吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 596-601.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240302
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
尿石素A对小鼠异氟醚麻醉所致术后认知功能障碍的改善作用及其机制
许敏慧1,程晓雷2,许继岩1,2,江林昊1,2,夏天娇1( )
)
- 1.南京大学医学院,江苏 南京 210008
2.南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院麻醉科,江苏 南京 210008
Effect of urolithin A on postoperative cognitive dysfunction induced by isoflurane anesthesia in mice and its mechanism
Minhui XU1,Xiaolei CHENG2,Jiyan XU1,2,Linhao JIANG1,2,Tianjiao XIA1( )
)
- 1.School of Medical Sciences,Nanjing University,Nanjing 210008,China
2.Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital,School of Medical Sciences,Nanjing University,Nanjing 210008,China
摘要:
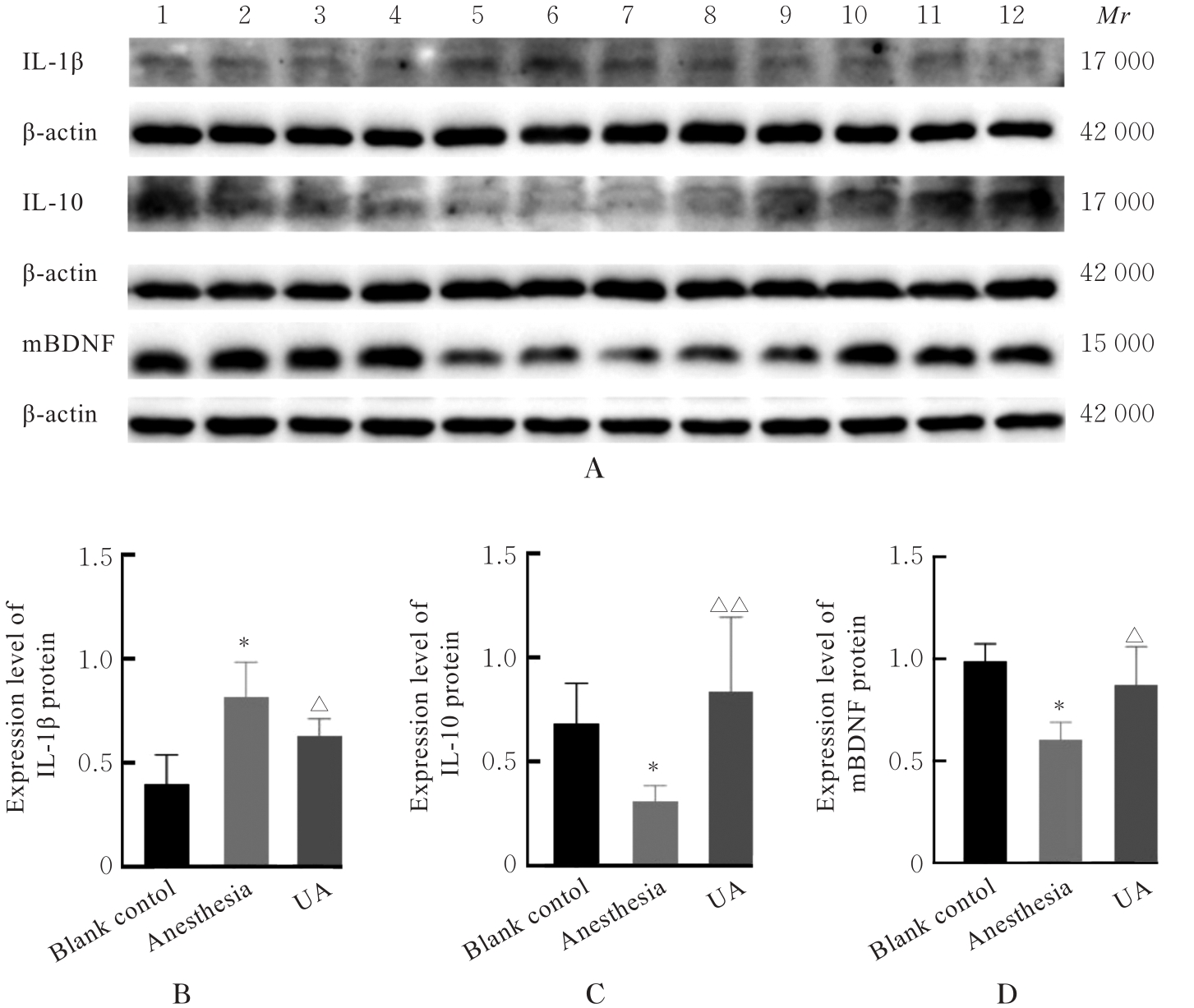
目的 探讨尿石素A(UA)对长时程异氟醚麻醉所致小鼠术后认知功能障碍(POCD)的改善作用,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 24只健康雄性C57BL/6小鼠随机分为空白对照组、麻醉组和UA组,每组8只。UA组小鼠于麻醉前2 d每天腹腔注射200 μL UA溶液,空白对照组和麻醉组小鼠给予等体积生理盐水,麻醉组和UA组小鼠制备长时程异氟醚麻醉模型,空白对照组小鼠不作处理。采用Y迷宫实验检测各组小鼠轮替正确率、移动距离和移动速度,条件恐惧实验检测各组小鼠僵直时间百分率,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠海马组织中白细胞介素(IL)-1β、IL-10和成熟脑源性神经营养因子(mBDNF)蛋白表达水平。 结果 Y迷宫实验,与空白对照组比较,麻醉组小鼠轮替正确率明显降低(P<0.01);与麻醉组比较,UA组小鼠轮替正确率明显升高(P<0.01)。条件恐惧实验中情境记忆测试,与空白对照组比较,麻醉组小鼠僵直时间百分率明显降低(P<0.01);与麻醉组比较,UA组小鼠僵直时间百分率明显升高(P<0.05);线索记忆测试,各组小鼠僵直时间百分率比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。Western blotting法,与空白对照组比较,麻醉组小鼠海马组织中IL-1β蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01),IL-10和mBDNF蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01);与麻醉组比较,UA组小鼠海马组织中IL-1β蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),IL-10和mBDNF蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。 结论 UA可以改善小鼠的POCD,其作用机制可能与UA的抗炎活性可抑制POCD小鼠的中枢炎症且上调mBDNF蛋白表达有关。
中图分类号:
- R742