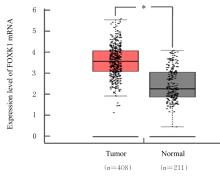
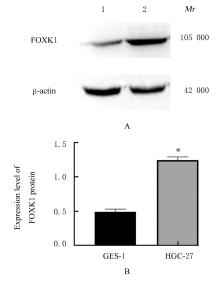
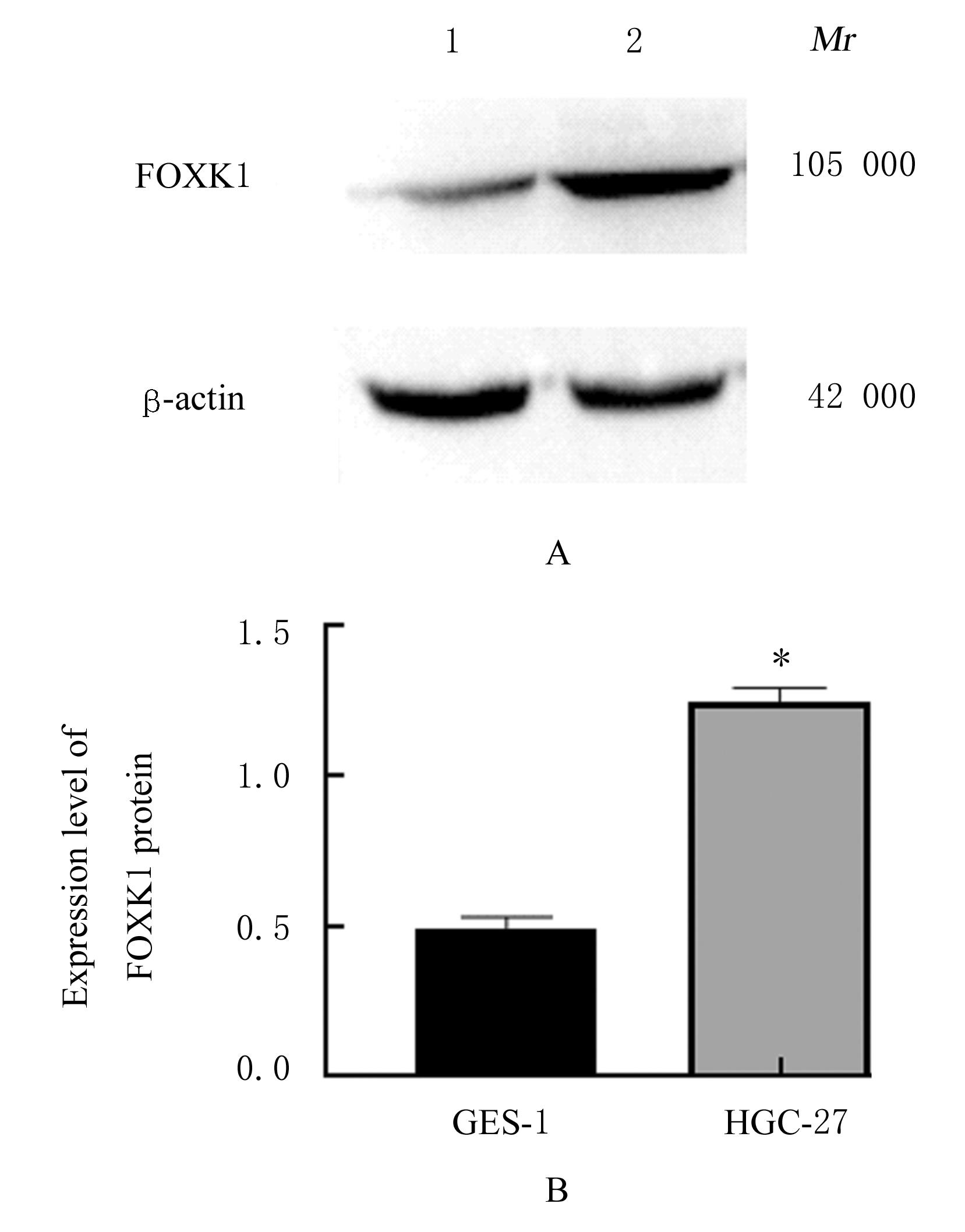
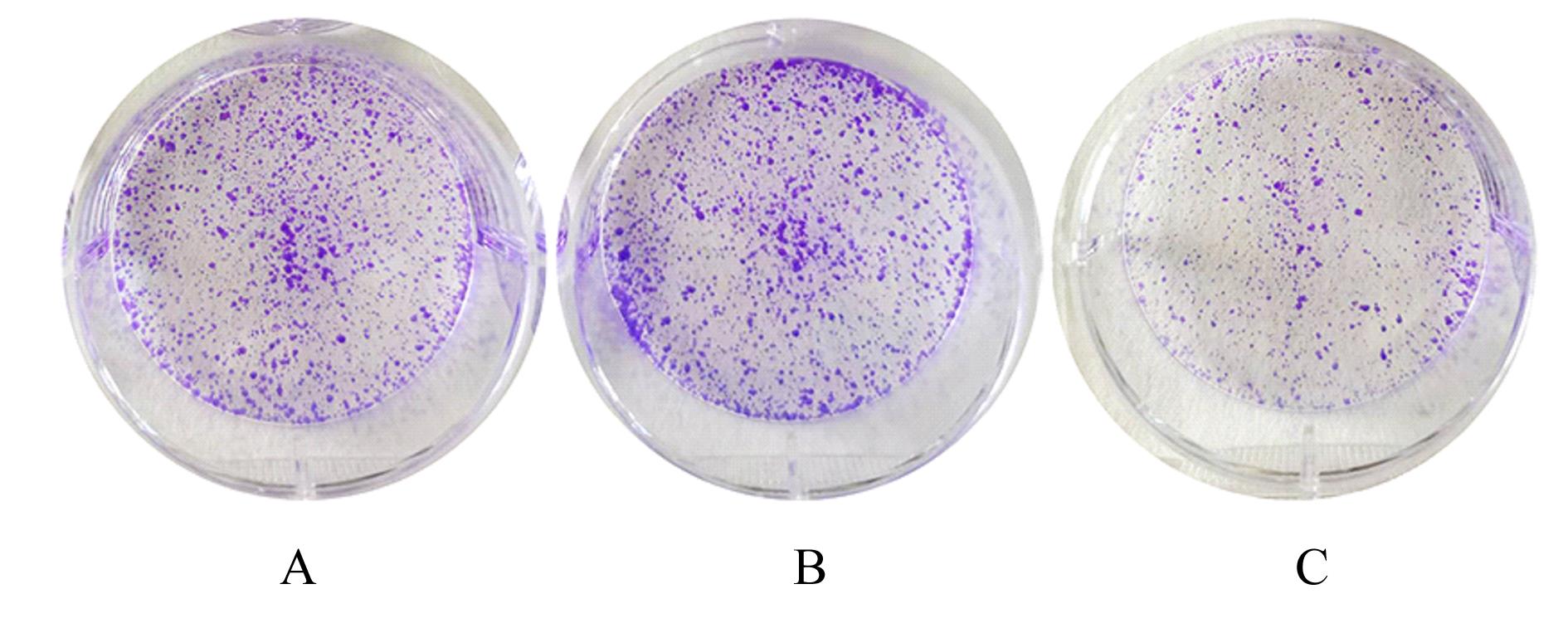
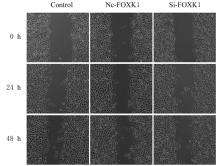
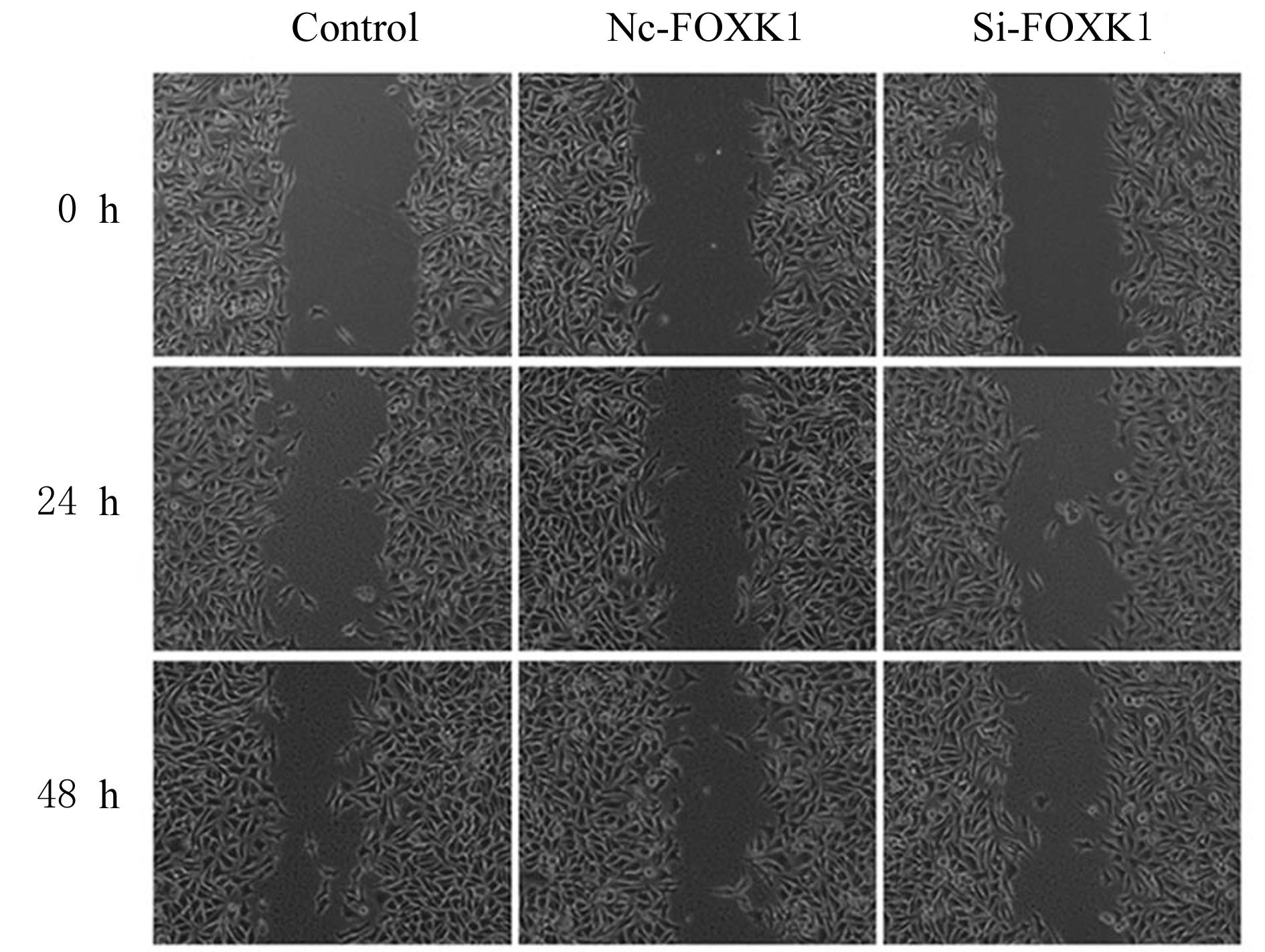
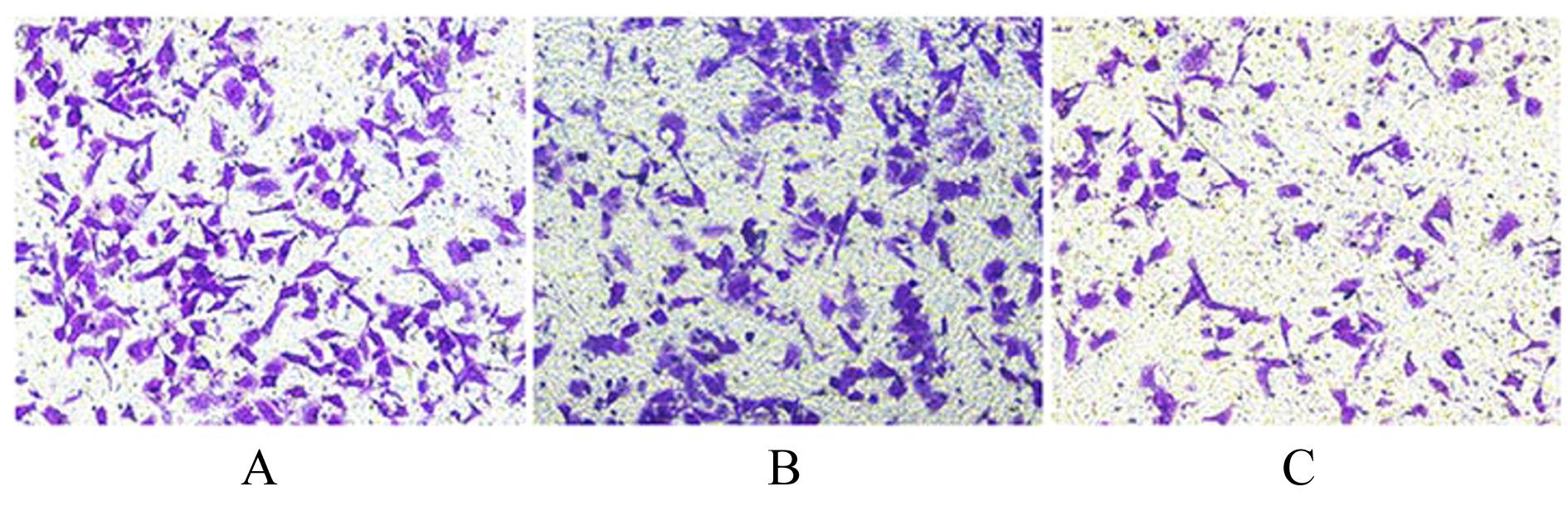
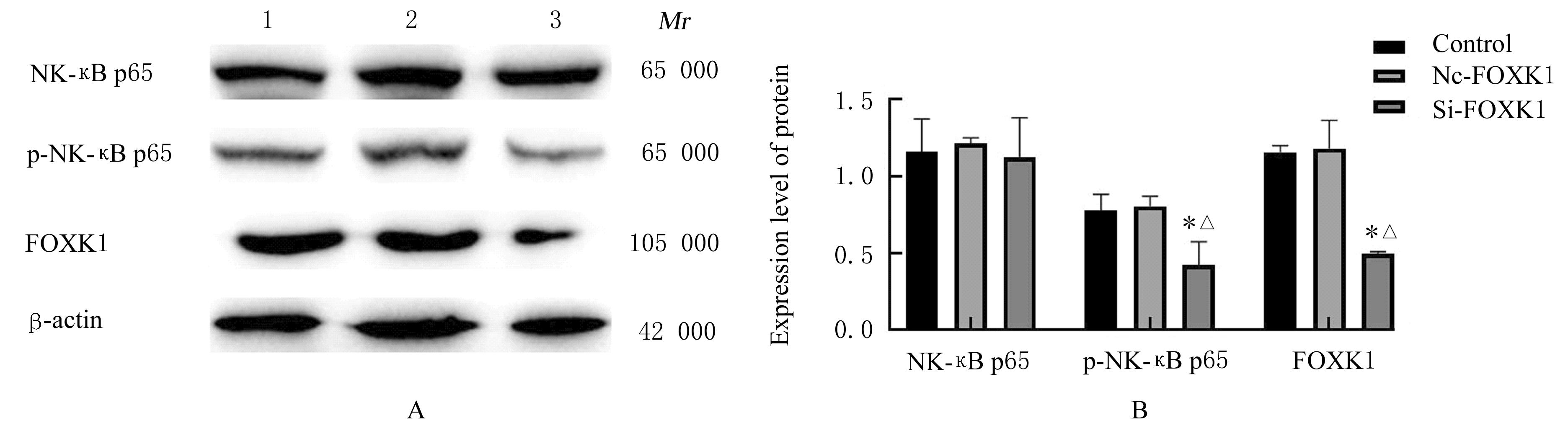
| [1] |
Haifeng WEI,Zhiqiang NI,Yanhong WEI,Qilai WANG,Shouqing LI,Yinfu MA,Yan TAN,Yanqiu FANG.
Effects of miR-126 over-expression and ADAM9 gene silencing on biological behavior of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 310-319.
|
| [2] |
Huijuan SONG,Zhenhua XU,Dongning HE.
Effect of apolipoprotein C1 expression on proliferation and apoptosis of human liver cancer HepG2 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 128-135.
|
| [3] |
Yanhong WEI,Chenxue YANG,Guangmin YANG,Shuai SONG,Ming LI,Haijiao YANG,Haifeng WEI.
Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 143-149.
|
| [4] |
Jie ZENG,Xueyan YU,Ting LUO,Jiang XU.
Effect of PD-L1 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of human oral squamous carcinoma cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 18-24.
|
| [5] |
Jia ZHOU,Zhidong QIU,Zhe LIN,Guangfu LYU,Jiaming XU,He LIN,Kexin WANG,Yuchen WANG,Xiaowei HUANG.
Effect of chelerythrine on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 25-32.
|
| [6] |
Yuxue SUN,Ziqiang LIU,Hao WU,Liming ZHAO,Tao GAO,Haiyan HUANG,Chaoyue LI.
Inhibitory effect of berberine on migration and invasion of human glioma T98G cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 50-57.
|
| [7] |
Xiaoni WANG,Tao GUO,Qiyun LUO,Lifeng GUAN.
Effect of usnic acid on biological behaviors of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts and JNK/MAPK signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1445-1451.
|
| [8] |
Aihua REN,Xinda JU,Aofei LIU,Yongchao LIU,Yanfeng LIU.
Effect of ganoderic acid A on proliferation and apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer PC-9 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1466-1472.
|
| [9] |
Manying OU,Chunxia HU,Yueping LI.
Effect of expression of microtubule inhibitory assembly protein 1 in placenta tissue of pre-eclampsia patients on trophoblast cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1519-1527.
|
| [10] |
Dandan WANG,Ning ZHOU,Dongqin LIU,Jie ZHAO,Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Yan WU.
Effect of miR-491-5p over-expression on proliferation and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1134-1139.
|
| [11] |
Na NI,Hongliang DONG,Haiyang GAO,Weiwei CHEN,Xinyu MENG,Bingjie CUI,Jing DU.
Construction of human lncRNA-GACAT2 over-expression vector and its effect on proliferation and stemness of lung cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1147-1153.
|
| [12] |
Qi WU,Jianfeng CHEN,Hao LI,Feng WEN.
Effect of paeonol on proliferation, migration, and CXCR4/STAT3 pathway of human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1202-1209.
|
| [13] |
Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI.
Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1217-1226.
|
| [14] |
Wenjun DENG,Liantao HU,Binnan ZHAO,Xinyu DONG,Xuebin LI,Jie LI,Xinyan YANG,Xiaoli GUO,Yue LI,Yikun QU,Weiqun WANG.
Effect of CXC chemokine ligand 10 on proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1227-1233.
|
| [15] |
Yuesheng ZHAO,Zubin LI,Haiou LIU,Kunlin TAO,Qihai ZHAO,Na LI.
Inhibitory effect of silencing CDKL1 gene on proliferation and invasion of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by regulating PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1234-1242.
|