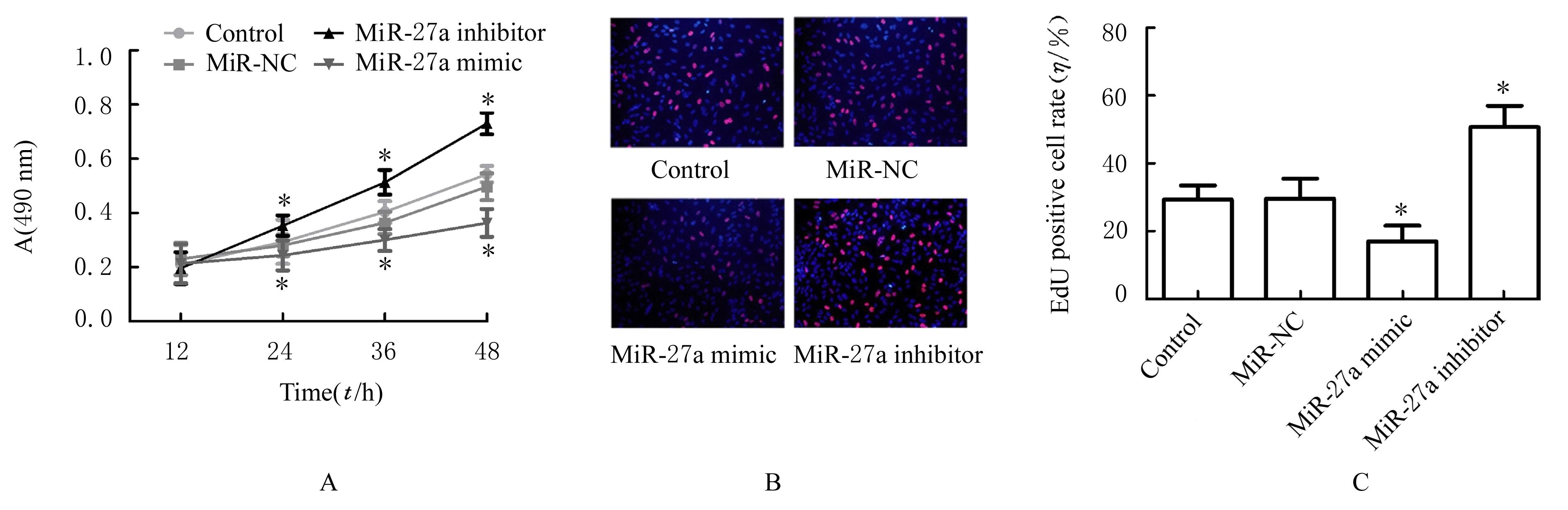
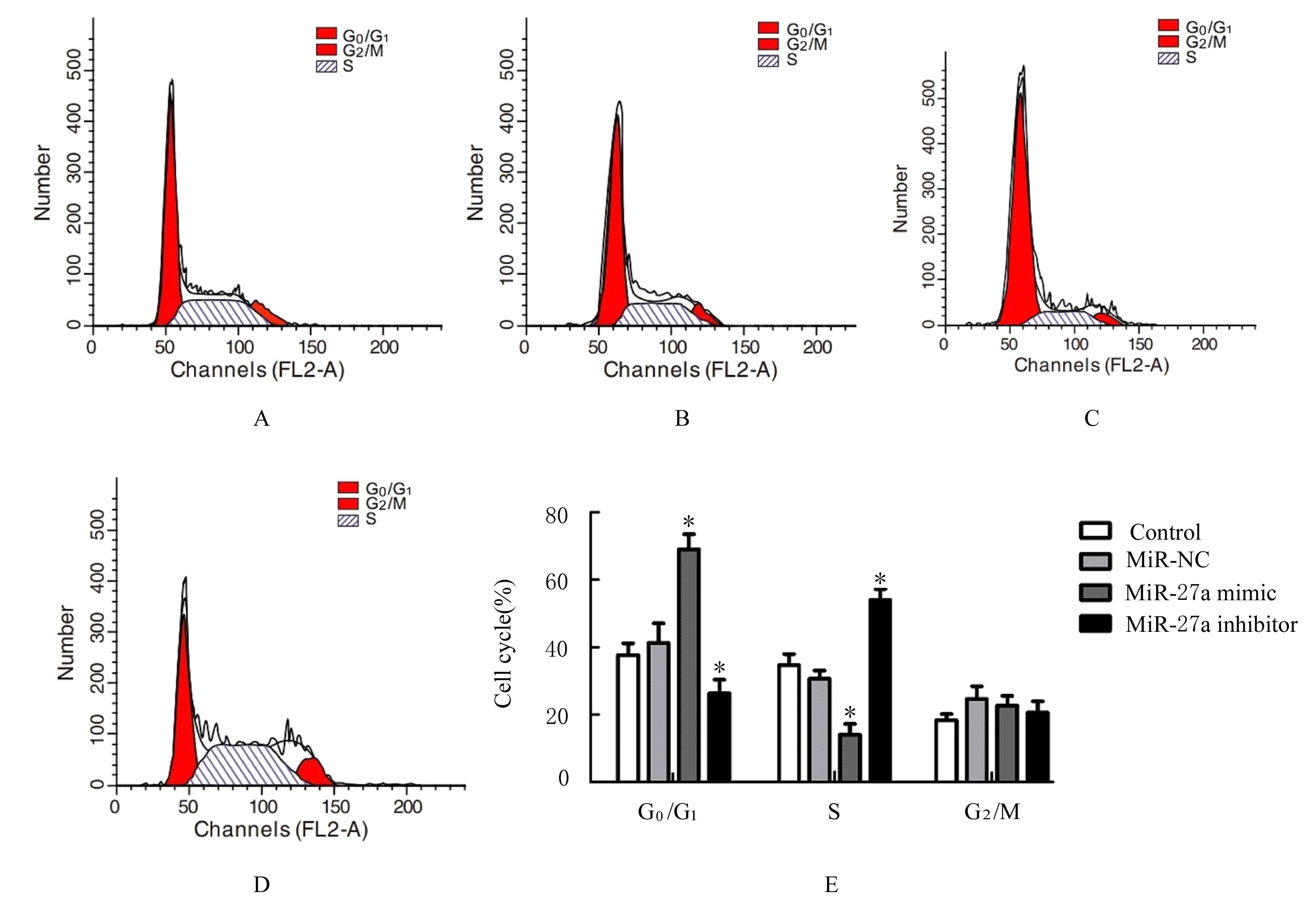
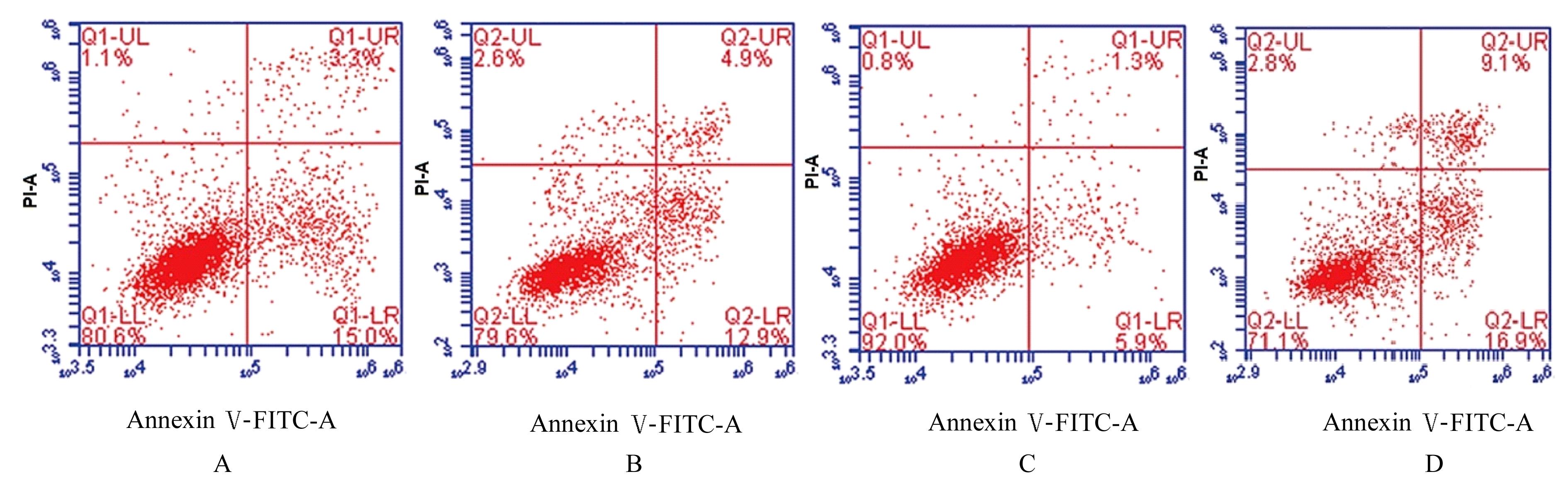
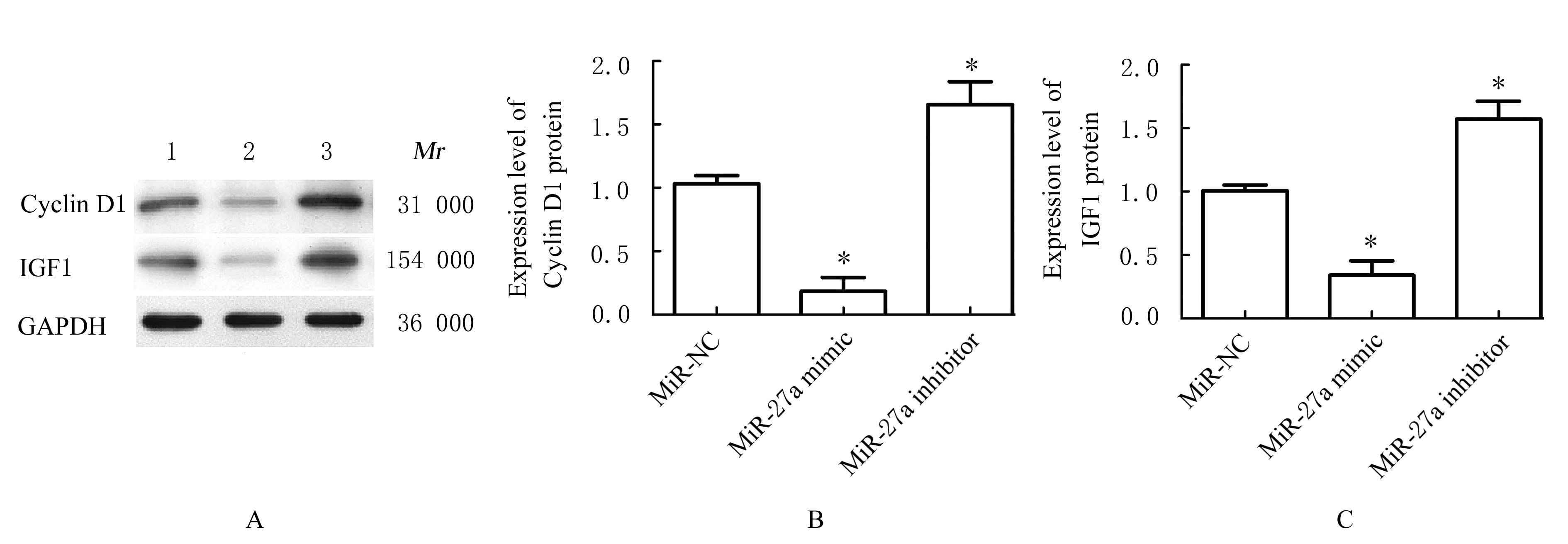
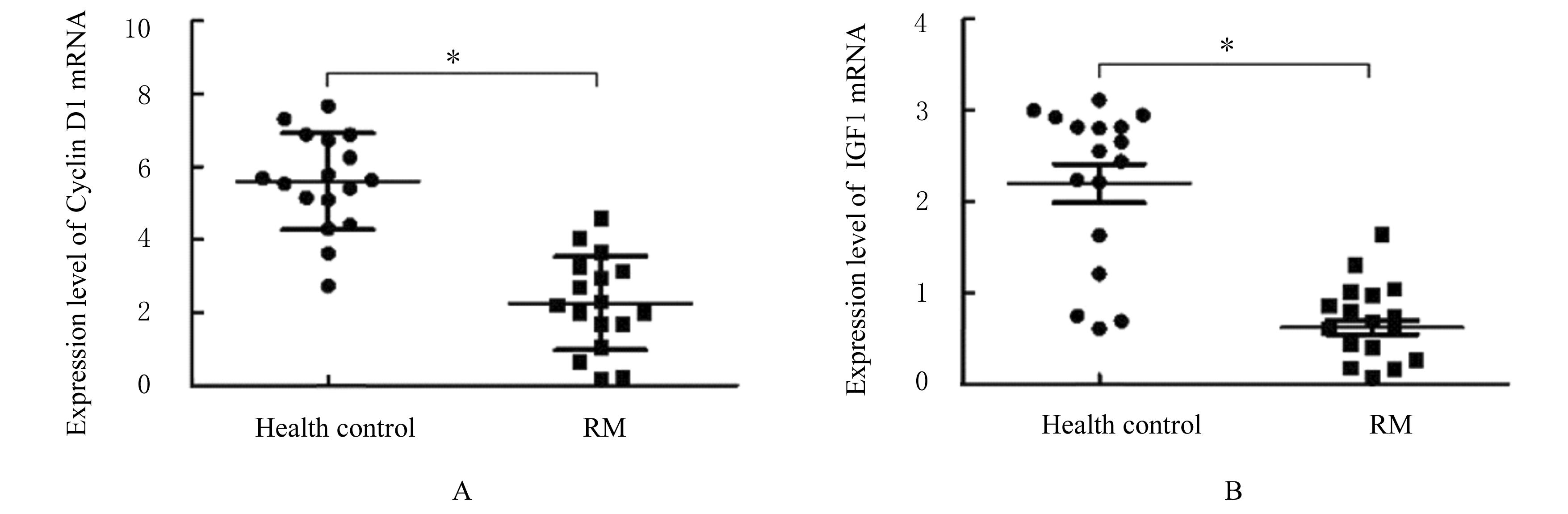
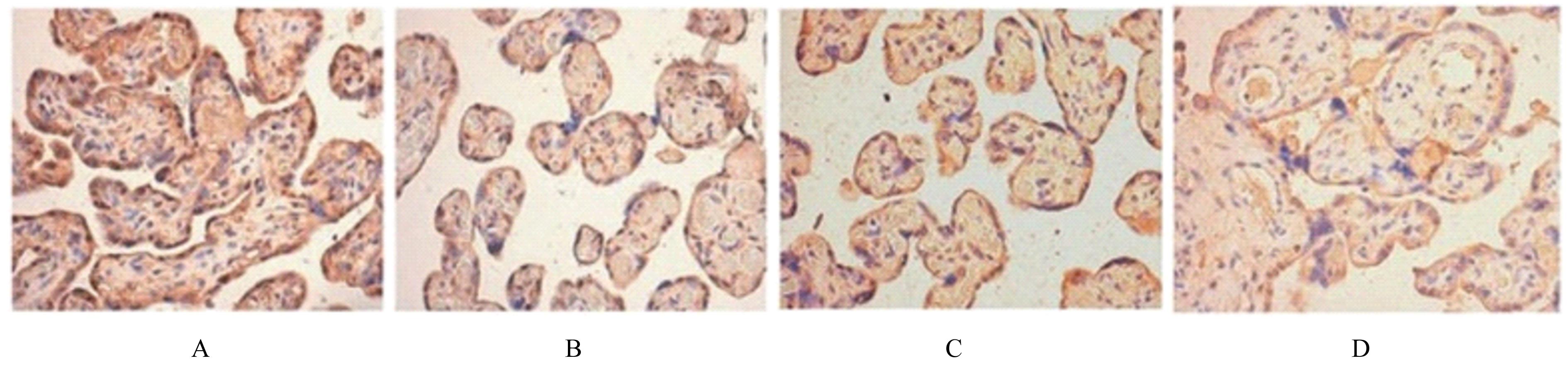
| 1 |
自然流产诊治中国专家共识编写组, 赵爱民.自然流产诊治中国专家共识(2020年版)[J].中国实用妇科与产科杂志,2020,36(11):1082-1090.
|
| 2 |
QUENBY S, GALLOS I D, DHILLON-SMITH R K, et al. Miscarriage matters: the epidemiological, physical,psychological, and economic costs of early pregnancy loss[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10285): 1658-1667.
|
| 3 |
GARRIDO-GIMENEZ C, ALIJOTAS-REIG J. Recurrent miscarriage: causes, evaluation and management[J].Postgrad Med J,2015,91(1073):151-162.
|
| 4 |
TUR-TORRES M H, GARRIDO-GIMENEZ C, ALIJOTAS-REIG J. Genetics of recurrent miscarriage and fetal loss[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol, 2017, 42: 11-25.
|
| 5 |
KOKAWA K, SHIKONE T, NAKANO R. Apoptosis in human chorionic villi and decidua during normal embryonic development and spontaneous abortion in the first trimester[J]. Placenta, 1998, 19(1): 21-26.
|
| 6 |
LU T X, ROTHENBERG M E. microRNA[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 141(4): 1202-1207.
|
| 7 |
JIANG G, SHI W, FANG H, et al. miR‑27a promotes human breast cancer cell migration by inducing EMT in a FBXW7‑dependent manner[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018,18(6):5417-5426.
|
| 8 |
BAO Y H, CHEN Z G, GUO Y C, et al. Tumor suppressor microRNA-27a in colorectal carcinogenesis and progression by targeting SGPP1 and Smad2[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e105991.
|
| 9 |
LI Y Q, TIAN Z F, TAN Y, et al. Bmi-1-induced miR-27a and miR-155 promote tumor metastasis and chemoresistance by targeting RKIP in gastric cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 109.
|
| 10 |
RAH H, CHUNG K W, KO K H, et al. miR-27a and miR-449b polymorphisms associated with a risk of idiopathic recurrent pregnancy loss[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5): e0177160.
|
| 11 |
KIM J O, AHN E H, SAKONG J H, et al. Association of miR-27aA>G, miR-423C>a, miR-449bA>G, and miR-604A>G polymorphisms with risk of recurrent implantation failure[J]. Reprod Sci, 2020,27(1): 29-38.
|
| 12 |
CHAMLEY L W, BHALLA A, STONE P R, et al. Nuclear localisation of the endocannabinoid metabolizing enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) in invasive trophoblasts and an association with recurrent miscarriage[J]. Placenta, 2008, 29(11): 970-975.
|
| 13 |
LIU H N, TANG X M, WANG X Q, et al. miR-93 inhibits trophoblast cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis by targeting BCL2L2 in recurrent spontaneous abortion[J]. Reprod Sci, 2020, 27(1): 152-162.
|
| 14 |
ZHAO W, SHEN W W, CAO X M, et al. Novel mechanism of miRNA-365-regulated trophoblast apoptosis in recurrent miscarriage[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2017, 21(10): 2412-2425.
|
| 15 |
RUPAIMOOLE R, SLACK F J. microRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2017, 16(3): 203-222.
|
| 16 |
LYCOUDI A, MAVRELI D, MAVROU A, et al. miRNAs in pregnancy-related complications[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2015, 15(8): 999-1010.
|
| 17 |
YANG Q, GU W W, GU Y, et al. Association of the peripheral blood levels of circulating microRNAs with both recurrent miscarriage and the outcomes of embryo transfer in an in vitro fertilization process[J]. J Transl Med, 2018, 16(1): 186.
|
| 18 |
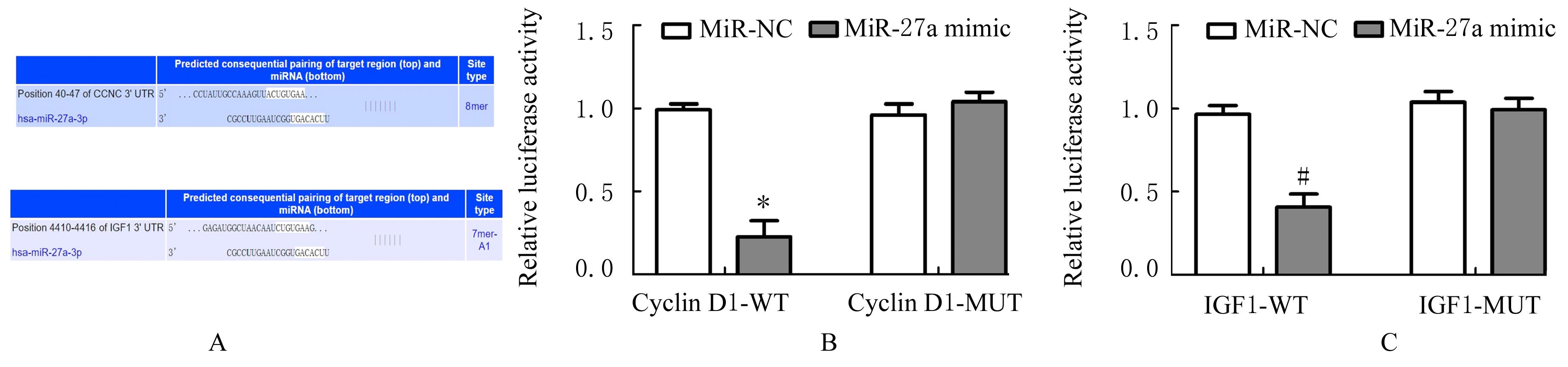
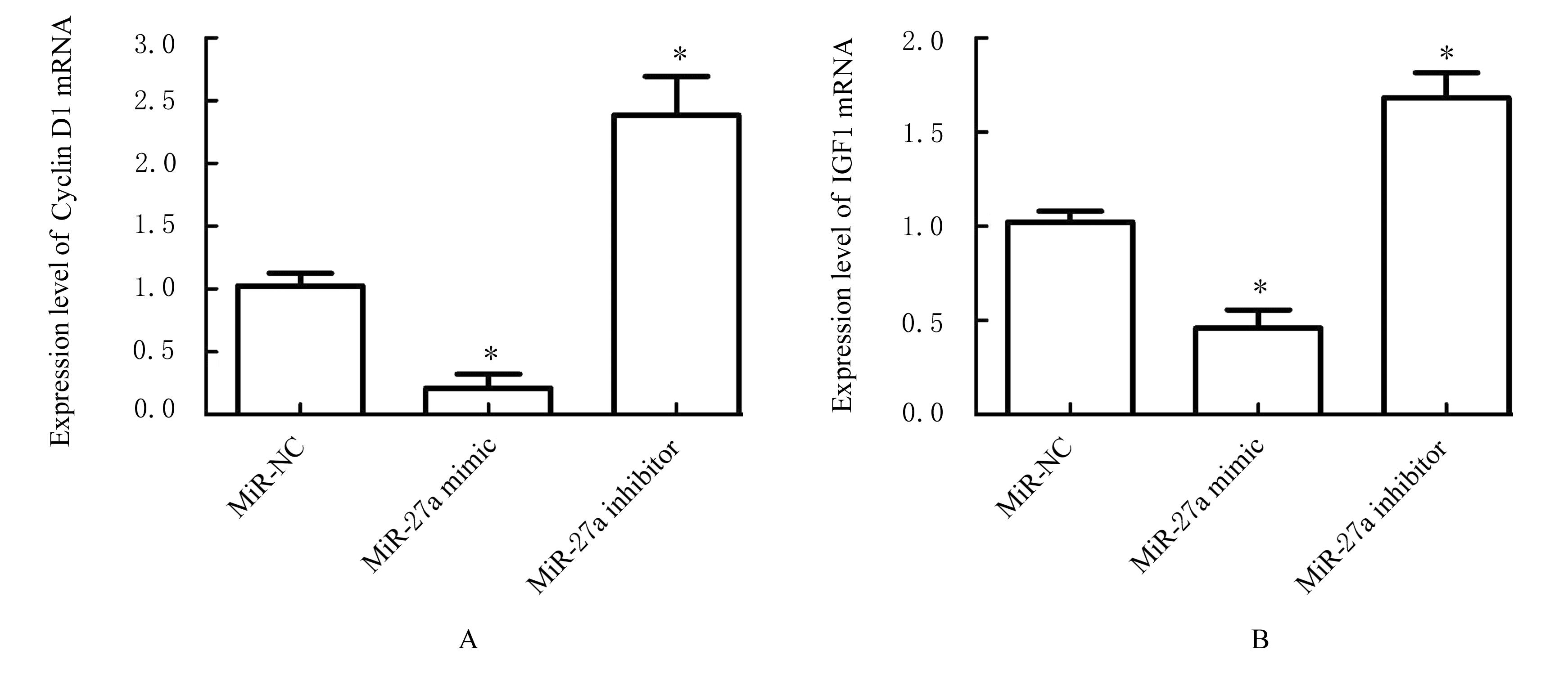
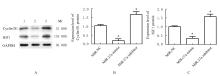
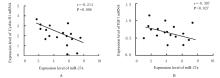
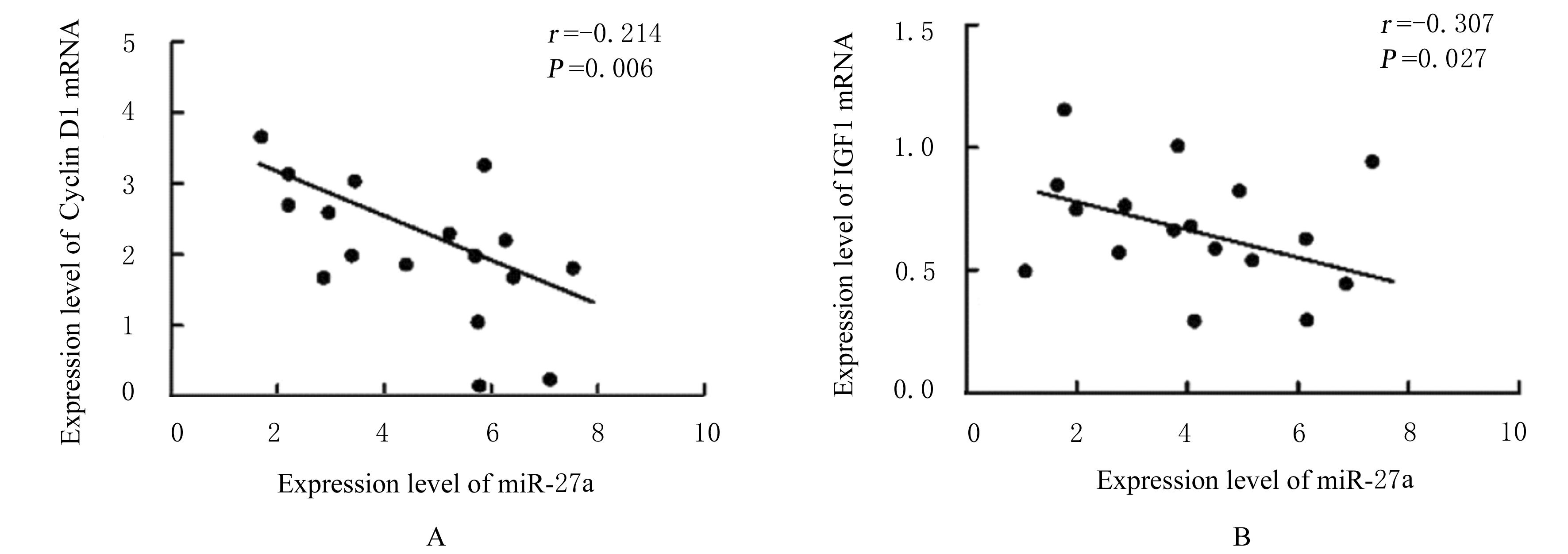
DING J L, CHENG Y X, ZHANG Y, et al. The miR-27a-3p/USP25 axis participates in the pathogenesis of recurrent miscarriage by inhibiting trophoblast migration and invasion[J].J Cell Physiol, 2019,234(11): 19951-19963.
|
| 19 |
ZHENG F X, WANG M, LI Y W, et al. CircNR3C1 inhibits proliferation of bladder cancer cells by sponging miR-27a-3p and downregulating cyclin D1 expression[J]. Cancer Lett, 2019, 460: 139-151.
|
| 20 |
CHEN Y Q, ZHANG X L, AN Y, et al. LncRNA HCP5 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis via miR-27a-3p/IGF-1 axis in human granulosa-like tumor cell line KGN[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2020, 503: 110697.
|
| 21 |
LIU Y, LIU C P, ZHANG A K, et al. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) through miR-27a-3p/IGF1 axis in periodontitis[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2019, 11(15): 5334-5350.
|
| 22 |
ADU-GYAMFI E A, LAMPTEY J, CHEN X M,et al. Iodothyronine deiodinase 2 (DiO2) regulates trophoblast cell line cycle, invasion and apoptosis; and its downregulation is associated with early recurrent miscarriage[J]. Placenta, 2021, 111: 54-68.
|
| 23 |
FLUHR H, SPRATTE J, HEIDRICH S, et al. The molecular charge and size of heparins determine their impact on the decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells[J].Mol Hum Reprod,2011,17(6):354-359.
|
| 24 |
王 珺, 郭 颖, 宗 实, 等. 胰岛素样生长因子家族成员在早期自然流产中作用的研究[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2012, 41(3): 241-243.
|