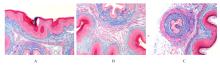
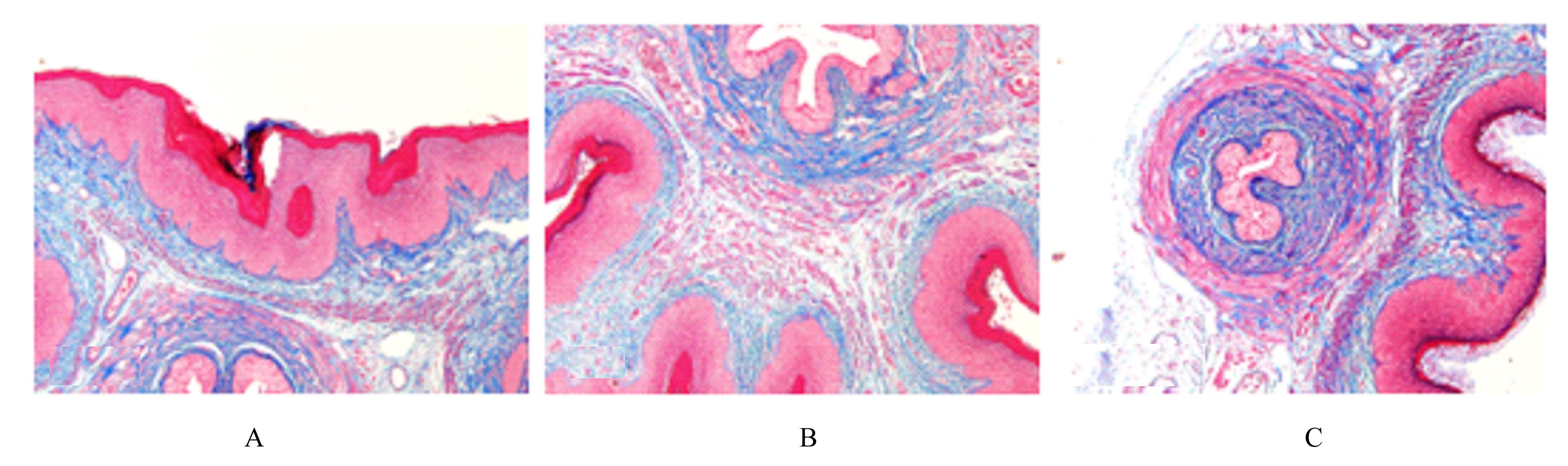
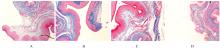
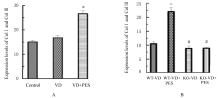
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 557-564.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230302
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effectof Cav3.2 gene in treatment of stress urinary incontinence in mice by pelvic floor electrical stimulation and its mechanism
Jianfeng LIU,Jianming TANG,Lian YANG,Shufei ZHANG,Li HONG( )
)
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,People’s Hospital,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430060,China
-
Received:2021-06-27Online:2023-05-28Published:2023-06-20 -
Contact:Li HONG E-mail:drhongli777@163.com
CLC Number:
- R714.6
Cite this article
Jianfeng LIU, Jianming TANG, Lian YANG, Shufei ZHANG, Li HONG. Effectof Cav3.2 gene in treatment of stress urinary incontinence in mice by pelvic floor electrical stimulation and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 557-564.
share this article
| 1 | WU J M. Stress incontinence in women[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(25): 2428-2436. |
| 2 | 中华医学会妇产科学分会妇科盆底学组. 女性压力性尿失禁诊断和治疗指南(2017)[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2017, 52(5): 289-293. |
| 3 | WU X L, ZHENG X, YI X H, et al. Electromyographic biofeedback for stress urinary incontinence or pelvic floor dysfunction in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Adv Ther, 2021, 38(8): 4163-4177. |
| 4 | HAN X, SHEN H Y, CHEN J M, et al. Efficacy and safety of electrical stimulation for stress urinary incontinence in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2022, 33(4): 789-799. |
| 5 | CHEN B, YEH J. Alterations in connective tissue metabolism in stress incontinence and prolapse[J]. J Urol, 2011, 186(5): 1768-1772. |
| 6 | HARTEN I A, EVANKO S P, CHOE C H, et al. The extracellular matrix molecules versican and hyaluronan in urethral and vaginal tissues in stress urinary incontinence[J].Neurourol Urodyn,2021,40(3):771-782. |
| 7 | MIN J, LI B S, LIU C, et al. Therapeutic effect and mechanism of electrical stimulation in female stress urinary incontinence[J]. Urology, 2017, 104: 45-51. |
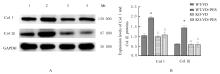
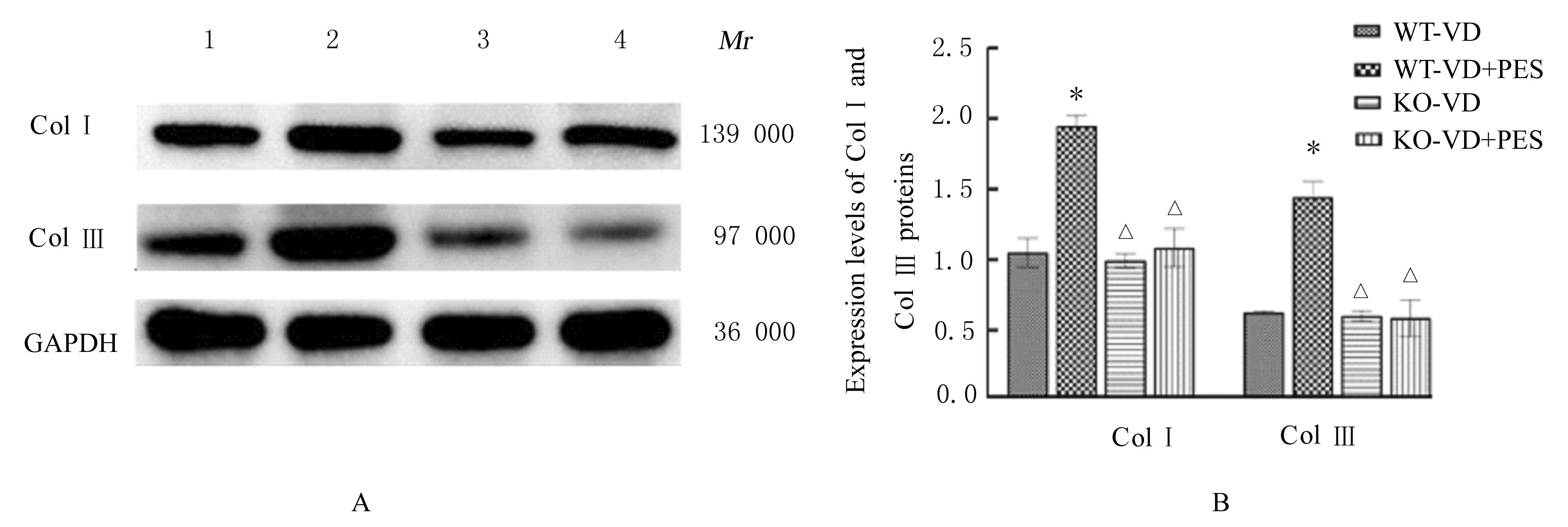
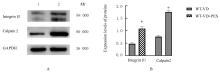
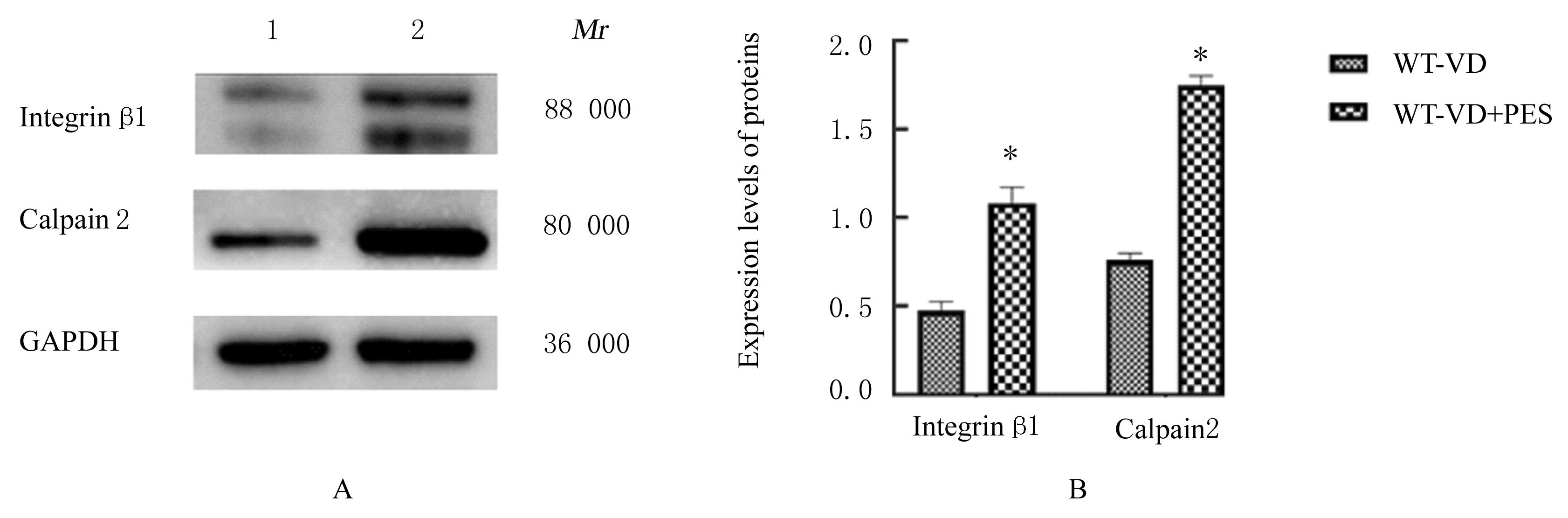
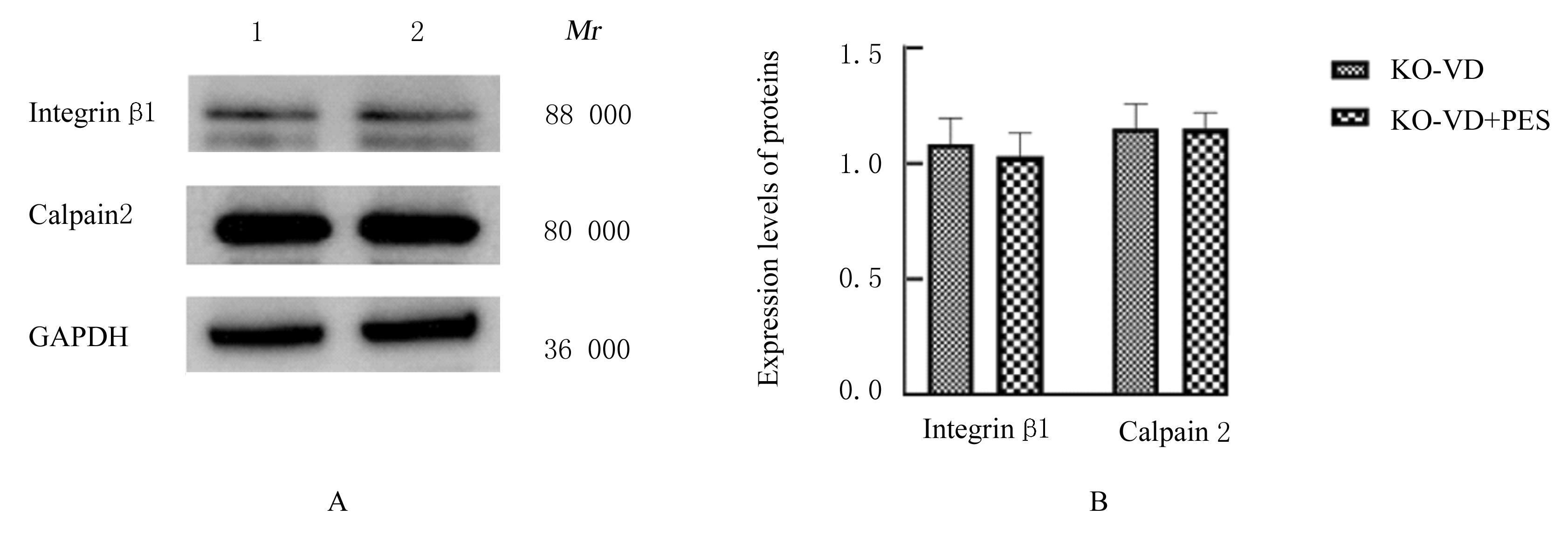
| 8 | LI Y, LIU C, LI B S, et al. Electrical stimulation activates calpain 2 and subsequently upregulates collagens via the integrin β1/TGF-β1 signaling pathway[J]. Cell Signal, 2019, 59: 141-151. |
| 9 | 汤剑明, 洪 莉, 刘 成, 等. 压力性尿失禁小鼠模型的建立及效果评价[J]. 中华妇幼临床医学杂志(电子版), 2016, 12(5): 540-546. |
| 10 | HIJAZ A, DANESHGARI F, SIEVERT K D, et al. Animal models of female stress urinary incontinence[J]. J Urol, 2008, 179(6): 2103-2110. |
| 11 | YANG J, BALOG B, DENG K L, et al. Therapeutic potential of muscle growth promoters in a stress urinary incontinence model[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2020, 319(3): F436-F446. |
| 12 | LI S T, LU D H, TANG J M, et al. Electrical stimulation activates fibroblasts through the elevation of intracellular free Ca2+: potential mechanism of pelvic electrical stimulation therapy[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 7387803. |
| 13 | ZHANG R Q, XIA M C, CUI F, et al. Epidemiological survey of adult female stress urinary incontinence[J].BMC Womens Health,2021,21(1): 172. |
| 14 | SANGSAWANG B, SANGSAWANG N. Stress urinary incontinence in pregnant women: a review of prevalence, pathophysiology, and treatment[J]. Int Urogynecol J, 2013, 24(6): 901-912. |
| 15 | ŽIVKOVIĆ K, ŽIVKOVIĆ N, ŽUPIĆ T, et al. Effect of delivery and episiotomy on the emergence of urinary incontinence in women: review of literature[J]. Acta Clin Croat, 2016, 55(4): 615-624. |
| 16 | SAYED R F. Magnetic resonance imaging of the female pelvic floor: anatomy overview, indications, and imaging protocols[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 2020, 58(2): 291-303. |
| 17 | 杨春波, 赵彦侠, 金杭美. 钙蛋白酶及其抑制蛋白在女性压力性尿失禁患者尿道周围组织中的表达[J]. 全科医学临床与教育, 2016, 14(2):131-134. |
| 18 | 杨梦伊, 屈之榆, 李超楠, 等. 电针对压力性尿失禁大鼠阴道前壁胶原分解与合成的影响[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2022, 56(6): 63-72. |
| 19 | KANEKO Y, MURPHY C R, DAY M L. Calpain 2 activity increases at the time of implantation in rat uterine luminal epithelial cells and administration of calpain inhibitor significantly reduces implantation sites[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 2014, 141(4): 423-430. |
| 20 | YANO J, WELLS R, LAM Y W, et al. Ciliary Ca2+ pumps regulate intraciliary Ca2+ from the action potential and may co-localize with ciliary voltage-gated Ca2+ channels[J]. J Exp Biol, 2021, 224(9): jeb232074. |
| 21 | BOEKHORST V, JIANG L Y, MÄHLEN M,et al. Calpain-2 regulates hypoxia/HIF-induced plasticity toward amoeboid cancer cell migration and metastasis[J]. Curr Biol, 2022, 32(2): 412-427. |
| [1] | Meng ZHANG,Qi ZHOU,Zheng HU. Establishment of liver in situ xenograft reconstruction model of Fah-/-Rag2-/-IL2Rg-/- mice and its evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1358-1365. |
| [2] | Tianzhen ZHANG,Hongtao SHEN,Zheng GONG,Bin ZHAO,Yan WANG. Effect of GRK5 over-expression on depression- like behavior in P301S Tau transgenic mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 573-579. |
| [3] | Yanchun QIN,Yanqiang HUANG,Gang LU,Ganrong HUANG,Huaying TANG,Yuanyuan DAI. Distribution characteristics of micrflora in various regions of intestinal tract of mice with chronic gastritis infected with Helicobacter Pylori andits mechannism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 289-297. |
| [4] | Qing YAO,Dan WANG,Xiaoshuang WANG,Yingjie WU,Liyuan RAN. Effect of ovariectomy on glucose and lipid metabolism in hyperinsulinemia MKR mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1229-1237. |
| [5] | Ying LIU,Zhou YANG,Xiaobo WANG,Feng ZHAN. Therapeutic effect of Toll-like receptor 3-treated umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on lupus nephritis in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1256-1265. |
| [6] | Henan ZHENG,Yijun ZHOU,Shuangshuang WANG,Feilong REN,Xinyi FAN,Ce SHI,Hong LIU. Expressions of integrin β1 and laminin receptor 1 in mouse tooth germs at different stages of tooth development and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 866-874. |
| [7] | Zhaowei WANG,Yanan LYU,Zheng HU,Yongguang YANG. Construction of LDLR gene knockout immunodeficient mouse model and its phenotypic analysis based on CRISPR/cas9 technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 271-276. |
| [8] | Manying WANG,Baoyu FU,Xiaohao XU,Xiangzhu LI,Hong CHEN,Liwei SUN,Daqing ZHAO. Anti-fatigue effect of ginseng adventitious root protein in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 18-25. |
| [9] | Kangning LI,Zhiling SONG,Lilong JIA,Miao CHU,Chaohui XIONG. Anti-inflammatory effect of honeysuckle extract on acute anterior uveitis mice induced by LPS and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 978-983. |
| [10] | LIU Lanqing, LI Ruilin, ZHOU Xiaomin, MENG Jun. Dynamic expression and localization of CDC14B in each cell cycle of mouse one-cell fertilized eggs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 675-679. |
| [11] | WANG Xinxin, LI Sijia, GUAN Hongquan, HOU Diandong. Induction effect of DNCB on atopic dermatitis BALB/c mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 439-443. |
| [12] | LIN Jiuhan, TIAN Lin, ZHANG Nana, DONG Ying, LYU Hang, WANG Dan, QU Meng, ZHANG Yong, SUN Liankun, YU Chunyan, LIU Xi. Inhibitory effect of mitochondrial dynamics changes on growth of transplanted melanoma in APP/PS1 mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 476-481. |
| [13] | YANG Yun, MA Xixing, WANG Dahu, ZHANG Huanhuan, MA Yaohui, REN Cuimin, LIU Qiang. Influence of tanshinone Ⅱ A on expressins of Cosmc and AOPP in kidney tissue of allergic purpura nephritis mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 867-871. |
| [14] | ZHOU Haixia, HOU Lijian, WANG Zhengming, TIAN Yu, HAN Liang, LI Mifu. Inhibitory effect of HOXA4 on transplantationglioma of nude mice through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 474-478. |
| [15] | ZOU Jun, CHEN Bing, FANG Minghui, HU Zheng. Establishment and identification of humanized mouse models with human immune system and allogeneic human melanoma growth [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 718-724. |