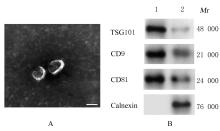
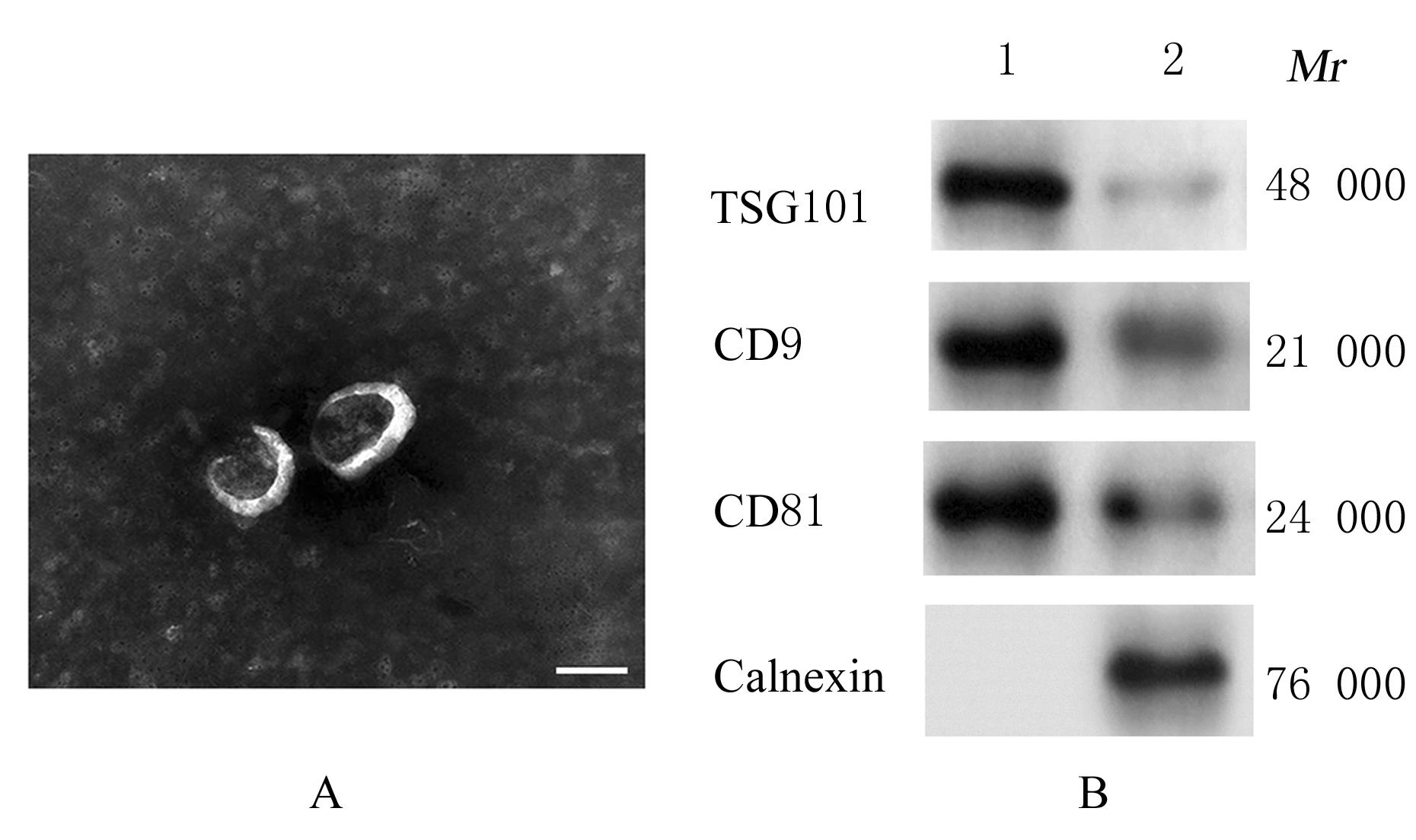
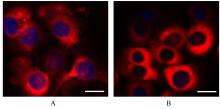
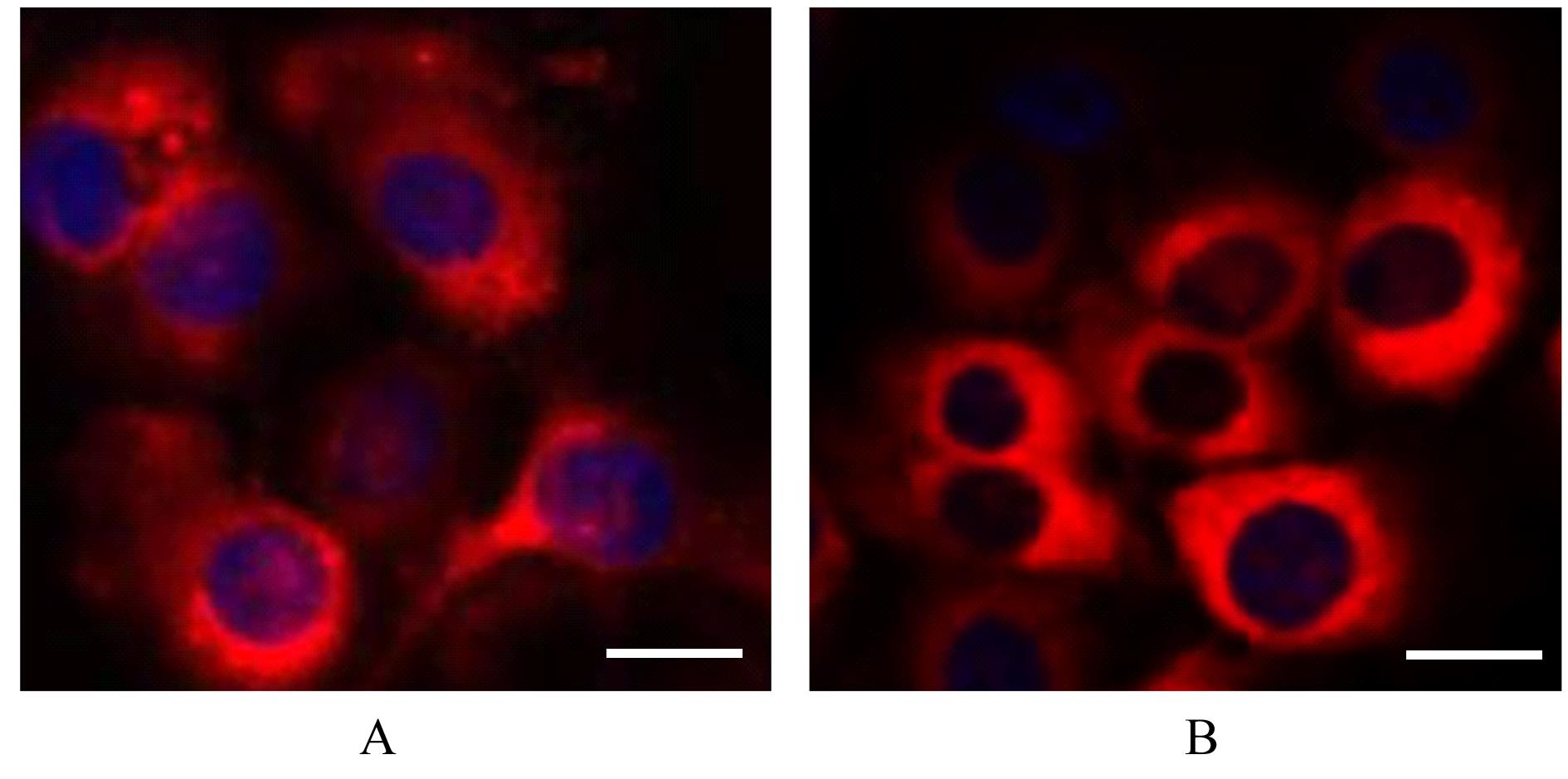
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1217-1226.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230515
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
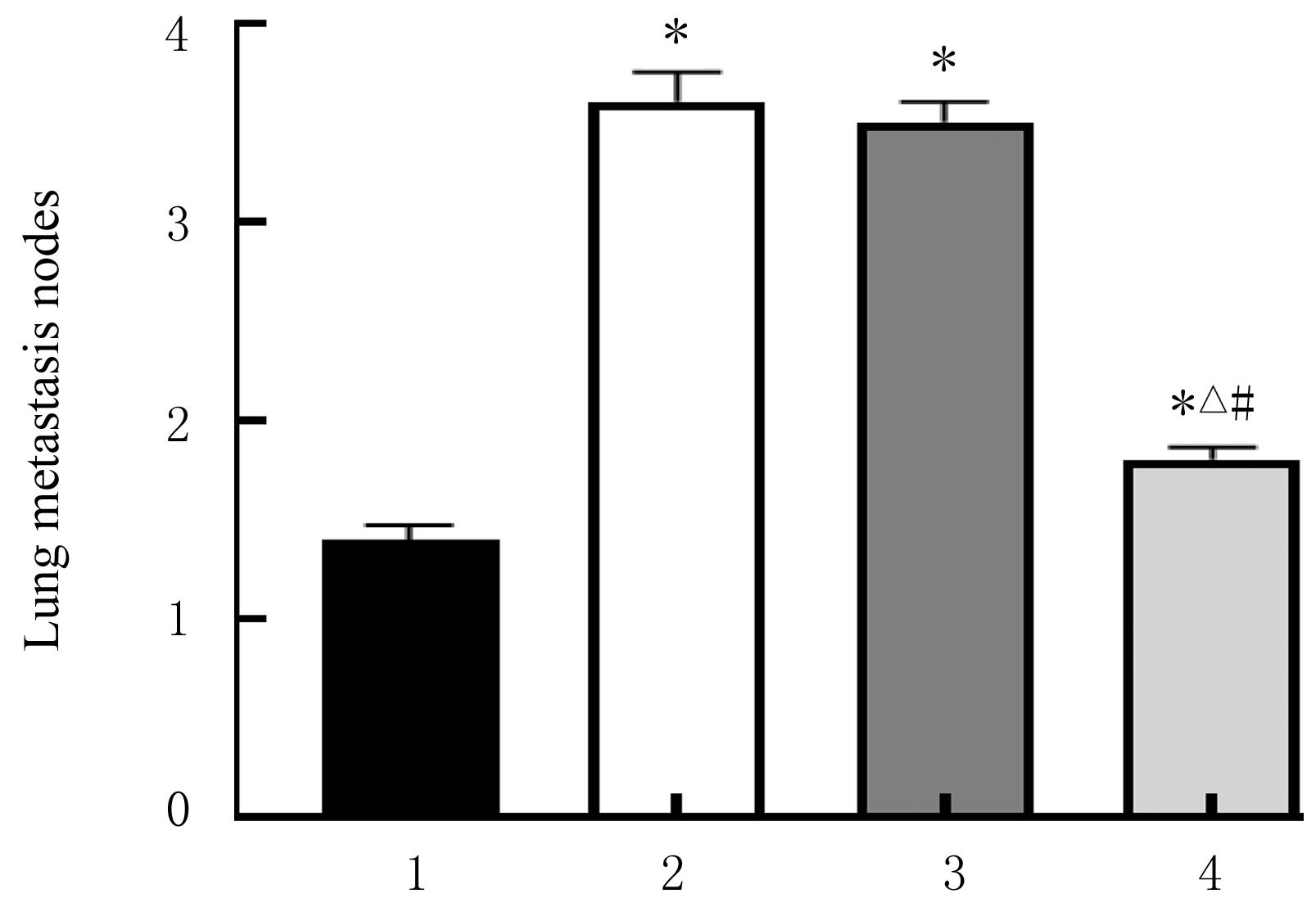
Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism
Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI( )
)
- Department of Gastroenterology,First Affiliated Hospital,Henan University,Kaifeng 475100,China
-
Received:2022-12-27Online:2023-09-28Published:2023-10-26 -
Contact:Shutang WEI E-mail:13460772602@163.com
CLC Number:
- R735.7
Cite this article
Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI. Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1217-1226.
share this article
| 1 | LLOVET J M, PINYOL R, KELLEY R K, et al. Molecular pathogenesis and systemic therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Cancer, 2022, 3(4): 386-401. |
| 2 | 郝 新, 樊 蓉, 侯金林. 原发性肝癌高危人群的早期预警和精准筛查[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2022,38(3):499-504. |
| 3 | KONYN P, AHMED A, KIM D. Current epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 15(11): 1295-1307. |
| 4 | YANG Y, YE Y C, CHEN Y, et al. Crosstalk between hepatic tumor cells and macrophages via Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes M2-like macrophage polarization and reinforces tumor malignant behaviors[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(8): 793. |
| 5 | LIANG Y J, DUAN L, LU J P, et al. Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(7): 3183-3195. |
| 6 | 郑乃盛, 汪婷婷, 袁向亮, 等. 肿瘤相关巨噬细胞来源外泌体激活IFN通路促进胃癌细胞免疫逃逸[J]. 现代免疫学, 2021, 41(1): 24-31. |
| 7 | CIANCIARUSO C, BELTRAMINELLI T, DUVAL F,et al. Molecular profiling and functional analysis of macrophage-derived tumor extracellular vesicles[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 27(10): 3062-3080.e11. |
| 8 | XIN L, ZHOU L Q, LIU C, et al. Transfer of LncRNA CRNDE in TAM-derived exosomes is linked with cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer[J]. EMBO Rep, 2021, 22(12): e52124. |
| 9 | 王 欣, 王耀霞, 纪芝民, 等. 肿瘤相关巨噬细胞外泌体lnc-SLC2A12-10: 1调节miR-296-5p促进乳腺癌细胞增殖、侵袭[J].中华内分泌外科杂志,2022(2):155-159. |
| 10 | ZHANG H W, LIAO Z B, LIU F R, et al. Long noncoding RNA HULC promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Aging, 2019, 11(20): 9111-9127. |
| 11 | GHAFOURI-FARD S, ESMAEILI M, TAHERI M, et al. Highly upregulated in liver cancer (HULC): an update on its role in carcinogenesis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(12): 9071-9079. |
| 12 | 全丽娟, 古丽娜·阿巴拜克力. 肿瘤相关巨噬细胞外泌体对卵巢癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭的影响及机制研究[J]. 中国性科学, 2022, 31(11): 55-59. |
| 13 | 张学政, 吴冬冰, 张学娟, 等. 胃癌细胞外泌体lncRNA LOXL1-AS1诱导M2型巨噬细胞极化功能及机制研究[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022, 30(8): 1374-1380. |
| 14 | 孙 倩, 刘盛力, 马 钰, 等. 大黄酸通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制喉癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2022, 51(5): 415-419. |
| 15 | SICA A, ERRENI M, ALLAVENA P, et al. Macrophage polarization in pathology[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2015, 72(21): 4111-4126. |
| 16 | 韩晨阳, 杨 毅, 王 瑾, 等. M2型巨噬细胞促进肝癌肿瘤血管生成的作用[J]. 中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2020, 40(4): 283-289. |
| 17 | 纪晓权, 张爱民, 张 弢, 等. 立体定向放疗序贯仑伐替尼治疗中晚期原发性肝癌的效果与安全性分析[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2021,37(9):2120-2124. |
| 18 | YIN Z, ZHOU Y, MA T T, et al. Down-regulated lncRNA SBF2-AS1 in M2 macrophage-derived exosomes elevates miR-122-5p to restrict XIAP, thereby limiting pancreatic cancer development[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(9): 5028-5038. |
| 19 | WANG X, ZHOU Y, DONG K, et al. Exosomal lncRNA HMMR-AS1 mediates macrophage polarization through miR-147a/ARID3A axis under hypoxia and affects the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Environ Toxicol, 2022, 37(6): 1357-1372. |
| 20 | LIU G D, OUYANG X W, SUN Y, et al. The miR-92a-2-5p in exosomes from macrophages increases liver cancer cells invasion via altering the AR/PHLPP/p-AKT/β-catenin signaling[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2020, 27(12): 3258-3272. |
| 21 | YIN T T, WU J, HU Y C, et al. Long non-coding RNA HULC stimulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process and vasculogenic mimicry in human glioblastoma[J].Cancer Med, 2021, 10(15):5270-5282. |
| 22 | LU W J, WAN X B, TAO L M, et al. Long non-coding RNA HULC promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation,migration and invasion via miR-218/TPD52 axis[J].Onco Targets Ther,2020,13:1109-1118. |
| 23 | KIM M P, LI X Q, DENG J, et al. Oncogenic KRAS recruits an expansive transcriptional network through mutant p53 to drive pancreatic cancer metastasis[J]. Cancer Discov, 2021, 11(8): 2094-2111. |
| 24 | WU J, WANG Y P, YANG Y C, et al. TNFSF9 promotes metastasis of pancreatic cancer through Wnt/Snail signaling and M2 polarization of macrophages[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(17): 21571-21586. |
| 25 | LU C J, HE Y F, DUAN J, et al. Expression of Wnt3a in hepatocellular carcinoma and its effects on cell cycle and metastasis[J]. Int J Oncol, 2017, 51(4):1135-1145. |
| 26 | TIAN X H, WU Y Y, YANG Y T, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00662 promotes M2 macrophage polarization and hepatocellular carcinoma progression via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J].Mol Oncol,2020, 14(2): 462-483. |
|
||