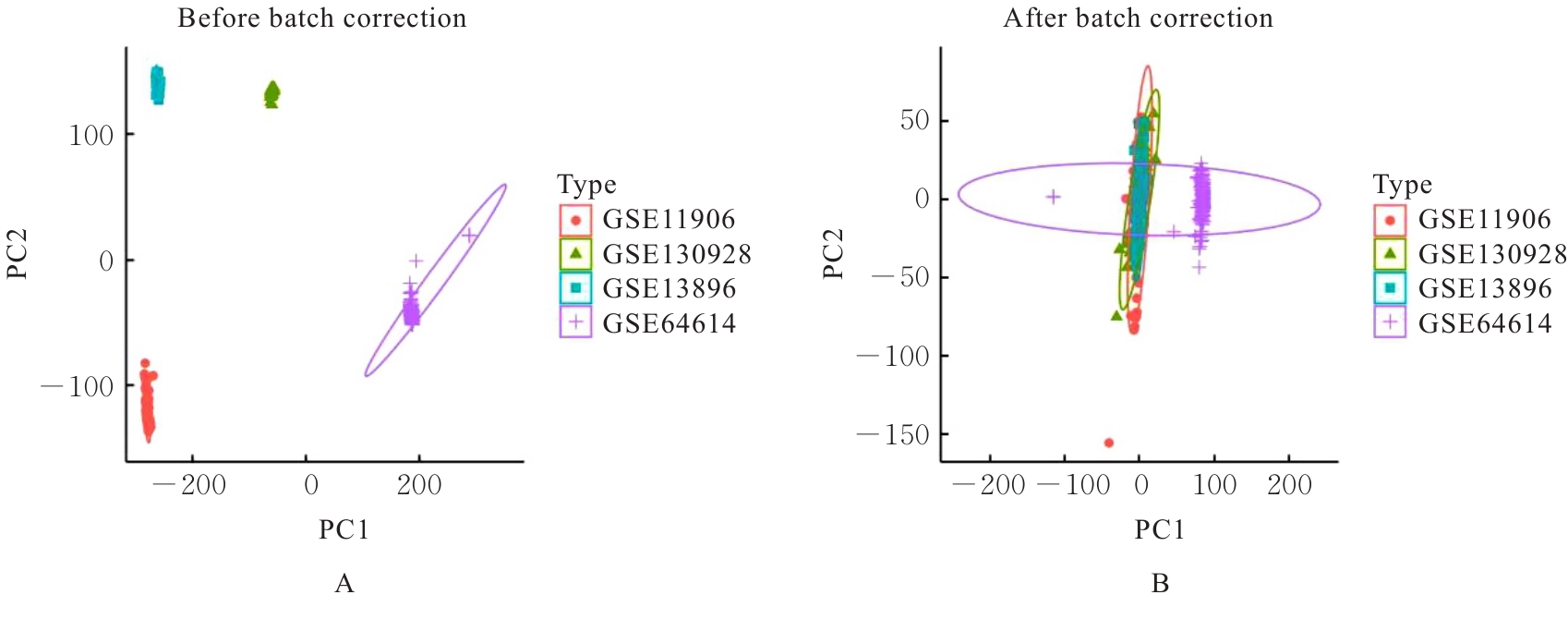
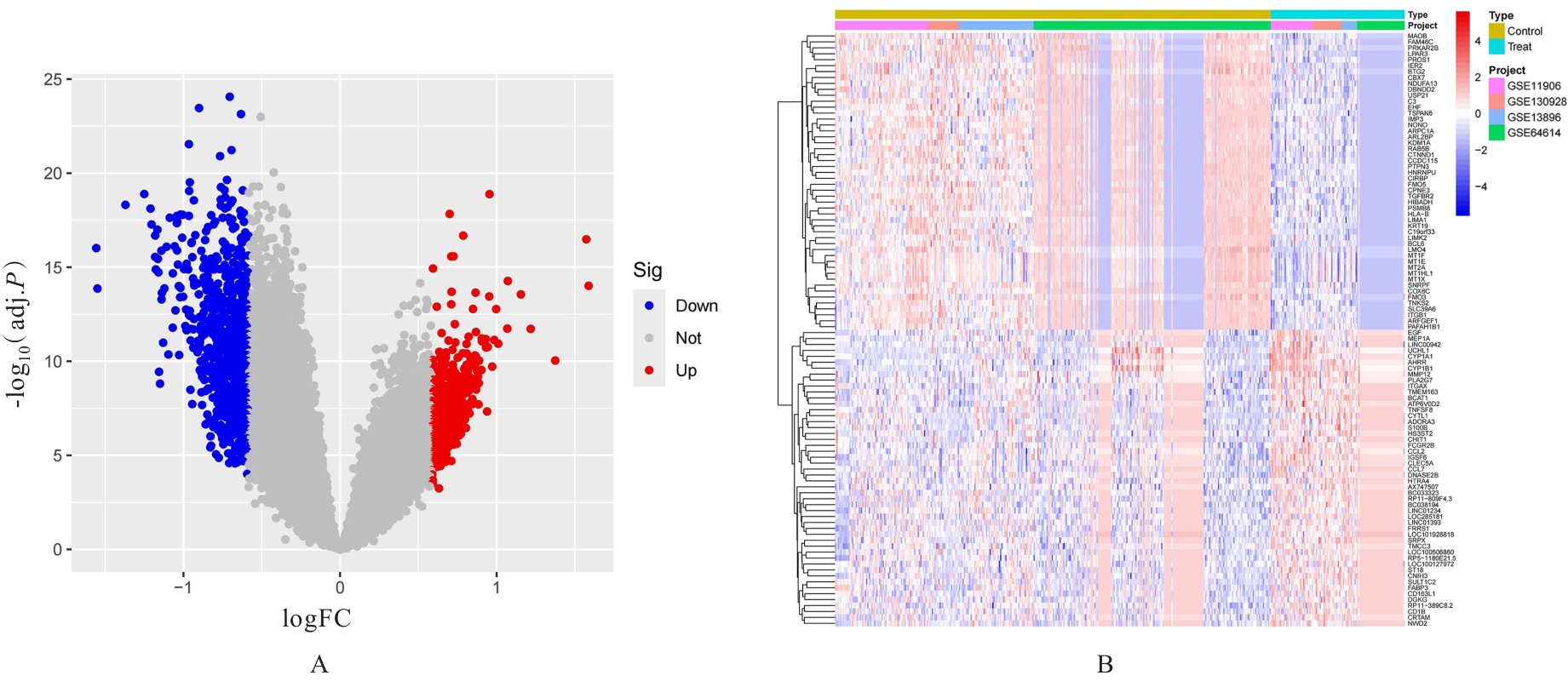
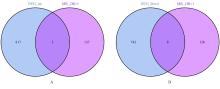
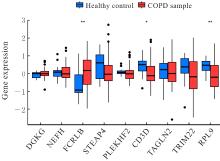
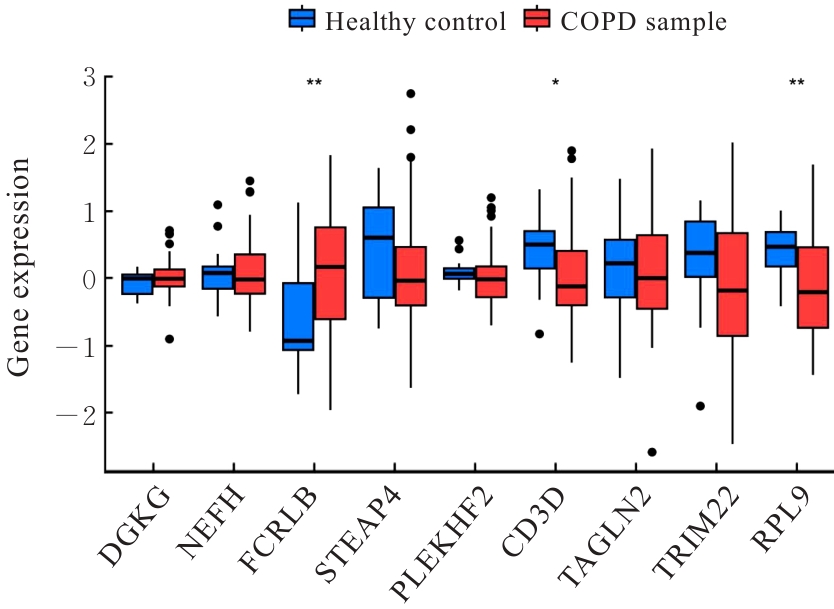
| [1] |
易 琼, 李 方, 雷 思, 等. 自主研发的藏四味清肺合剂联合常规治疗对慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者的临床疗效和安全性[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2024, 49(6): 921-931.
|
| [2] |
SIN D D, DOIRON D, AGUSTI A, et al. Air pollution and COPD: gold 2023 committee report[J]. Eur Respir J, 2023, 61(5): 2202469.
|
| [3] |
SAFIRI S, CARSON-CHAHHOUD K, NOORI M, et al. Burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. BMJ, 2022, 378: e069679.
|
| [4] |
DING Z, WANG K, LI J, et al. Association between glutathione S-transferase gene M1 and T1 polymorphisms and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease risk: a meta-analysis[J]. Clin Genet, 2019, 95(1): 53-62.
|
| [5] |
HUNNINGHAKE G M, CHO M H, TESFAIGZI Y, et al. MMP12, lung function, and COPD in high-risk populations[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 361(27): 2599-2608.
|
| [6] |
PILLAI S G, GE D L, ZHU G H, et al. A genome-wide association study in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): identification of two major susceptibility loci[J]. PLoS Genet, 2009, 5(3): e1000421.
|
| [7] |
SAKORNSAKOLPAT P, PROKOPENKO D, LAMONTAGNE M, et al. Genetic landscape of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease identifies heterogeneous cell-type and phenotype associations[J]. Nat Genet, 2019, 51(3): 494-505.
|
| [8] |
MILNE S, LI X, HERNANDEZ CORDERO A I, et al. Protective effect of club cell secretory protein (CC-16) on COPD risk and progression: a Mendelian randomisation study[J]. Thorax, 2020, 75(11): 934-943.
|
| [9] |
VÕSA U, CLARINGBOULD A, WESTRA H J, et al. Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression[J]. Nat Genet, 2021, 53(9): 1300-1310.
|
| [10] |
BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO M F, MINELLI C, et al. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: moving beyond the NOME assumption[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2019, 48(3): 728-742.
|
| [11] |
HARTWIG F P, DAVEY SMITH G, BOWDEN J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2017, 46(6): 1985-1998.
|
| [12] |
BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through egger regression[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44(2): 512-525.
|
| [13] |
CHOI J Y, RHEE C K. Diagnosis and treatment of early chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD)[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(11): 3426.
|
| [14] |
中华医学会, 中华医学会杂志社, 中华医学会全科医学分会, 等. 中国慢性阻塞性肺疾病基层诊疗与管理指南(2024年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2024, 23(6): 578-602.
|
| [15] |
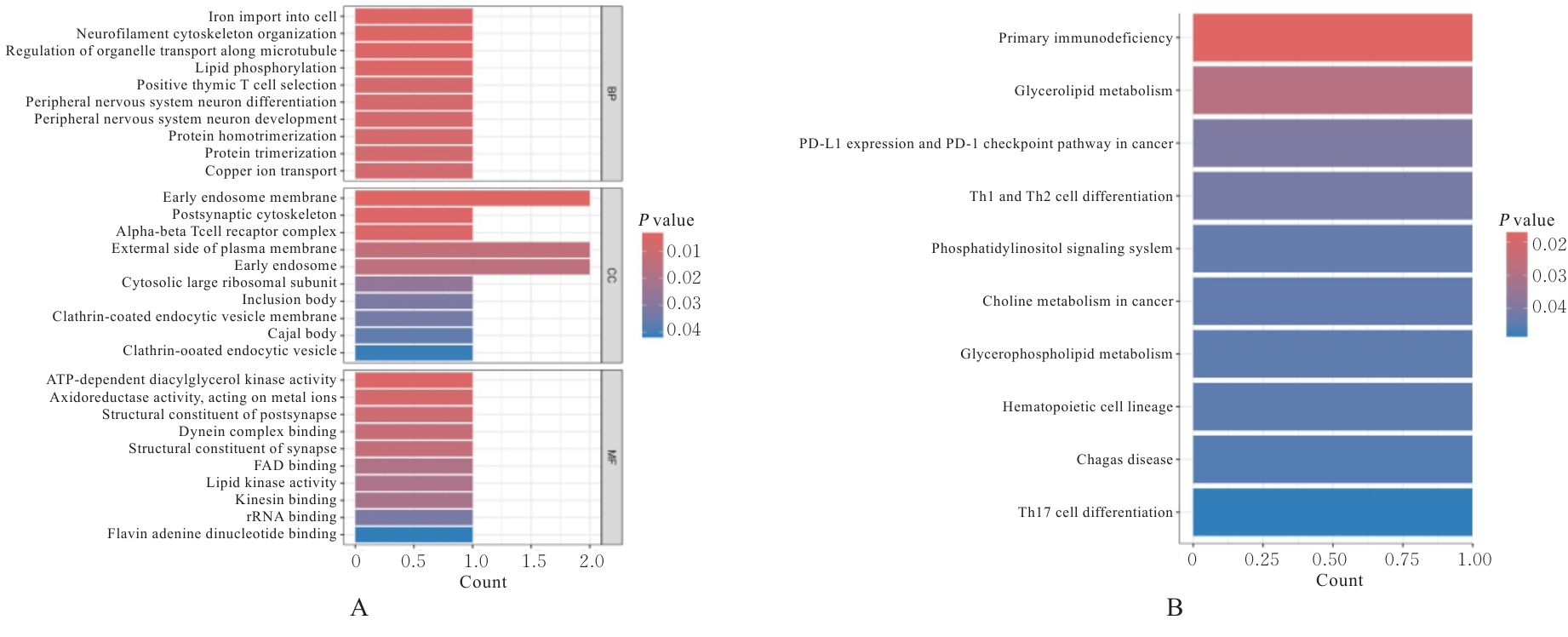
OHNISHI H, EITOKU M, YOKOYAMA A. A systematic review and integrated analysis of biologics that target Type 2 inflammation to treat COPD with increased peripheral blood eosinophils[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(6): e09736.
|
| [16] |
WANG C X, ZHOU J D, WANG J Q, et al. Progress in the mechanism and targeted drug therapy for COPD[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5(1): 248.
|
| [17] |
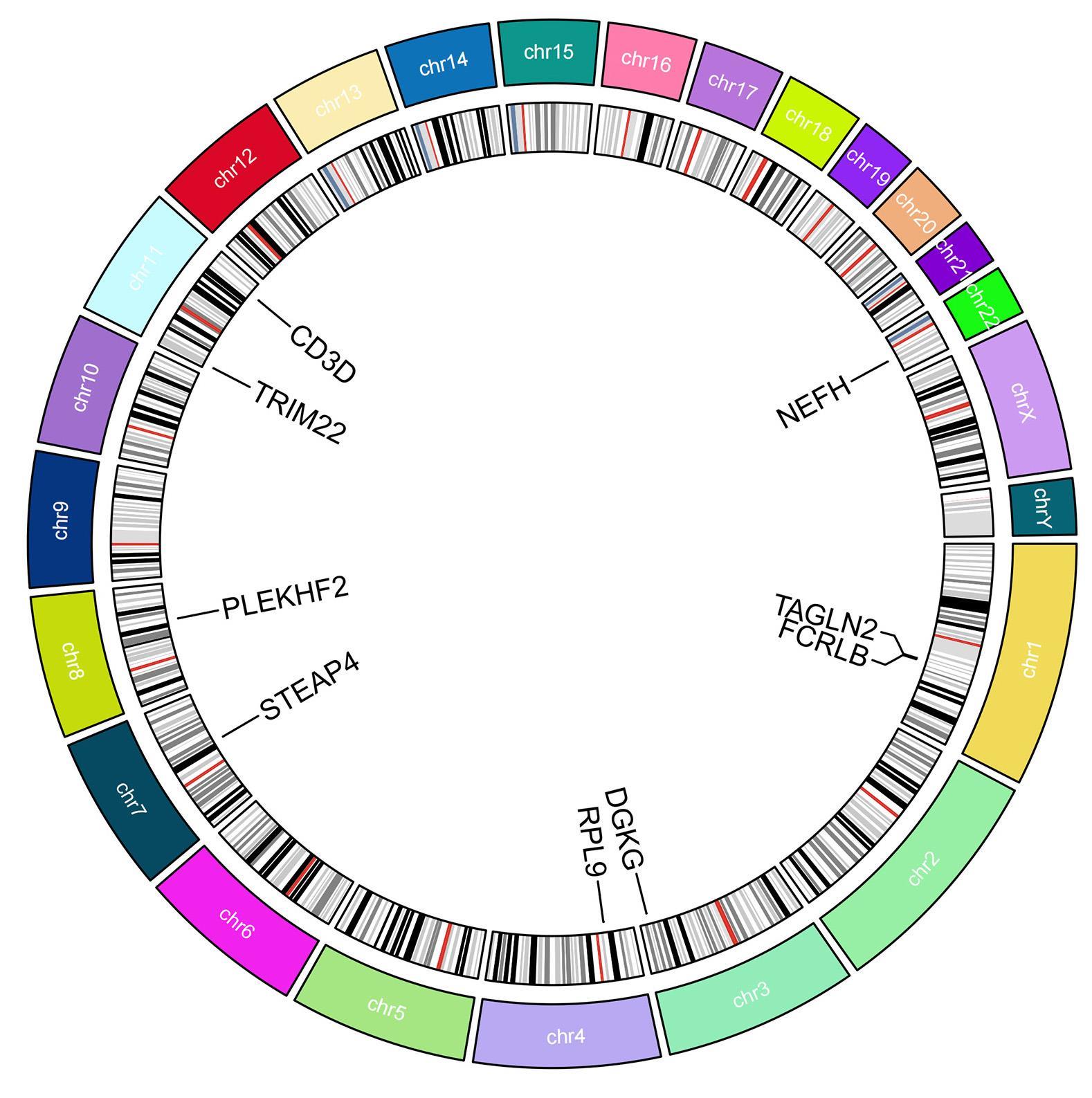
ZHANG L R, XU J L, ZHOU S Q, et al. Endothelial DGKG promotes tumor angiogenesis and immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2024, 80(1): 82-98.
|
| [18] |
TAN L F, YANG X F, ZHANG J X, et al. Correlation between HIF1-a expression and airway remodeling in COPD[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2024, 19: 921-931.
|
| [19] |
SONG Y B, QU Z, FENG H, et al. Genomic and immunological characterization of pyroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022: 6905588.
|
| [20] |
LIU X L, HUANG X L, XU F. The influence of pyroptosis-related genes on the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2023, 23(1): 167.
|
| [21] |
WANG Z L, HE Y, CUN Y P, et al. Identification of potential key genes for immune infiltration in childhood asthma by data mining and biological validation[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 957030.
|
| [22] |
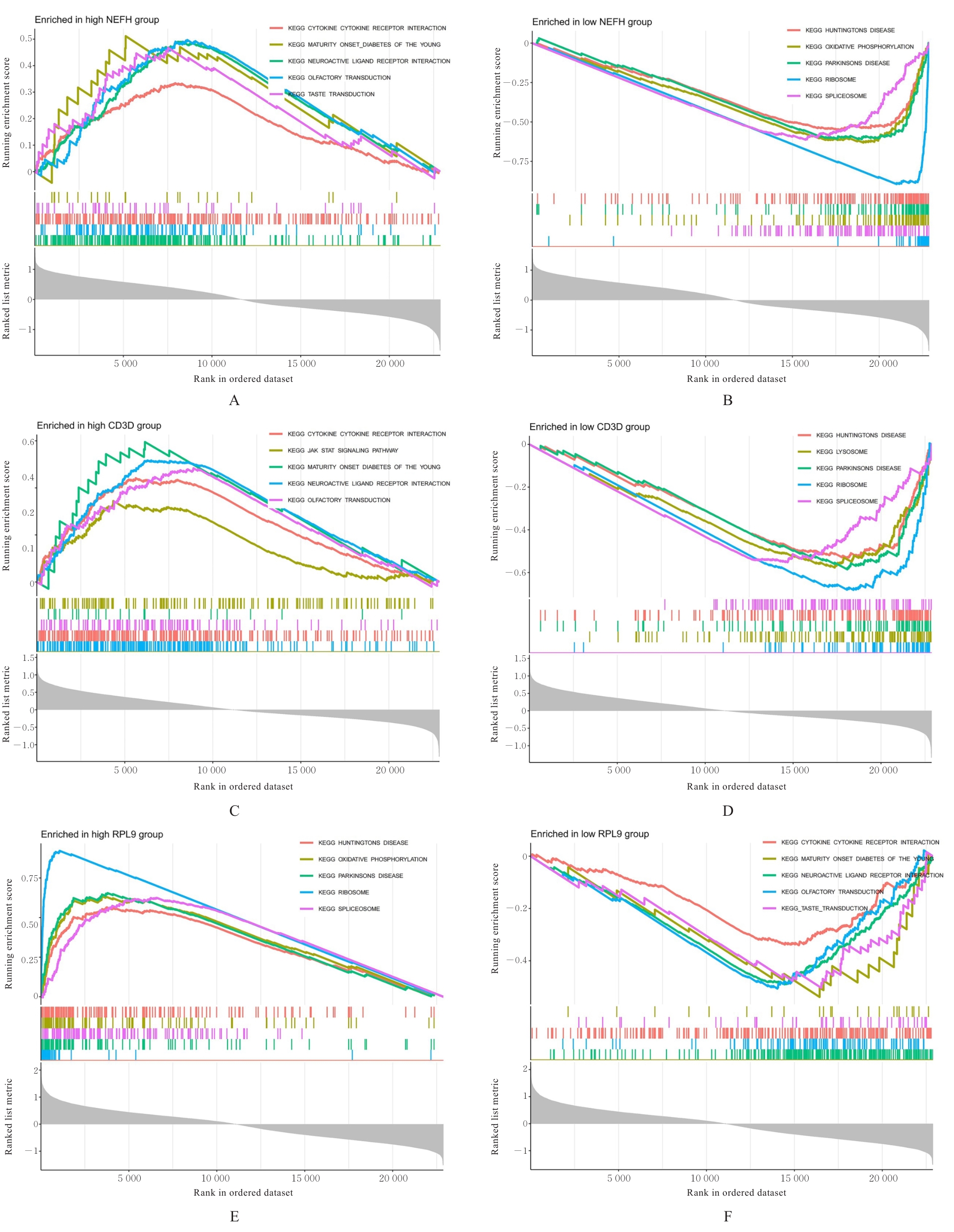
SUN J, LIU T, YAN Y, et al. The role of Th1/Th2 cytokines played in regulation of specific CD4+ Th1 cell conversion and activation during inflammatory reaction of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2018, 88(1): e12674.
|
| [23] |
WATANABE M, TOYOMURA T, WAKE H, et al. Cationic ribosomal proteins can inhibit pro-inflammatory action stimulated by LPS+HMGB1 and are hindered by advanced glycation end products[J]. Biotechnol Appl Biochem, 2024, 71(2): 264-271.
|
| [24] |
WATANABE M, TOYOMURA T, WAKE H, et al. Identification of ribosomal protein L9 as a novel regulator of proinflammatory damage-associated molecular pattern molecules[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2022, 49(4): 2831-2838.
|
| [25] |
FARRE-GARROS R, LEE J Y, NATANEK S A, et al. Quadriceps miR-542-3p and-5p are elevated in COPD and reduce function by inhibiting ribosomal and protein synthesis[J]. J Appl Physiol (1985), 2019, 126(6): 1514-1524.
|
| [26] |
NAJAFINOBAR N, VENKATESAN S, VON SYDOW L, et al. ToF-SIMS mediated analysis of human lung tissue reveals increased iron deposition in COPD (GOLD IV) patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9: 10060.
|
| [27] |
ZHANG W Z, OROMENDIA C, KIKKERS S A, et al. Increased airway iron parameters and risk for exacerbation in COPD: an analysis from SPIROMICS[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 10562.
|
| [28] |
VARRICCHI G, POTO R. Towards precision medicine in COPD: targeting type 2 cytokines and alarmins[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2024, 125: 28-31.
|
| [29] |
PROBOSZCZ M, GORYCA K, NEJMAN-GRYZ P, et al. Phenotypic variations of mild-to-moderate obstructive pulmonary diseases according to airway inflammation and clinical features[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2021, 14: 2793-2806.
|
| [30] |
HAYDEN L P, HOBBS B D, BUSCH R, et al. X chromosome associations with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and related phenotypes: an X chromosome-wide association study[J]. Respir Res, 2023, 24(1): 38.
|
| [31] |
LUTZ S M, CHO M H, YOUNG K, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies risk loci for spirometric measures among smokers of European and African ancestry[J]. BMC Genet, 2015, 16: 138.
|
| [32] |
ALMUNTASHIRI S, ZHU Y, HAN Y, et al. Club cell secreted protein CC16: potential applications in prognosis and therapy for pulmonary diseases[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(12): 4039.
|
| [33] |
YEW-BOOTH L, BIRRELL M A, LAU M S, et al. JAK-STAT pathway activation in COPD[J]. Eur Respir J, 2015, 46(3): 843-845.
|
| [34] |
LERNER C A, SUNDAR I K, RAHMAN I. Mitochondrial redox system, dynamics, and dysfunction in lung inflammaging and COPD[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2016, 81(Pt B): 294-306.
|
| [35] |
BOZINOVSKI S, VLAHOS R, ANTHONY D, et al. COPD and squamous cell lung cancer: aberrant inflammation and immunity is the common link[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2016, 173(4): 635-648.
|
| [36] |
HE S R, TIAN R Y, ZHANG X Y, et al. PPARγ inhibits small airway remodeling through mediating the polarization homeostasis of alveolar macrophages in COPD[J]. Clin Immunol, 2023, 250: 109293.
|
| [37] |
KUME H, YAMADA R, SATO Y, et al. Airway smooth muscle regulated by oxidative stress in COPD[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2023, 12(1): 142.
|
| [38] |
KOLAROV V, STEVULJEVIĆ J K, ILIĆ M, et al. Factorial analysis of N-acetylcysteine and propolis treatment effects on symptoms, life quality and exacerbations in patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 26(9): 3192-3199.
|
 ),李慧茹1,2,董晓升1,2,刘元元1,2
),李慧茹1,2,董晓升1,2,刘元元1,2
 ),Huiru LI1,2,Xiaosheng DONG1,2,Yuanyuan LIU1,2
),Huiru LI1,2,Xiaosheng DONG1,2,Yuanyuan LIU1,2