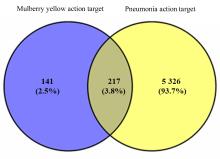
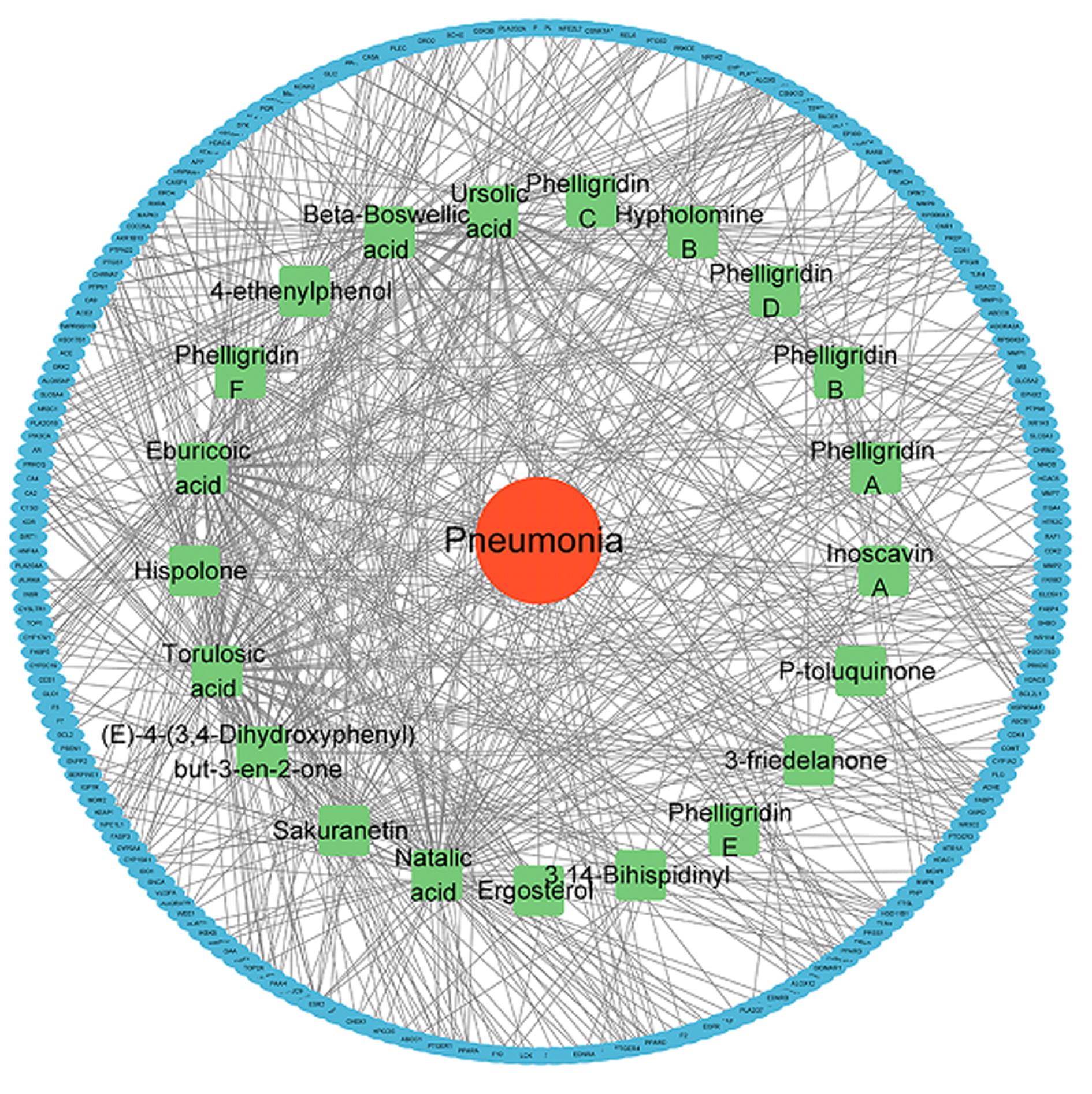
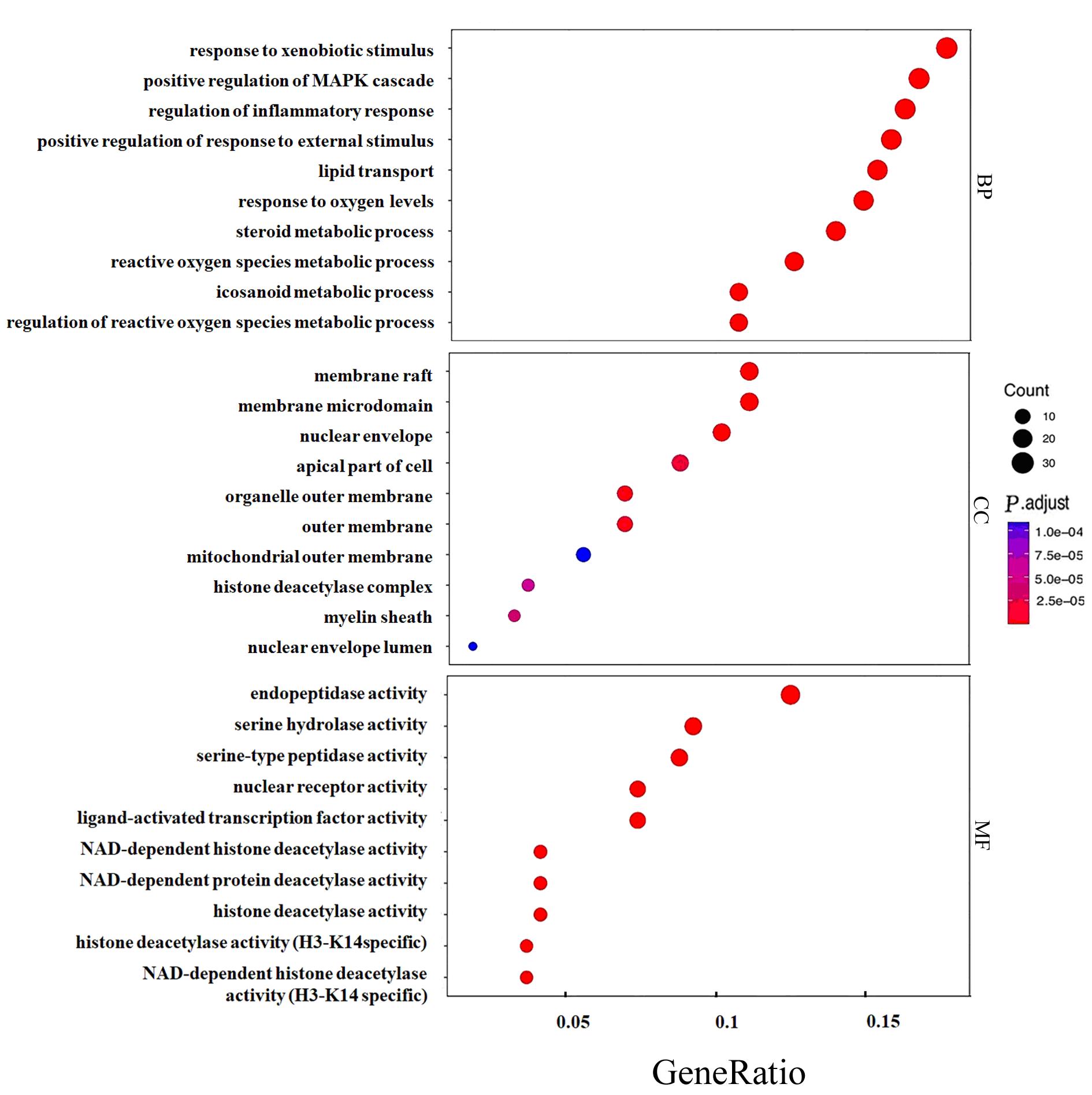
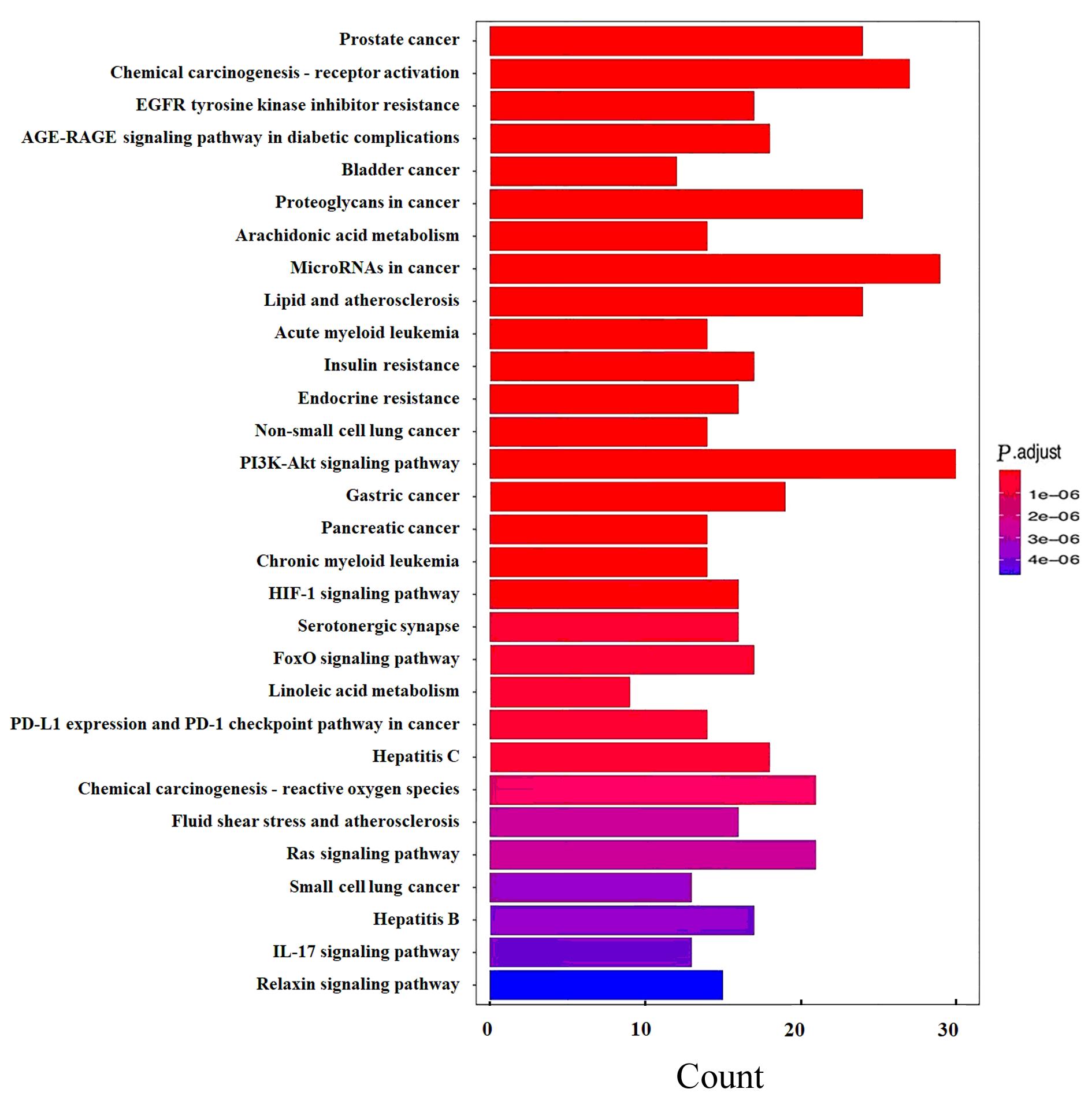
| 1 |
梁 佳, 孙梦伊, 张 腾, 等. 响应曲面法优化桑黄菌丝体中三萜的微波提取工艺[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(10):235-238.
|
| 2 |
刘爽爽, 王昀睿, 李德海. 粗毛纤孔菌三萜的提取及胆酸盐结合研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(10):132-138.
|
| 3 |
WAN X L, JIN X, WU X M, et al. Structural characterisation and antitumor activity against non-small cell lung cancer of polysaccharides from Sanghuang porus vaninii[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2022, 276: 118798.
|
| 4 |
WU Y, LIU H, LI Z H, et al. Purification of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus by using an aqueous two-phase system and evaluation of the physicochemical and antioxidant properties of polysaccharides in vitro [J]. Prep Biochem Biotechnol, 2022, 52(1): 89-98.
|
| 5 |
张维博, 王家国, 李正阔, 等. 药用真菌桑黄的研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2014, 39(15):2838-2845.
|
| 6 |
刘 鑫. 粗毛纤孔菌胞外多糖对酒精肝损伤保护作用及其液体发酵条件优化[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学.
|
| 7 |
张 倩, 孙瑞祥, 王 妍, 等. 桑黄、蛹虫草超临界CO2萃取物的抗氧化活性及其黄酮和三萜含量[J]. 食用菌, 2020, 42(5): 65-67.
|
| 8 |
李剑梅, 张疏雨, 于广丰, 等. 珍稀药用真菌桑黄菌丝体粉中黄酮含量测定[J]. 食用菌, 2020, 42(3):72-74.
|
| 9 |
程鑫颖. 瓦宁木层孔菌子实体抗肿瘤及抗氧化活性成分的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学.
|
| 10 |
葛均波, 徐永健. 内科学[M]. 8版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013: 7.
|
| 11 |
王子怡, 王 鑫, 张岱岩, 等. 中医药网络药理学: 《指南》引领下的新时代发展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(1): 7-17.
|
| 12 |
牛 明, 张斯琴, 张 博, 等. 《网络药理学评价方法指南》解读[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(14): 4119-4129.
|
| 13 |
PARK H J, SHIN M R. A clinical pilot study to evaluate the efficacy of oral intake of phellinus linteus (Sanghuang) extract on knee joint and articular cartilage: study protocol clinical trial (SPIRIT Compliant):Erratum[J].Medicine,2020,99(33):e21990.
|
| 14 |
YANG Y, ZHANG J S, LIU Y F, et al. Structural elucidation of a 3-O-methyl-D-galactose-containing neutral polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of Phellinus igniarius[J]. Carbohydr Res, 2007, 342(8): 1063-1070.
|
| 15 |
JIANG J H, WU S H, ZHOU L W. The first whole genome sequencing of Sanghuangporus sanghuang provides insights into its medicinal application and evolution[J]. J Fungi (Basel), 2021, 7(10): 787.
|
| 16 |
HOU R L, LIU X, XIANG K K, et al. Characterization of the physicochemical properties and extraction optimization of natural melanin from Inonotus hispidus mushroom[J]. Food Chem, 2019, 277: 533-542.
|
| 17 |
ANGELINI P, GIROMETTA C, TIRILLINI B,et al. A comparative study of the antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Inonotus hispidus fruit and their mycelia extracts[J].Int J Food Prop,2019,22(1):768-783.
|
| 18 |
BAO H Y, WANG C Y, BAU T. Herbalogical textual research on “sanghuang” [J]. Mycosystema, 2013,32(1):70-78.
|
| 19 |
CHENG J W, SONG J L, WEI H L, et al. Structural characterization and hypoglycemic activity of an intracellular polysaccharide from Sanghuangporus sanghuang mycelia[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2020, 164: 3305-3314.
|
| 20 |
刘璟贤, 张建永, 李晓飞. 功能代谢组学在生物医药领域中的应用[J].解放军医学杂志,2022,47(6):631-638.
|
| 21 |
FU H Q, Li Y, FU H Y. The research of extraction craft of Phellinus igniarius mycelia polysaccharide by ultrasonic wave[J].Chin Agricult Sci Bull,2012,28(36):282-286.
|
| 22 |
HAN J, YUE W P, HE G Z, et al.. Effects of polysaccharide of eight traditional Chinese medicine on cytokine releasing from mouse macrophages[J]. Curr Immunol, 2011, 31(6):495-498.
|
| 23 |
HAO C Y, CHENG Y F, XU L J, et al. Regulatory effects of Sparassis latifolia polysaccharide on intestinal immune function in immunosuppressed mice[J]. Mycosystema, 2020, 39(7):1380-1390 .
|
| 24 |
HIRJA A R, VORONEANU L, SIRIOPOL D, et al. Evaluation of low-dose glucocorticoid regimen in association with cyclophosphamide in patients with glomerulonephritis[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2019,51(10): 1805-1813.
|
| 25 |
JIE D, SHAN Z S, MA Z L, et al. Ma-Nuo-Xi Decoction has an immunostimulating effect in cyclophosphamide-immunosuppressed mice[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2020, 9(5): 3249-3260.
|
| 26 |
KANG H L, FAN W P, et al. The immunosuppression and immunoenhancement effects of cyclophosphamide on normal mice[J]. J. Immunol, 2018, 34(4):308-312.
|
| 27 |
李 钦, 范 强, 胡继宏, 等. 富硒黄芪提取物对免疫抑制大鼠细胞因子IL-2、IL-4、IFN-γ及TNF-α的影响[J]. 西部中医药, 2018, 31(3): 22-25.
|
| 28 |
LI Z T, ZHU H X, SUN J X, et al. A study on the extraction and immune effect of polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius mycelia[J]. Food Research and Development, 2018, 39(20):35-39.
|
| 29 |
LIN W C, DENG J S, HUANG S S, et al. Evaluation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative activities of ethanol extracts from different varieties of Sanghuang species[J].RSC Adv,2017,7(13):7780-7788.
|
| 30 |
刘 帅, 莫俊恺, 潘丹阳, 等. 桑黄多糖的药理作用及提取方法研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2018, 34(12): 63-67.
|
| 31 |
PARKER A R, PARK M A, HARDING S, et al. The total IgM, IgA and IgG antibody responses to pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination (Pneumovax® 23) in a healthy adult population and patients diagnosed with primary immunodeficiencies[J]. Vaccine, 2019, 37(10): 1350-1355.
|
| 32 |
MENG F, ZONG W W, WANG C, et al. Antioxidant activities and mmunomodulatory effects of the polysaccharides from fruiting bodies of Cordyceps japonica[J]. Mycosystema, 2020, 9(7):1391-1399.
|
| 33 |
GUENGERICH F P, WATERMAN M R, EGLI M. Recent structural insights into cytochrome P450 function[J].Trends Pharmacol Sci,2016,37(8):625-640.
|
| 34 |
ELFAKI I, MIR R, ALMUTAIRI F M, et al. Cytochrome P450: polymorphisms and roles in cancer, diabetes and atherosclerosis[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2018, 19(8): 2057-2070.
|
| 35 |
MENG M, GUO M Z, FENG C C, et al. Water-soluble polysaccharides from Grifola Frondosa fruiting bodies protect against immunosuppression in cyclophosphamide-induced mice via JAK2/STAT3/SOCS signal transduction pathways[J]. Food Funct, 2019, 10(8): 4998-5007.
|
 )
)