吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1267-1273.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250513
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
IFN-γ对神经母细胞瘤细胞增殖的抑制作用及神经母细胞瘤组织中SULT2B1蛋白表达的临床意义
杨映然1,王靖1,仇友政1,张杉杉2,李娜2,申伟2,陈瑛3,王宁1( )
)
- 1.大理大学临床医学院外科教研室,云南 大理 671000
2.大理大学第一附属医院小儿外科,云南 大理 671000
3.大理大学第一附属医院体检中心,云南 大理 671000
Inhibitory effect of IFN-γ on proliferation of neuroblastoma cells and clinical significance of SULT2B1 protein expression in neuroblastoma tissue
Yingran YANG1,Jing WANG1,Youzheng QIU1,Shanshan ZHANG2,Na LI2,Wei SHEN2,Ying CHEN3,Ning WANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Surgery,School of Clinical Medicine,Dali University,Dali 671000,China
2.Department of Pediatric Surgery,First Affiliated Hospital,Dali University,Dali 671000,China
3.Physical Examination Center,First Affiliated Hospital,Dali University,Dali 671000,China
摘要:
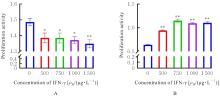
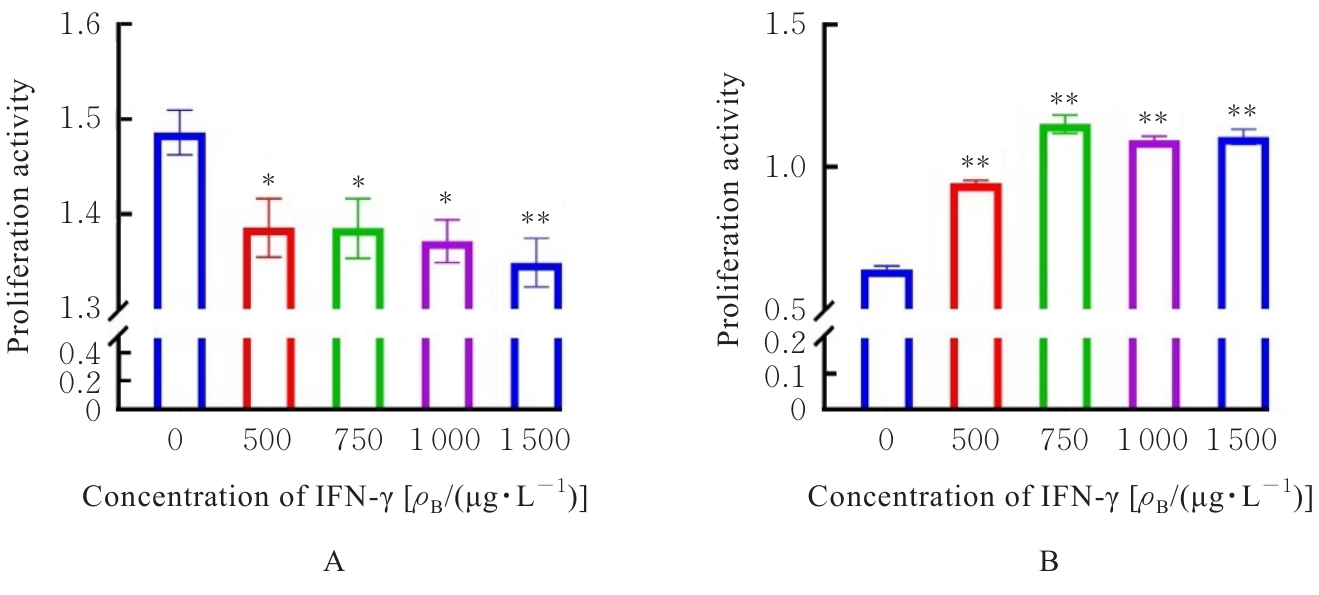
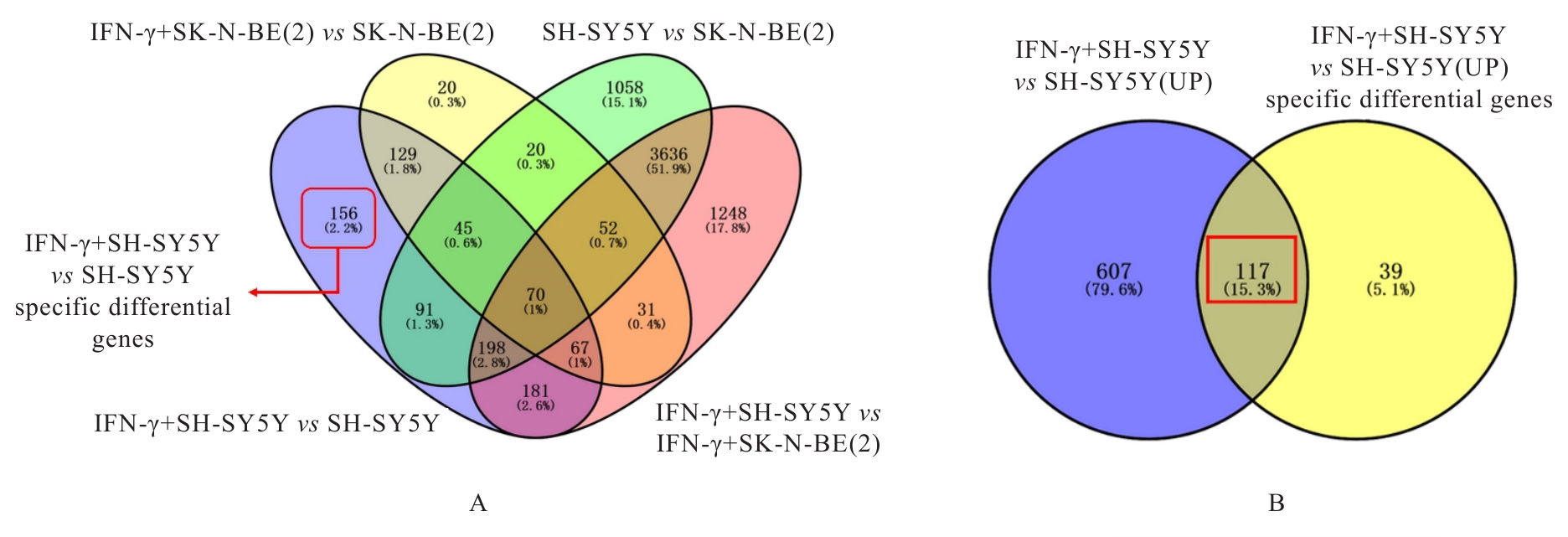
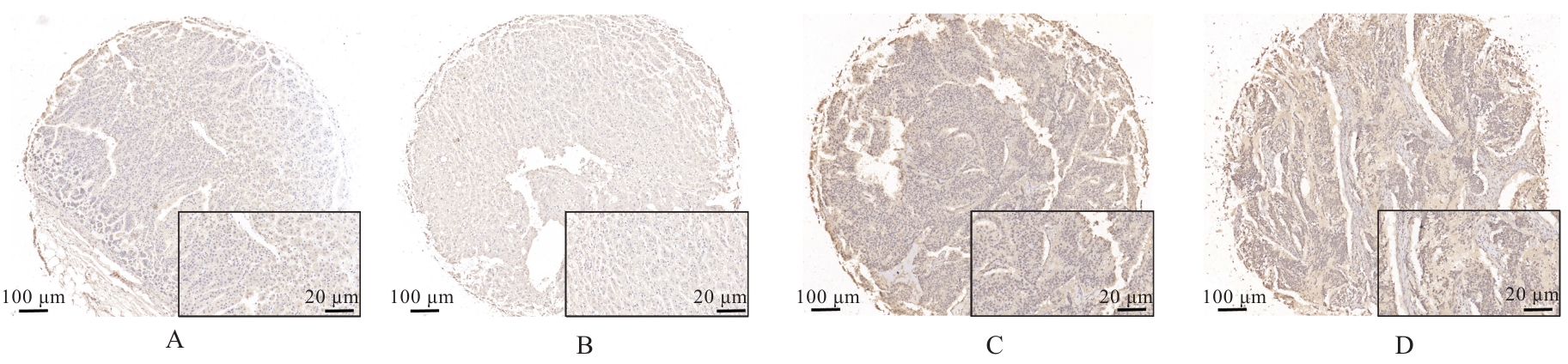
目的 探讨干扰素γ(IFN-γ)对神经母细胞瘤细胞增殖的影响和IFN-γ潜在的基因签名,以及该基因签名在神经母细胞瘤细胞中的表达及其与不良预后的关系,阐明IFN-γ及其基因签名在神经母细胞瘤中的作用。 方法 选取神经母细胞瘤细胞SK-N-BE(2)(原癌基因N-MYC扩增型)和SH-SY5Y(原癌基因N-MYC 非扩增型)细胞,分别使用不同浓度(0、500、750、1 000和1 500 μg·L-1)IFN-γ处理24 h后,采用细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)法检测细胞增殖活性,并收集细胞样本进行转录组测序,确定IFN-γ基因签名。收集23例神经母细胞瘤组织和6例正常肾上腺组织,采用免疫组织化学法(IHC)检测IFN-γ基因签名的表达。根据IFN-γ基因签名表达水平将神经母细胞瘤组织分为SULT2B1低表达和高表达组,分析IFN-γ基因签名表达水平与患者不良预后的关系。 结果 CCK-8法,随着IFN-γ浓度增加,SK-N-BE(2)细胞增殖活性明显降低(P<0.01),4组SK-N-BE(2)细胞抑制率分别为6.73%、6.77%、7.67%和9.19%;随着IFN-γ浓度升高,SH-SY5Y细胞增殖活性明显升高(P<0.01),4组SH-SY5Y细胞增殖率分别为46.80%、79.19%、70.30%和72.33%。转录组测序分析确定了IFN-γ的基因签名可能为羟基类固醇磺基转移酶2B1(SULT2B1)。IHC检测,神经母细胞瘤组织中SULT2B1蛋白表达量明显升高。临床资料分析,SULT2B1低表达组与高表达组患者年龄(Z=-2.618,P=0.018)、淋巴结转移(χ2=4.439,P=0.035)和远处转移(χ2=5.856,P=0.016)情况比较差异有统计学意义。 结论 IFN-γ可以抑制SK-N-BE(2)细胞增殖,促进SH-SY5Y细胞增殖;IFN-γ的基因签名可能为SULT2B1;SULT2B1在神经母细胞瘤组织中表达上调,且SULT2B1高表达与神经母细胞瘤患者不良预后有关联。
中图分类号:
- R739.4