Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 129-135.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220116
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Therapeutic effect of alpinetin in letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome model rats and its mechanism
Yanmin SUN,Junpan HU,Bingyu WANG,Jinying FU( )
)
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,Henan Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Second Affiliated Hospital,Henan University of Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450002,China
-
Received:2021-03-19Online:2022-01-28Published:2022-01-17 -
Contact:Jinying FU E-mail:fujinying2003@163.com
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Yanmin SUN,Junpan HU,Bingyu WANG,Jinying FU. Therapeutic effect of alpinetin in letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome model rats and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 129-135.
share this article
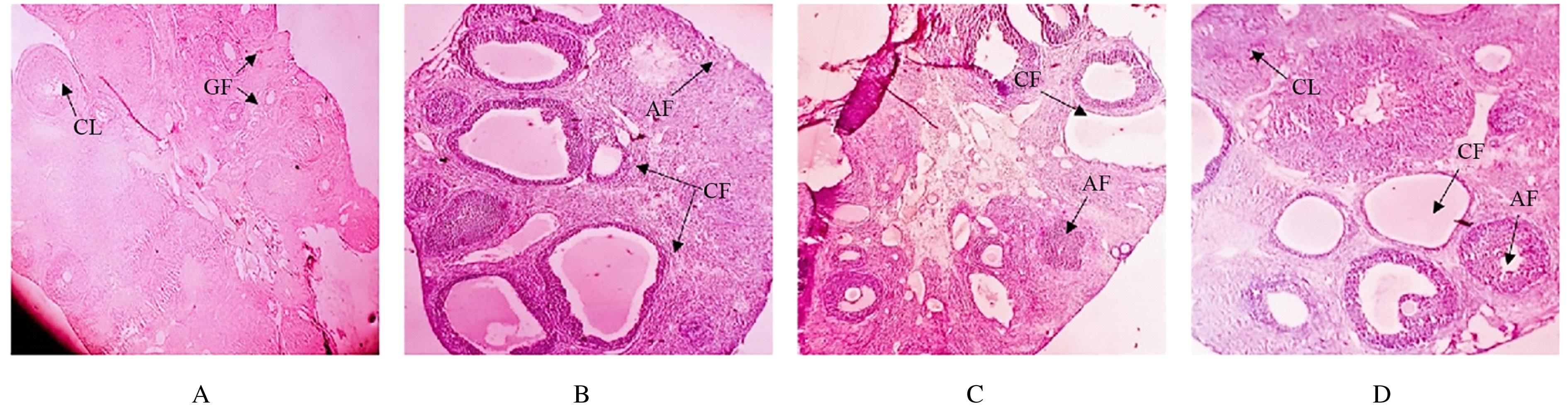
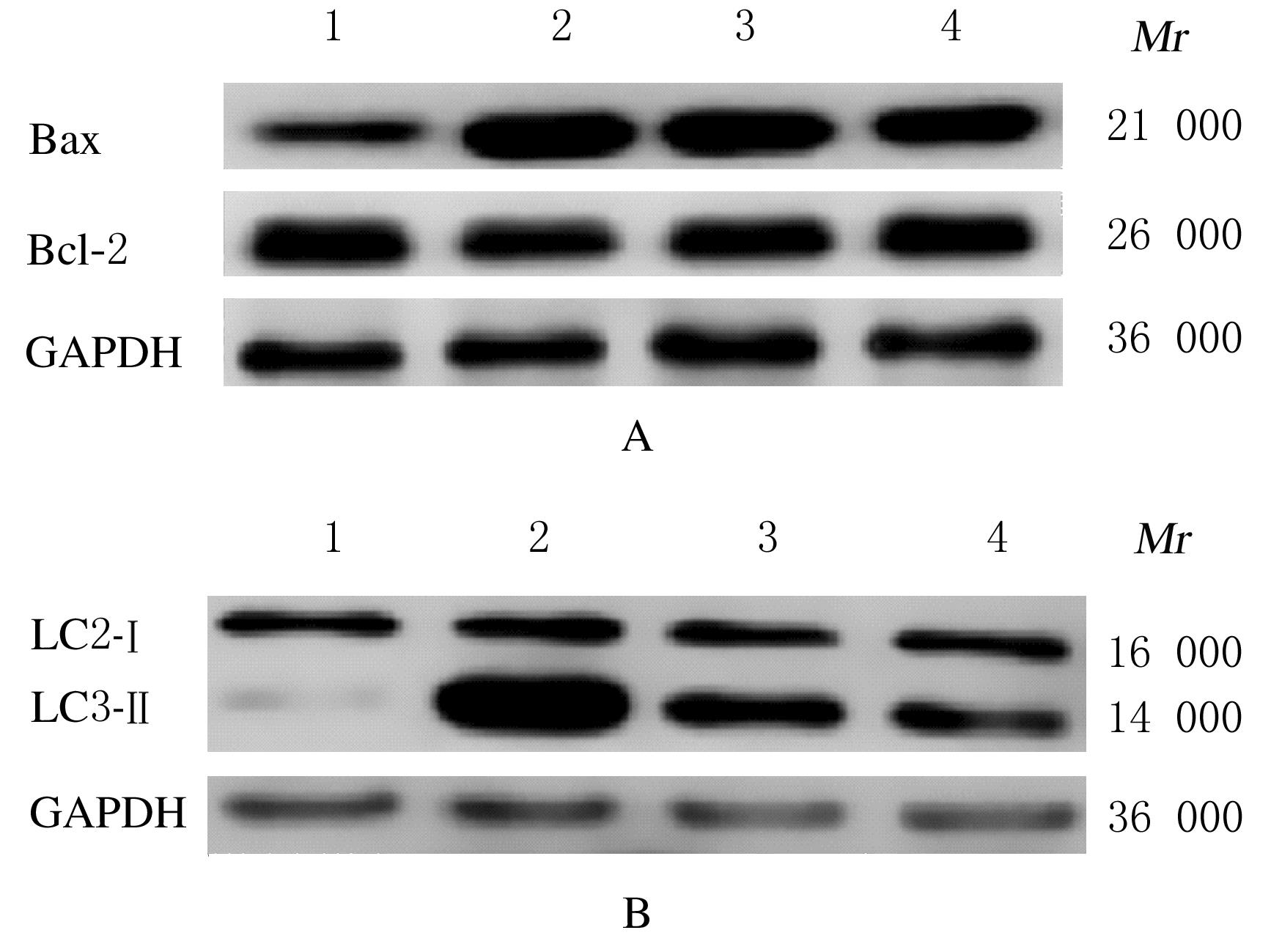
Tab.1
Body weights, ovary weight/body weight ratios and percentages of diestrous phase of rats in various groups"
| Group | Body weight(m/g) | Ovary weight/body weight ratio (η/%) | Percentage of diestrous phase (η/%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 195.35±23.42 | 0.21±0.03 | 59.36±5.77 |
| Model | 228.29±27.49* | 0.35±0.08* | 85.21±11.48* |
| ALP | |||
| Low dose | 211.52±8.91△ | 0.29±0.03△ | 75.16±14.19△ |
| High dose | 202.16±15.21△△ | 0.26±0.06△△ | 70.53±6.76△△ |
| 1 | BRENNAN L, TEEDE H, SKOUTERIS H, et al. Lifestyle and behavioral management of polycystic ovary syndrome [J].J Womens Health (Larchmt),2017,26(8):836-848. |
| 2 | 孙春玲, 乔 杰, 高冬霞. 凋亡调控蛋白Bcl-2、Bax、P53和PDCD5在多囊卵巢综合征各级卵泡的表达 [J]. 中国妇产科临床杂志, 2006, 7(2):122-125. |
| 3 | LI X, QI J, ZHU Q, et al. The role of androgen in autophagy of granulosa cells from PCOS [J]. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2019, 35(8):669-672. |
| 4 | YING Y, LIU Y X, LIU X, et al. Effects of Gui Zhu Yi Kun formula on the P53/AMPK pathway of autophagy in granulosa cells of rats with polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 13(6):3567-3573. |
| 5 | TAO T, XU H. Autophagy and obesity-related reproductive dysfunction [J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020, 1207:463-466. |
| 6 | SAHA P, KUMAR S, DATTA K, et al. Upsurge in autophagy, associated with mifepristone-treated polycystic ovarian condition, is reversed upon thymoquinone treatment [J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2021, 208:105823. |
| 7 | TAN Y, ZHENG C. Effects of alpinetin on intestinal barrier function, inflammation and oxidative stress in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis mice [J]. Am J Med Sci, 2018, 355(4):377-386. |
| 8 | JIANG Z, SANG H, FU X, et al. Alpinetin enhances cholesterol efflux and inhibits lipid accumulation in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-loaded human macrophages [J]. Biotechnol Appl Biochem, 2015, 62(6):840-847. |
| 9 | ZHOU Y, DING Y L, ZHANG J L, et al. Alpinetin improved high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through improving oxidative stress, inflammatory response and lipid metabolism [J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 97:1397-1408. |
| 10 | MIAO Y, LV Q, QIAO S, et al. Alpinetin improves intestinal barrier homeostasis via regulating AhR/suv39h1/TSC2/mTORC1/autophagy pathway [J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2019, 384:114772. |
| 11 | SU Y, TAO X, XU J. Protective effect of alpinetin on rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Food Sci Nutr, 2020, 8(12):6603-6611. |
| 12 | ZHAO X, ZHANG S, LIU D, et al. Analysis of flavonoids in dalbergia odorifera by ultra-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(2):389. |
| 13 | RAJAN R K, M S S, BALAJI B. Soy isoflavones exert beneficial effects on letrozole-induced rat polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) model through anti-androgenic mechanism [J]. Pharm Biol, 2017, 55(1):242-251. |
| 14 | RODGERS R J, SUTURINA L, LIZNEVA D, et al. Is polycystic ovary syndrome a 20th century phenomenon? [J]. Med Hypotheses, 2019, 124:31-34. |
| 15 | ZENG X, XIE Y J, LIU Y T, et al. Polycystic ovarian syndrome: Correlation between hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance and obesity [J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2020, 502:214-221. |
| 16 | PATEL S. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), an inflammatory, systemic, lifestyle endocrinopathy [J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2018, 182:27-36. |
| 17 | ABDULGHANI M, HUSSIN A H, SULAIMAN S A, et al. The ameliorative effects of eurycoma longifolia jack on testosterone-induced reproductive disorders in female rats [J]. Reprod Biol, 2012, 12(2):247-255. |
| 18 | ZHANG C, MA J, WANG W, et al. Lysyl oxidase blockade ameliorates anovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Hum Reprod, 2018, 33(11):2096-2106. |
| 19 | WANG M, LIU M, SUN J, et al. MicroRNA-27a-3p affects estradiol and androgen imbalance by targeting Creb1 in the granulosa cells in mouse polycytic ovary syndrome model [J]. Reprod Biol,2017,17(4):295-304. |
| 20 | DEWAILLY D, ROBIN G, PEIGNE M, et al. Interactions between androgens, FSH, anti-mullerian hormone and estradiol during folliculogenesis in the human normal and polycystic ovary [J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2016, 22(6):709-724. |
| 21 | HENRÍQUEZ S, KOHEN P, XU X, et al. Significance of pro-angiogenic estrogen metabolites in normal follicular development and follicular growth arrest in polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Hum Reprod, 2020, 35(7):1655-1665. |
| [1] | Wentao WANG,Xuguang MI,Yang ZHOU,Wenxing PU,Jiaxu GAO,Meng JING,Fankai MENG. Effect of autophagy induced by exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on survival of SH-SY5Y cells inhibited by MPP+ and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 606-614. |
| [2] | Yabo MA,Xiaotan YUAN,Xianguo XIE,Xinfeng LIU,Jinrui XU,Yi YANG. Expression levels of Wnt5a protein in ovary tissue of mice at different development stages and its effect on oocyte autophagy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 277-283. |
| [3] | Ying DONG,Jianyu GUO,Siyi WANG,Dan GUO,Like WANG,Xu WEN,Lifeng LIU,Meng QU,Chunyan YU,Nannan LIU,Dan WANG,Changjie CHEN. Effect of endoplasmic reticulum stress PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 signaling pathway on delaying transplanted tumor growth in APP/PS1 mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 324-330. |
| [4] | Yang ZHOU,Xuguang MI,Wenxing PU,Wentao WANG,Meng JING,Fankai MENG. Ameliorative effect of melatonin on oxidative stress of human neuroblastoma SHSY5Y cells induced by hydrogen peroxide and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 340-347. |
| [5] | Wenxiong SUN,Pu LI. Expression of SOCS3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its effect on autophagy and apoptosis of OCI-LY7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 172-179. |
| [6] | Chaofeng ZHOU,Shifan ZHOU,Qing TIAN,Sai WANG,Honglin LI,Chunzheng MA. Effect of lncRNA-NORAD overexpression on biological behaviors of esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 33-43. |
| [7] | Lu LU,Dongming LI,Xueguo WANG,Dan SONG,Taicheng WANG,Hongyan ZHAO,Xiaoyong WU. Effect of chloroquine on gemcitabine-resistant cells by affecting autophagy and mitochondrial function of pancreatic cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 926-933. |
| [8] | Xining LI, Wei WENG, Zheyuan SHEN, Xiaojie DOU, Yu ZHAO, Jikang MIN. Effect of mTOR phosphorylation level on proliferation,autophagy,and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 575-586. |
| [9] | Lei XIE, Xiaoli LIU, Jing GE, Yawei LI. Effects of baicalin combined with metformin on endocrine, inflammatory factors and insulin resistance in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 623-629. |
| [10] | Meijuan LU,Xiande MA,Lu REN. Effect of acupuncture combined with medicine-induced autophagy on cognitive function of mice with ApoE gene knockout [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1124-1130. |
| [11] | ZENG Ruixia, ZHANG Yibo. Promotion effect of p62 gene deletion on adipogenesis of human adipose-derived stromal cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 979-984. |
| [12] | YU Lei, WANG Ce, HAN Bing, LI Xin, HAN Yuchen, SUN Yuying, GUO Xiangshu, LIU Weiwu, WANG Zhicheng. Enhancement of mitochondria-targeted KillerRed in autophagy caused by radiation in HeLa cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 693-698. |
| [13] | LIN Jiuhan, TIAN Lin, ZHANG Nana, DONG Ying, LYU Hang, WANG Dan, QU Meng, ZHANG Yong, SUN Liankun, YU Chunyan, LIU Xi. Inhibitory effect of mitochondrial dynamics changes on growth of transplanted melanoma in APP/PS1 mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 476-481. |
| [14] | WANG Yingying, SUN Lijuan, FAN Ziwei, GU Hong, YOU Xianmei, GUAN Tianhao, ZHANG Chengyi, CHEN Xi. Inhibitory effect of baicalin on autophagy of synovial RSC-364 cells of rats induced by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 498-503. |
| [15] | YAN Shengyu, XIE Yafeng, XU Zhijie, LIU Ying, DING Yating, ZHANG Qiao, LIU Wanying, LIU Libing. Inhibitory effect of antimicrobial peptide LL-37 on tumorgrowth of mice with colon cancer and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 575-581. |