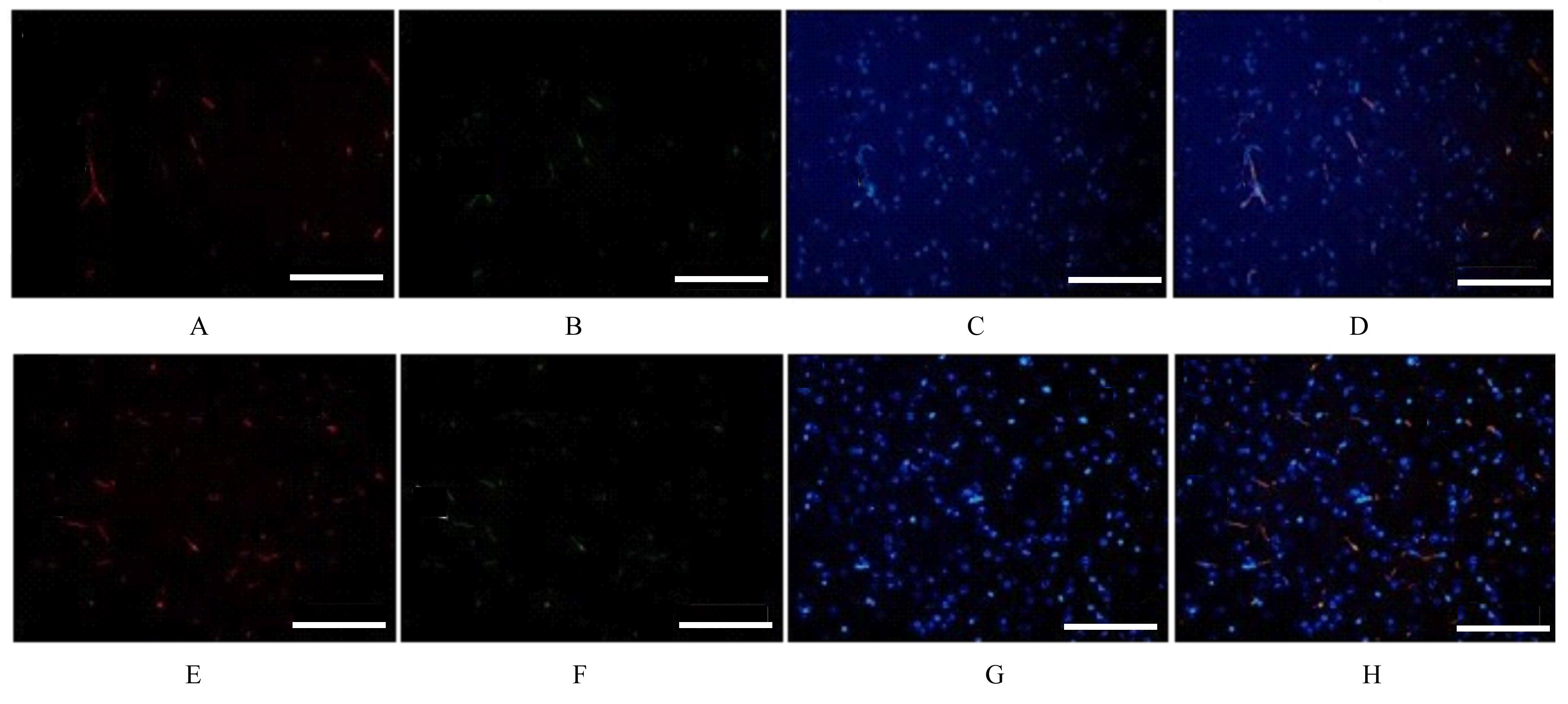
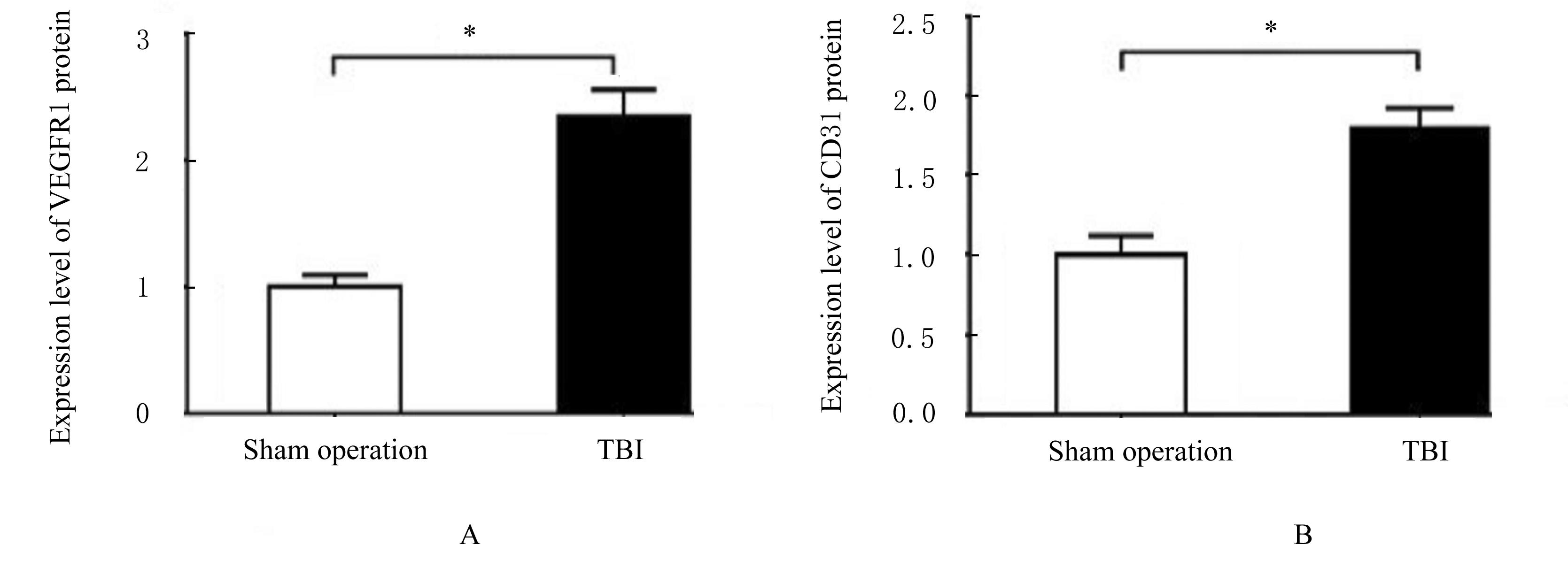
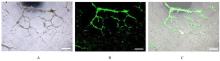
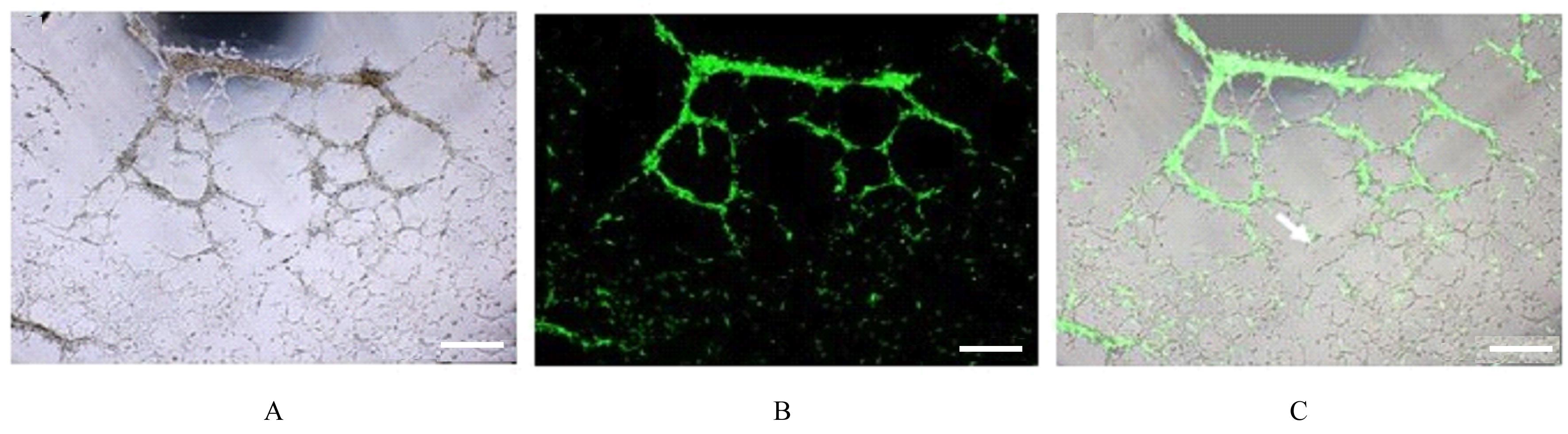
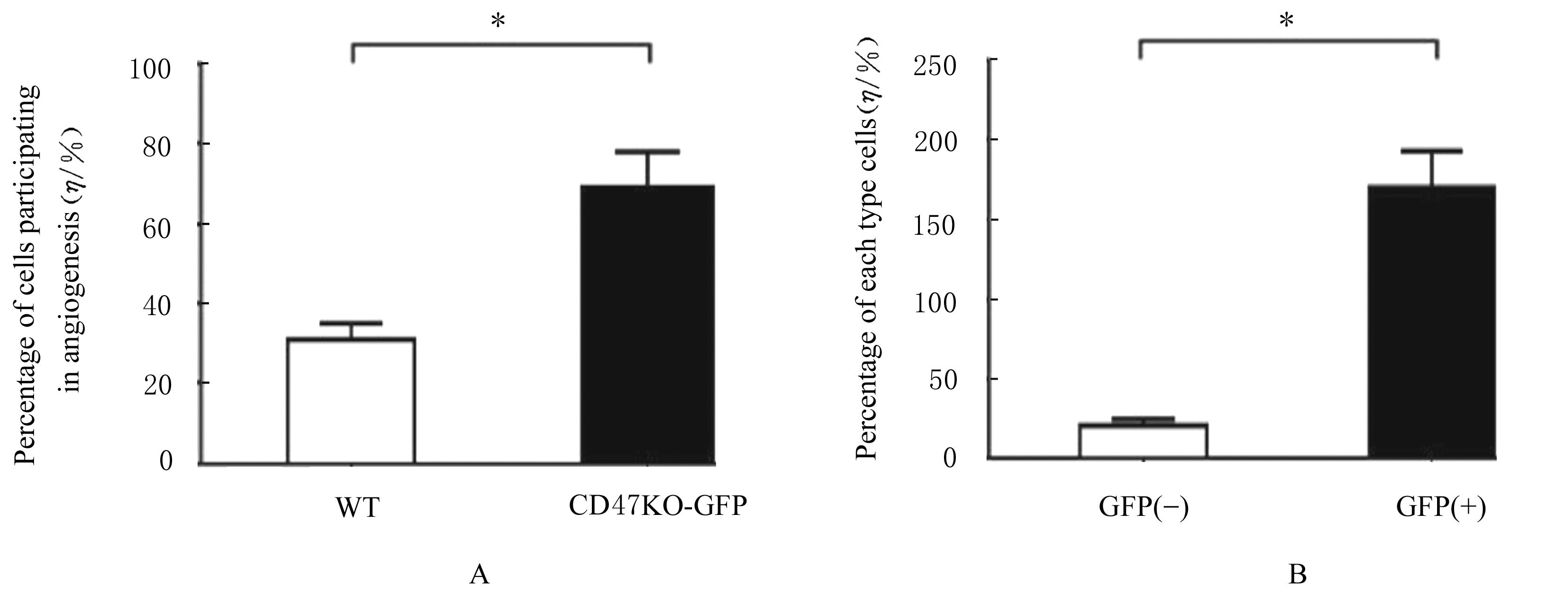
| 1 |
JOHNSON W D, GRISWOLD D P. Traumatic brain injury:a global challenge[J].Lancet Neurol, 2017,16(12): 949-950.
|
| 2 |
JIANG J Y, GAO G Y, FENG J F, et al. Traumatic brain injury in China[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2019, 18(3): 286-295.
|
| 3 |
SALEHI A, ZHANG J H, OBENAUS A. Response of the cerebral vasculature following traumatic brain injury[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2017, 37(7): 2320-2339.
|
| 4 |
LOTZE F P, RIESS M L. Poloxamer 188 exerts direct protective effects on mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells in an in vitro traumatic brain injury model[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9(8): 1043.
|
| 5 |
SANDSMARK D K, BASHIR A, WELLINGTON C L,et al. Cerebral microvascular injury: a potentially treatable endophenotype of traumatic brain injury-induced neurodegeneration[J]. Neuron, 2019, 103(3): 367-379.
|
| 6 |
SOLANKI A, BHATT L K, JOHNSTON T P. Evolving targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 187: 1-12.
|
| 7 |
LOGTENBERG M E W, SCHEEREN F A, SCHUMACHER T N. The CD47-SIRPα immune checkpoint[J]. Immunity, 2020, 52(5): 742-752.
|
| 8 |
DOU M M, CHEN Y, HU J, et al. Recent advancements in CD47 signal transduction pathways involved in vascular diseases[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 4749135.
|
| 9 |
KAUR S, MARTIN-MANSO G, PENDRAK M L,et al.Thrombospondin-1 inhibits VEGF receptor-2 signaling by disrupting its association with CD47[J]. J Biol Chem, 2010, 285(50): 38923-38932.
|
| 10 |
SU X, JOHANSEN M, LOONEY M R, et al. CD47 deficiency protects mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and Escherichia coli pneumonia[J]. J Immunol, 2008, 180(10): 6947-6953.
|
| 11 |
ARNAOUTOVA I, KLEINMAN H K. In vitro angiogenesis: endothelial cell tube formation on gelled basement membrane extract[J]. Nat Protoc,2010,5(4): 628-635.
|
| 12 |
ARNAOUTOVA I, GEORGE J, KLEINMAN H K, et al. The endothelial cell tube formation assay on basement membrane turns 20: state of the science and the art[J]. Angiogenesis, 2009, 12(3): 267-274.
|
| 13 |
KUBOTA Y, KLEINMAN H K, MARTIN G R,et al. Role of laminin and basement membrane in the morphological differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like structures[J].J Cell Biol,1988,107(4): 1589-1598.
|
| 14 |
KHELLAF A, KHAN D Z, HELMY A. Recent advances in traumatic brain injury[J]. J Neurol, 2019, 266(11): 2878-2889.
|
| 15 |
SHLOSBERG D, BENIFLA M, KAUFER D, et al. Blood-brain barrier breakdown as a therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2010, 6(7): 393-403.
|
| 16 |
SWEENEY M D, KISLER K, MONTAGNE A,et al. The role of brain vasculature in neurodegenerative disorders[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2018, 21(10): 1318-1331.
|
| 17 |
JULLIENNE A, OBENAUS A, ICHKOVA A, et al. Chronic cerebrovascular dysfunction after traumatic brain injury[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2016, 94(7): 609-622.
|
| 18 |
JIN G, TSUJI K, XING C H, et al. CD47 gene knockout protects against transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice[J].Exp Neurol,2009,217(1): 165-170.
|
| 19 |
ISENBERG J S, ROMEO M J, MAXHIMER J B,et al. Gene silencing of CD47 and antibody ligation of thrombospondin-1 enhance ischemic tissue survival in a porcine model: implications for human disease[J]. Ann Surg, 2008, 247(5): 860-868.
|
| 20 |
SOTO-PANTOJA D R, RIDNOUR L A, WINK D A, et al. Blockade of CD47 increases survival of mice exposed to lethal total body irradiation[J]. Sci Rep, 2013, 3: 1038.
|
| 21 |
MANDLER W K, NURKIEWICZ T R, PORTER D W,et al.Microvascular dysfunction following multiwalled carbon nanotube exposure is mediated by thrombospondin-1 receptor CD47[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2018, 165(1): 90-99.
|
| 22 |
WU X, LUO X, ZHU Q Q, et al. The roles of thrombospondins in hemorrhagic stroke[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2017, 2017: 8403184.
|
| 23 |
STEIN E V, MILLER T W, IVINS-O’KEEFE K,et al. Secreted thrombospondin-1 regulates macrophage interleukin-1β production and activation through CD47[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 19684.
|
| 24 |
BRAMBILLA R, HURTADO A, PERSAUD T,et al. Transgenic inhibition of astroglial NF-kappa B leads to increased axonal sparing and sprouting following spinal cord injury[J]. J Neurochem, 2009, 110(2): 765-778.
|
| 25 |
JAYAKUMAR A R, TONG X Y, RUIZ-CORDERO R,et al. Activation of NF-κB mediates astrocyte swelling and brain edema in traumatic brain injury[J]. J Neurotrauma, 2014, 31(14): 1249-1257.
|
| 26 |
杜延平, 梁建广, 王玉海, 等. 长时程亚低温治疗对重度颅脑损伤患者脑损伤标志物及氧化应激指标的影响[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2021,38(12):1544-1548.
|
| 27 |
ZHANG X Y, WANG Y C, FAN J J, et al. Blocking CD47 efficiently potentiated therapeutic effects of anti-angiogenic therapy in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2019, 7(1): 346.
|
 )
)