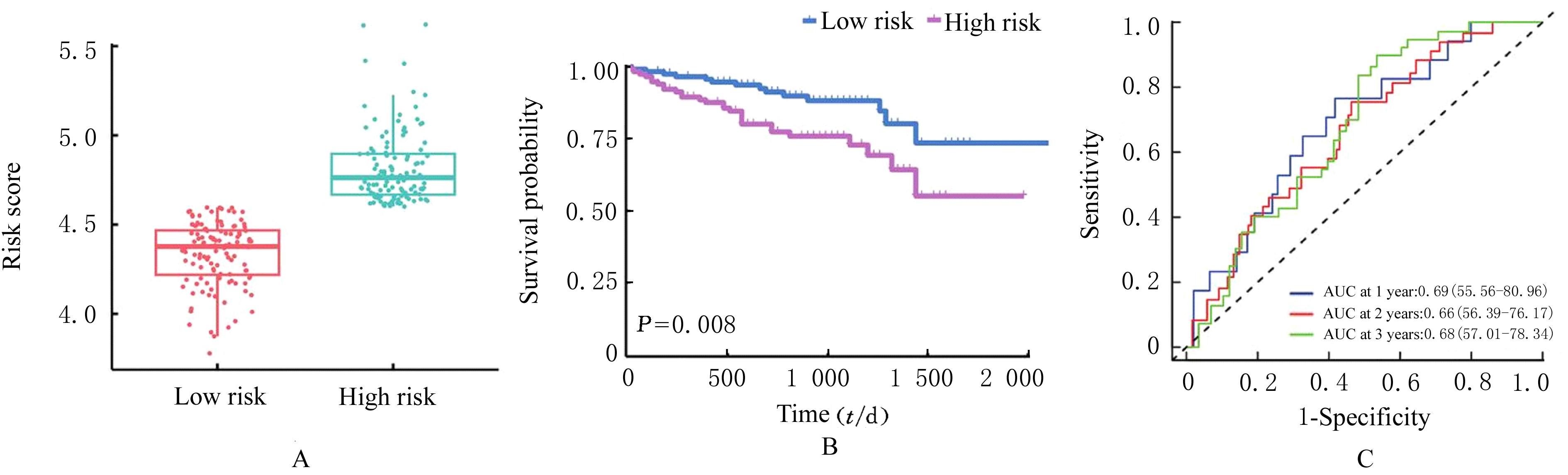
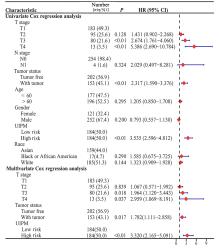
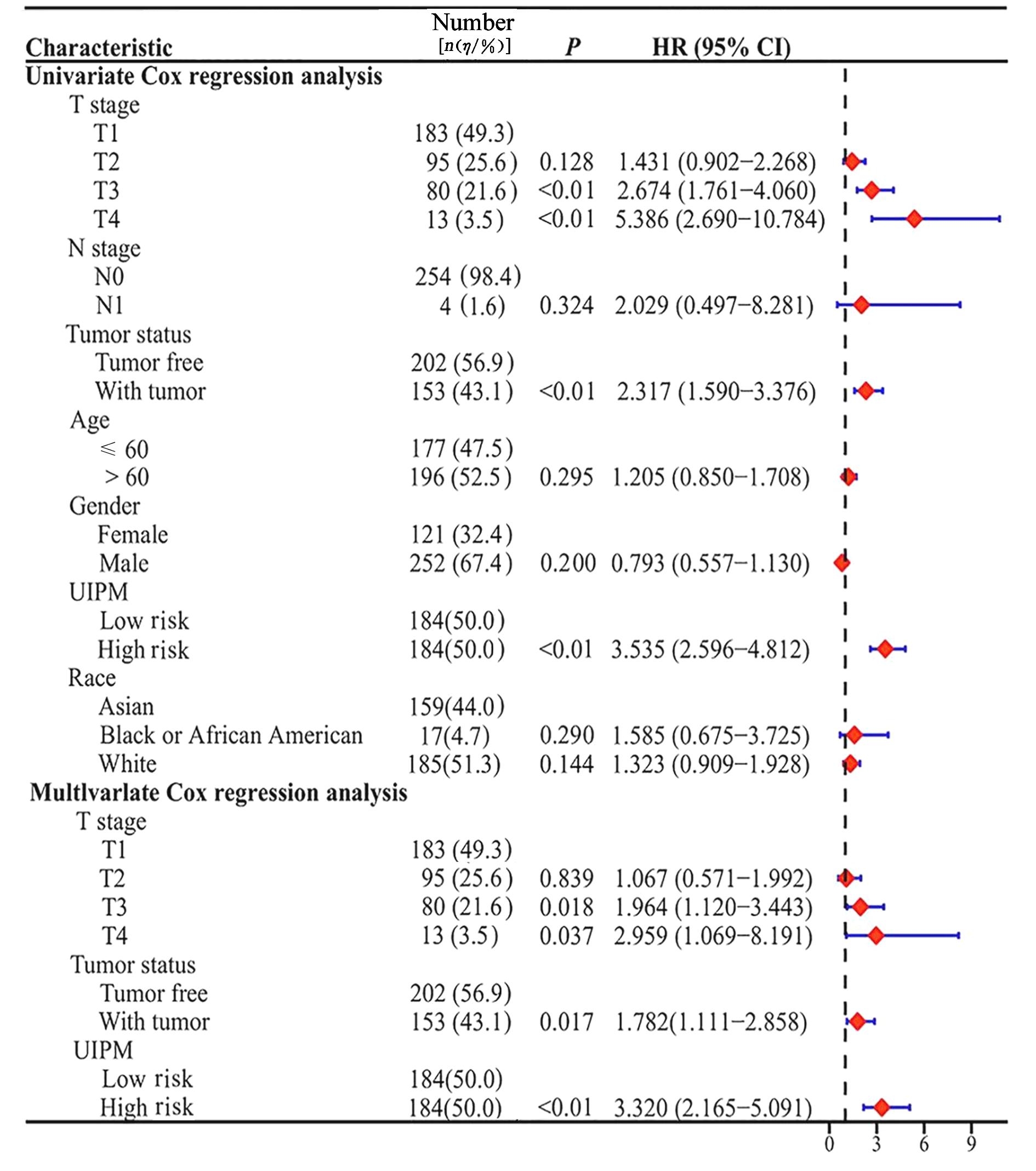
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 168-177.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240121
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Screening of UBE2S interacting protein and construction of prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
Xiaoyan WANG1,2,Hao ZHANG2,3,Zehao GUO2,3,Jun CAO2,3,Zhijing MO2,3( )
)
- 1.Department of Experimental Teaching Center, School of Intelligent Medicine and Biotechnology, Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541199, China
2.Key Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Guangxi Institutions of Higher Learning, Gulin Medical University, Guilin 541199, China
3.Department of Biochemistry, College of Intelligent Medicine and Biotechnology, Guilin Medical University, Guilin 541199, China
-
Received:2023-03-28Online:2024-01-28Published:2024-01-31 -
Contact:Zhijing MO E-mail:mozhijing@glmc.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R735.7
Cite this article
Xiaoyan WANG,Hao ZHANG,Zehao GUO,Jun CAO,Zhijing MO. Screening of UBE2S interacting protein and construction of prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 168-177.
share this article
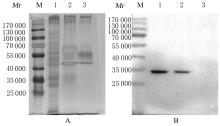
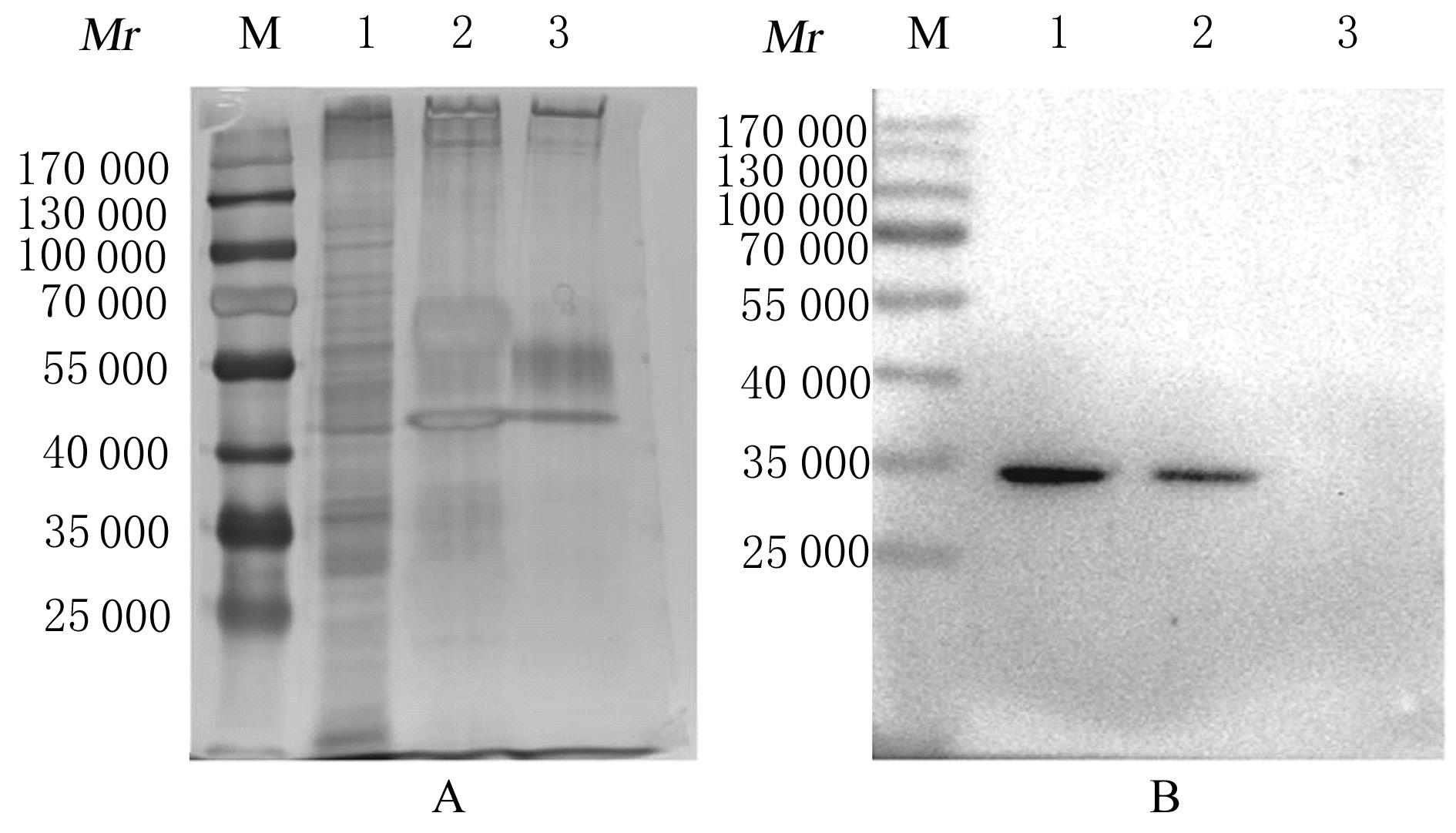
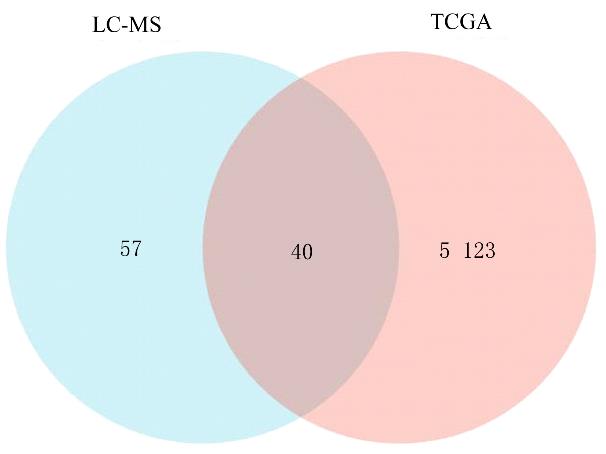
Tab.1
Informations of top 20 ranked proteins by score analyzed by LC-MS"
| PF number | Accession | Score | Mass | Match | Sequence | emPAI | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | P08670 | 873 | 53 676 | 24 | 16 | 3.17 | VIM |
| 6 | P62736 | 588 | 42 381 | 26 | 13 | 3.49 | ACTA2 |
| 9 | P13645 | 509 | 59 020 | 11 | 8 | 0.82 | KRT10 |
| 11 | Q92614 | 385 | 234 168 | 6 | 5 | 0.09 | MYO18A |
| 13 | P11142 | 330 | 71 082 | 6 | 5 | 0.31 | HSPA8 |
| 14 | P06733 | 314 | 47 481 | 6 | 5 | 0.50 | ENO1 |
| 15 | P35527 | 311 | 62 255 | 5 | 5 | 0.29 | KRT9 |
| 16 | P35908 | 294 | 65 678 | 7 | 6 | 0.41 | KRT2 |
| 17 | P02533 | 282 | 51 872 | 6 | 5 | 0.45 | KRT14 |
| 18 | P08779 | 277 | 51 578 | 6 | 5 | 0.45 | KRT16 |
| 20 | P25705 | 245 | 59 828 | 3 | 3 | 0.17 | ATP5F1A |
| 22 | P11021 | 231 | 72 402 | 5 | 5 | 0.25 | HSPA5 |
| 24 | Q9BQE3 | 212 | 50 548 | 5 | 4 | 0.37 | TUBA1C |
| 25 | P06396 | 195 | 86 043 | 6 | 4 | 0.25 | GSN |
| 26 | P23396 | 190 | 26 842 | 4 | 4 | 0.60 | RPS3 |
| 27 | P07437 | 175 | 50 095 | 4 | 4 | 0.29 | TUBB |
| 30 | A0A075B6S2 | 133 | 13 249 | 4 | 2 | 0.58 | IGKV2D-29 |
| 31 | P01023 | 125 | 164 613 | 2 | 2 | 0.04 | A2M |
| 32 | P52272 | 122 | 77 749 | 3 | 2 | 0.13 | HNRNPM |
| 33 | P13929 | 117 | 47 299 | 2 | 2 | 0.14 | ENO3 |
Tab.2
Informations of top 20 ranked proteins in Venn diagram"
| Gene name | Gene ID | Gene biotype | HR | 95% CI | PCox |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCT3 | ENSG00000163468 | Protein coding | 2.087 | 1.459-2.985 | 5.63687E-05 |
| TUBA1C | ENSG00000167553 | Protein coding | 2.040 | 1.433-2.904 | 7.63003E-05 |
| ARPC4 | ENSG00000241553 | Protein coding | 2.048 | 1.433-2.928 | 8.44439E-05 |
| ENO1 | ENSG00000074800 | Protein coding | 1.982 | 1.390-2.826 | 0.000 156 723 |
| HNRNPH1 | ENSG00000169045 | Protein coding | 1.950 | 1.366-2.784 | 0.000 236 773 |
| PRDX1 | ENSG00000117450 | Protein coding | 1.899 | 1.338-2.696 | 0.000 333 502 |
| H2AZ1 | ENSG00000164032 | Protein coding | 1.902 | 1.335-2.710 | 0.000 369 261 |
| IDH3B | ENSG00000101365 | Protein coding | 1.840 | 1.294-2.615 | 0.000 684 482 |
| RAB6A | ENSG00000175582 | Protein coding | 1.831 | 1.287-2.605 | 0.000 769 835 |
| SLC2A1 | ENSG00000117394 | Protein coding | 1.813 | 1.275-2.577 | 0.000 926 358 |
| PKM | ENSG00000067225 | Protein coding | 1.807 | 1.271-2.568 | 0.000 975 417 |
| EIF2S1 | ENSG00000134001 | Protein coding | 1.774 | 1.246-2.524 | 0.001 459 454 |
| SLC25A3 | ENSG00000075415 | Protein coding | 1.758 | 1.239-2.495 | 0.001 574 133 |
| YWHAZ | ENSG00000164924 | Protein coding | 1.758 | 1.238-2.496 | 0.001 614 956 |
| CAPZA2 | ENSG00000198898 | Protein coding | 1.740 | 1.221-2.477 | 0.002 150 215 |
| RPL18 | ENSG00000063177 | Protein coding | 1.723 | 1.214-2.447 | 0.002 339 329 |
| CALM1 | ENSG00000198668 | Protein coding | 1.709 | 1.200-2.432 | 0.002 938 229 |
| AKR1B10 | ENSG00000198074 | Protein coding | 1.711 | 1.198-2.444 | 0.003 143 354 |
| WTAP | ENSG00000146457 | Protein coding | 1.704 | 1.196-2.427 | 0.003 170 283 |
| ACTR3 | ENSG00000115091 | Protein coding | 1.670 | 1.177-2.369 | 0.004 042 542 |
| 1 | BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424. |
| 2 | CAO W, CHEN H D, YU Y W, et al. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: a secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020[J]. Chin Med J, 2021, 134(7): 783-791. |
| 3 | KIRKIN V, DIKIC I. Ubiquitin networks in cancer[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2011, 21(1): 21-28. |
| 4 | LI Z Y, WANG Y, LI Y D, et al. Ube2s stabilizes β-Catenin through K11-linked polyubiquitination to promote mesendoderm specification and colorectal cancer development[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(5): 456. |
| 5 | TANG H, FANG T, JI M, et al. UBE2S exerts oncogenic activities in urinary bladder cancer by ubiquitinating TSC1[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 578: 7-14. |
| 6 | HU L, CHENG X B, BINDER Z, et al. Molecular and clinical characterization of UBE2S in glioma as a biomarker for poor prognosis and resistance to chemo-radiotherapy[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 640910. |
| 7 | ZHANG M J, LIU Y, YIN Y, et al. UBE2S promotes the development of ovarian cancer by promoting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to regulate cell cycle and apoptosis[J]. Mol Med, 2022, 28(1): 62. |
| 8 | HU W J, LI M, CHEN Y G, et al. UBE2S promotes the progression and Olaparib resistance of ovarian cancer through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2021, 14(1): 121. |
| 9 | LIN T H, HSU W H, TSAI P H, et al. Dietary flavonoids, luteolin and quercetin, inhibit invasion of cervical cancer by reduction of UBE2S through epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling[J]. Food Funct, 2017, 8(4): 1558-1568. |
| 10 | LIU Z, XU L J. UBE2S promotes the proliferation and survival of human lung adenocarcinoma cells[J]. BMB Rep, 2018, 51(12): 642-647. |
| 11 | HO J Y, LU H Y, CHENG H H, et al. UBE2S activates NF-κB signaling by binding with IκBα and promotes metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells[J]. Cell Oncol (Dordr), 2021, 44(6): 1325-1338. |
| 12 | QIN Y N, DU J, FAN C F. Ube2S regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer[J].Int J Med Sci,2020,17(2): 274-279. |
| 13 | GUO Y J, CHEN X Y, ZHANG XW, et al. UBE2S and UBE2C confer a poor prognosis to breast cancer via downregulation of Numb [J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 992233. |
| 14 | PENG S M, CHEN X, HUANG C Y, et al. UBE2S as a novel ubiquitinated regulator of p16 and β-catenin to promote bone metastasis of prostate cancer[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(8): 3528-3543. |
| 15 | PAN Y H, YANG M, LIU L P, et al. UBE2S enhances the ubiquitination of p53 and exerts oncogenic activities in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 503(2): 895-902. |
| 16 | ZHANG R Y, LIU Z K, WEI D, et al. UBE2S interacting with TRIM28 in the nucleus accelerates cell cycle by ubiquitination of p27 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma development[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 64. |
| 17 | GUI L, ZHANG S C, XU Y Z, et al. UBE2S promotes cell chemoresistance through PTEN-AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7(1): 357. |
| 18 | MA Y L, LI K Z, LI S J, et al. Prognostic value of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 S overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2018, 119: 225-231. |
| 19 | GOEMAN J J. L1 penalized estimation in the Cox proportional hazards model[J]. Biom J, 2010, 52(1): 70-84. |
| 20 | COMBS J A, DENICOLA G M. The non-essential amino acid cysteine becomes essential for tumor proliferation and survival[J]. Cancers,2019,11(5): 678. |
| 21 | ANGELI J P F, SCHNEIDER M, PRONETH B,et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice[J].Nat Cell Biol,2014, 16(12): 1180-1191. |
| 22 | YANG W S, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH M E,et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4[J]. Cell, 2014, 156(1/2): 317-331. |
| 23 | JIANG X J, STOCKWELL B R, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J].Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2021,22(4):266-282. |
| 24 | MATSCHKE V, THEISS C, MATSCHKE J. Oxidative stress: the lowest common denominator of multiple diseases[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2019, 14(2): 238-241. |
| 25 | WANG J, CHEN W, WEI W W, et al. Oncogene TUBA1C promotes migration and proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts a poor prognosis[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(56): 96215-96224. |
| 26 | JIANG K Q, DONG C Y, YIN Z L, et al. Exosome-derived ENO1 regulates integrin α6β4 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(11): 972. |
| 27 | XU H, DONG X Y, CHEN Y M, et al. Serum exosomal hnRNPH1 mRNA as a novel marker for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2018, 56(3): 479-484. |
| 28 | CHEN Y H, PENG C H, CHEN J R, et al. WTAP facilitates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic silencing of ETS1[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 127. |
| 29 | YANG C X, SHAO Y D, WANG X J, et al. The effect of the histone chaperones HSPA8 and DEK on tumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2653. |
| 30 | DUAN F F, WU H, JIA D W, et al. O-GlcNAcylation of RACK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(6): 1191-1202. |
| 31 | HUANG S L, DONG C R, LI D, et al. ARPC2: a pan-cancer prognostic and immunological biomarker that promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 896080. |
| [1] | Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI. Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1217-1226. |
| [2] | Wenjun DENG,Liantao HU,Binnan ZHAO,Xinyu DONG,Xuebin LI,Jie LI,Xinyan YANG,Xiaoli GUO,Yue LI,Yikun QU,Weiqun WANG. Effect of CXC chemokine ligand 10 on proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1227-1233. |
| [3] | Yaqi XU,Yanyu WANG,Wenjing ZHANG,Mei HAN,Huaxia MU,Xi YANG,Weixiao BU,Zikun TAO,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of key genes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with prognosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1243-1252. |
| [4] | Yuanyuan LIANG,Song ZHAO,Jing HU,Ni AN,Yanlu WEI,Rongjian SU. Effect of motesanib combined with EZH2 inhibitor GSK126 on proliferation and apoptosis of liver cancer Huh7 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 896-904. |
| [5] | Junyi JIN,Mu LI,Yaoyuan HU,Yihui WANG. Targeting relationship between miR-150-5p and NCAPG and its inhibitory effect on hepatocellular carcinoma Huh7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 122-130. |
| [6] | Liantao HU,Wenjun DENG,Shizhen LU,Luo SUN,Xuebing LI,Chuhao LI,Xinran WANG,chunbing ZHANG,Yue LI,Weiqun WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on CC chemokine ligand 20 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its effect on prognostic assessment of liver hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1010-1017. |
| [7] | YUE Yuan, XU Yinglian, WANG Jingjing, SUN Minying, ZHANG Zenan, ZHAO Xinyue, LI Zongpu, TAI Guixiang. Inhibitory effects of down-regulation of JNK enzymatic activity on growth of human prostate cancer cells, hepatocellular carcinoma cells and breast cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1046-1051. |
| [8] | LI Chun, GUAN Xingang, WANG Yingnan, XU Congrui, GAI Xiaodong. Inhibitory effect of Tum-5 gene on growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its influence in angiogenesis [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(01): 58-62. |
| [9] | CUI Yinxing, KONG Fei, ZHAO Xu, GAO Pujun. Expression of O-GlcNAc transferase in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(05): 980-984. |
| [10] | SU Yingying, LIU Yingyu, ZHANG Yangyu, MA Yue, YANG Guang, YOU Yueyue, FU Yingli, KOU Changgui. Network Meta-analysis of 9 kinds of Chinese herb injections combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(06): 1126-1131. |
| [11] | KONG Fei,MA Hong-xi,JIANG Jing,SONG Ying,GUO Chang-song, JIN Mei-shan,NIU Jun-qi. Expressions of Galectin-3 and Galectin-9 in hepatocellular carcinoma patients and their relationship with prognosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(02): 351-357. |
| [12] | HUANG Wei-li,LYU Yong-chen,CHI Bao-rong. Application of phage-display peptide library in screening short peptides binding specifically to high metastatic potential hepa [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(01): 87-91. |
| [13] | LI Si-guang,LIU Kai-ge,CHANG Yuan-hong. Effect of hepatic stellate cell through chemotatic factor SDF-1/CXCR4 axis on promoting hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(4): 730-736. |
| [14] | WANG Su-zhen|MENG Wei-jing|AN Hong-qing|WANG Xiao-li. Comparison of effects between radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous etharol injection in treatment of hepatocellular arcinoma after balancing covariates between groups [J]. J4, 2012, 38(6): 1068-1072. |
| [15] | DUAN Xiu-mei,ZOU Ya-bin,MA Hong-xi,LI Shu-lei,WANG Yin-ping,WANG Chao,LI Yu-qin. Adjuvant effect of mycobacterium tuberculosis heat shock protein 70 stimulating epitope on fusion gene vaccine [J]. J4, 2012, 38(3): 506-511. |
|
||