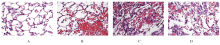
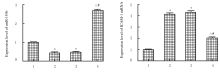
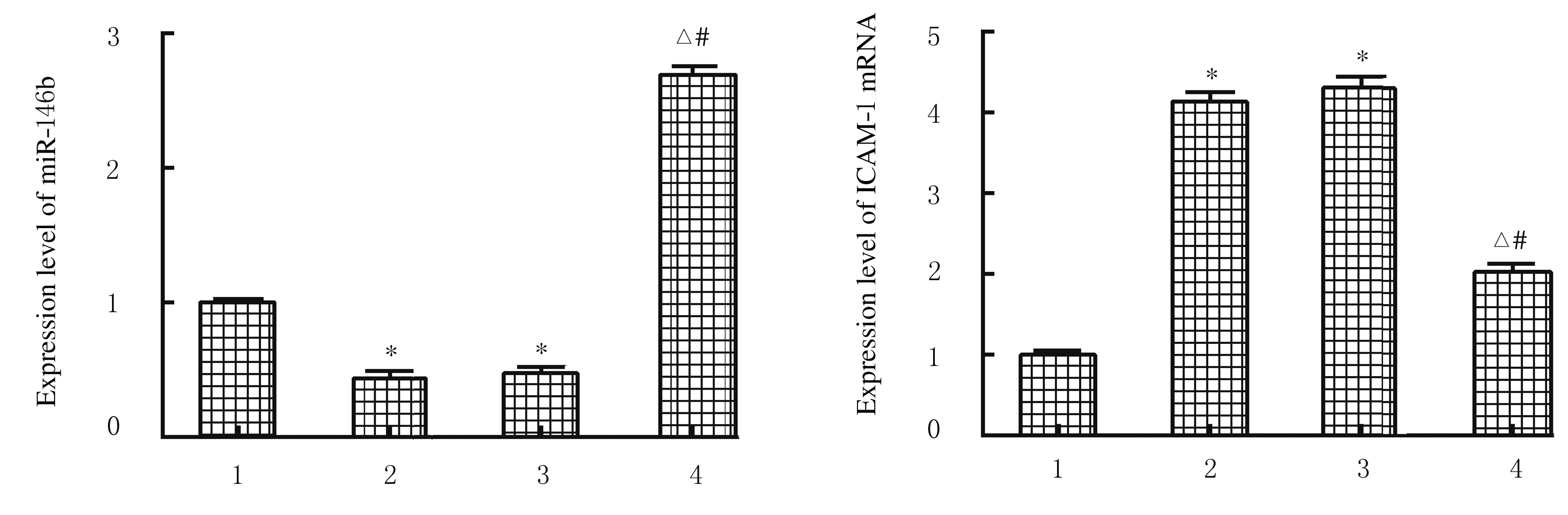
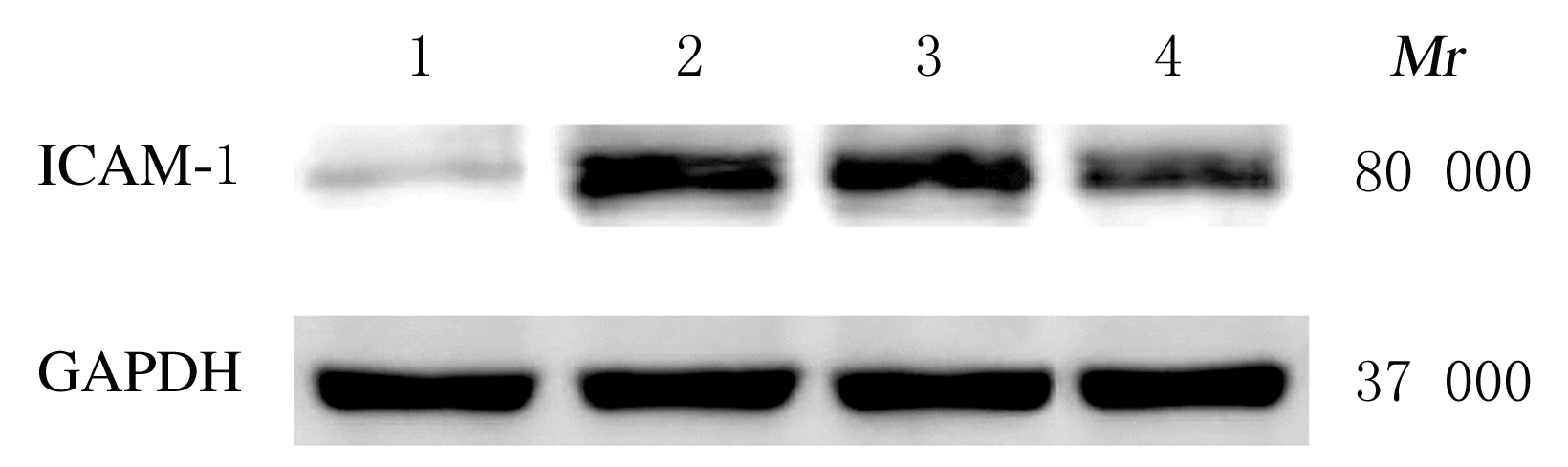
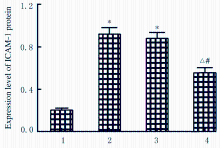
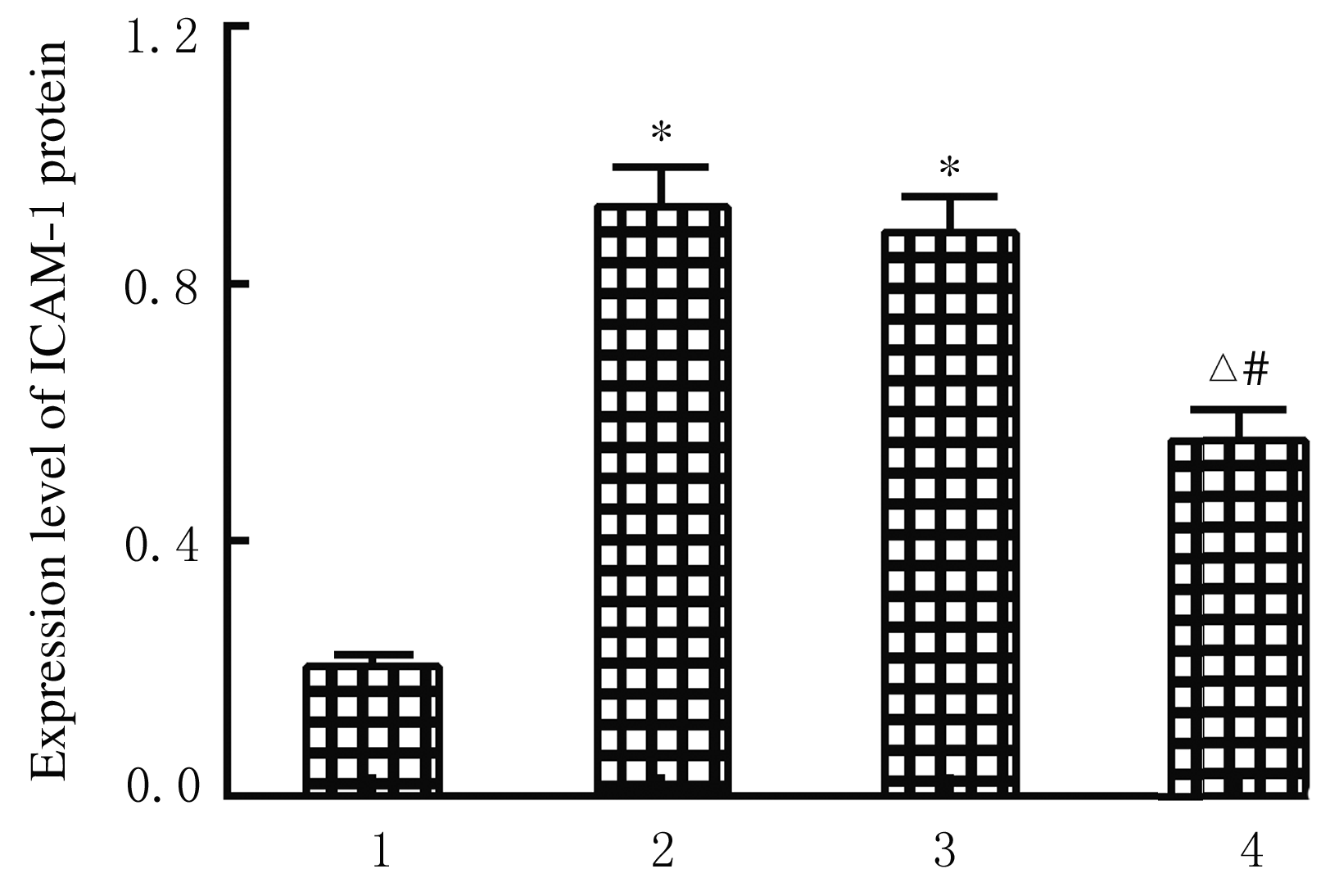
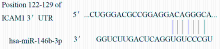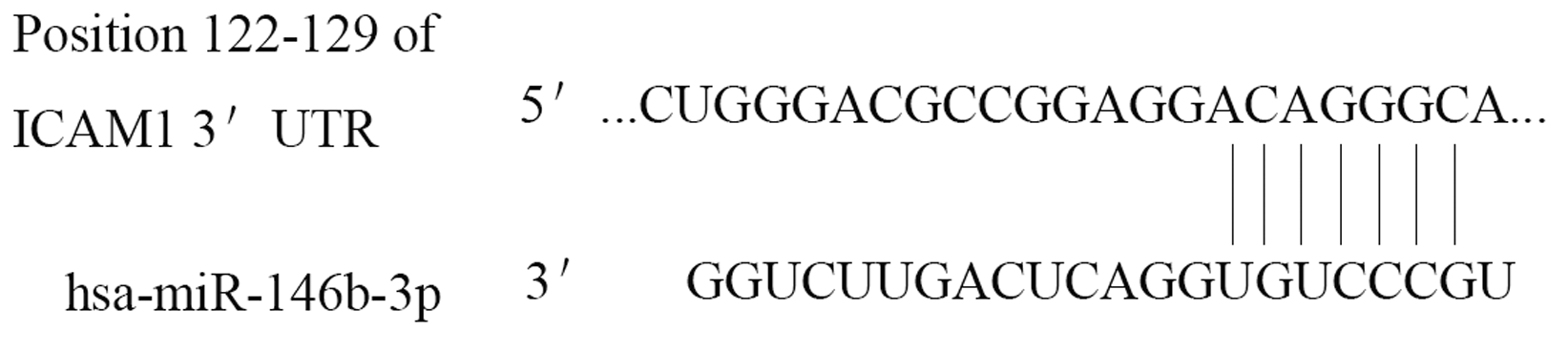| [1] |
Lei XIE, Xiaoli LIU, Jing GE, Yawei LI.
Effects of baicalin combined with metformin on endocrine, inflammatory factors and insulin resistance in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 623-629.
|
| [2] |
Jie WU,Xuehua YANG,Ling MA,Wenqiang FAN,Dongdong FU,Xiao GAO,Shufei ZUO,Shu LIANG,Yilu QIN,Peishan WANG,Jinyan GUO.
Effect of miR-26a-5p on apoptosis of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells through JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 460-468.
|
| [3] |
Xue BAI,Lu YU,Wenqiang YANG,Xin HE,Xinsheng YANG,Jing YANG.
Inhibitory effect of carnosine on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine release in astrocytes and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 330-337.
|
| [4] |
Shurong ZHANG,Qiying ZHANG.
Regulatory effect of luteolin on Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis through TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in rats
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 315-322.
|
| [5] |
LI Wei, ZHANG Haifeng, WANG Miao, HUO Jing, ZHANG Ying, ZHAO Cui.
Protective effect of Astragalus Injection on heart of rats with sleep deprivation and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 998-1003.
|
| [6] |
DU Xingxu, QIAO Zijing, YANG Shuo, XU Zhiying, YANG Bo, LI He, CHEN Jianguang, WANG Chunmei.
Effect of Schisandra chinensis polysaccharide on serum inflammatory factors in T2DM rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 50-55.
|
| [7] |
CAO Shuang, FAN Ziwei, WANG Yingying, SUN Lijuan, GU Hong, LI He, SUN Jinghui, WANG Chunmei, CHEN Jianguang, CHEN Xi, ZHANG Chengyi.
Effects of prunus tomentosa thunb total flavonoids on levels of inflammatory factors in RAW264.7 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 836-842.
|
| [8] |
CUI Yan, WANG Ruonan, WU Jiuru, WEI Shu, LIN Shengjuan, WANG Zhongnan.
Effect of water extract of spina date seed and albizzia julibrissin flower on hpa axis and inflammatory cytokines in anxious depression model rats
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 539-545.
|
| [9] |
HE Qi, SHI Hua, DAN Yang, SHAO Suju.
Effects of Jiawei Danshen Yin on cardiac function and serum inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α in rats with chronic heart failure
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 63-68.
|
| [10] |
CHEN Qiong, CAO Jie, ZHAO Lijun, YI Nan.
Effects of different exercise modes on body composition, inflammatory factors,and exercise capacity of obese teenagers
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(05): 1070-1075.
|
| [11] |
HE Jing, QI Di, WANG Daoxin.
Mechanism of insulin in up-regulating epithelial sodium channel α-subunit via mTORC2/SGK1 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(04): 716-720.
|
| [12] |
FU Qiao,YU Le-hua.
Influence of L- aminoguanidine in inflammatory factor levels in degenerate intervertebral disc cells in vitro
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(01): 35-38.
|
| [13] |
BIAN Wei-shuai,CHAO Yan-gong,CHEN Wei,WANG Lan,LI Li-ming,GUAN JianZHEN Jie,SHENG Bo,LIU Ping.
Comparison of effects between four kinds of methods on setting optimal positive end expiratory pressure in animal models with acute respiratory distress syndrome
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1132-1137.
|
| [14] |
ZHANG Qiang,YANG Li-hong,LI Han .
Protective effect of salvianolic acid B on myocardium of myocardial infarction model rats and its molecular mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(2): 268-272.
|
| [15] |
LUO Ling,WANG Dao-xin.
Influence of estradiol and progestogen in type Ⅱ alveolar ENaC in rats with acute lung injury
[J]. J4, 2012, 38(5): 836-840.
|
 ),Qian ZHANG,Xiulin YANG,Chunling JI,Yukang DONG
),Qian ZHANG,Xiulin YANG,Chunling JI,Yukang DONG