| [1] |
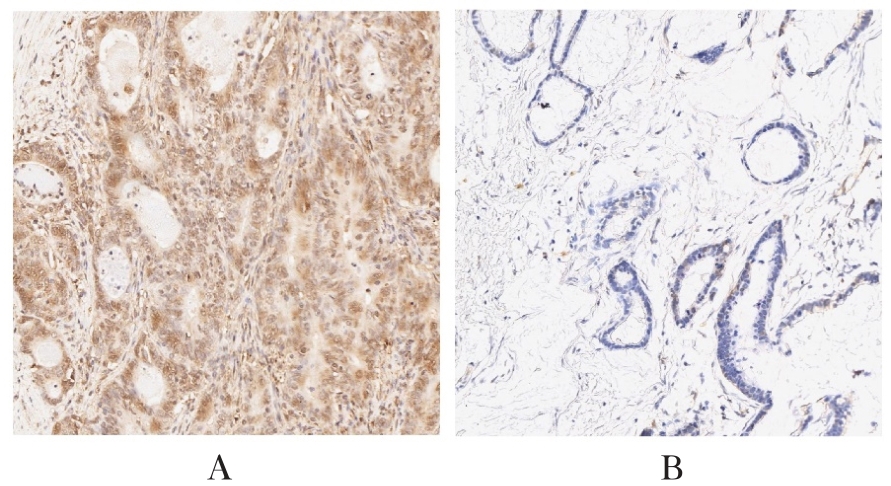
Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU.
Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043.
|
| [2] |
Jinlian LI,Lanzhen HUANG,Xishi HUANG,Kangzhi LI,Jiali JIANG,Miaomiao ZHANG,Qunying WU.
Bioinformatics analysis on key genes related to prognosis, diagnosis, and immune cell infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma and their potential therapeutic drugs
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1062-1075.
|
| [3] |
Yuanguo WANG,Peng ZHANG.
Bioinformatics analysis based on relationship between SSP1 and TGFB1 and occurrence, prognosis, and immune invasion of esophageal adenocarcinoma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1076-1086.
|
| [4] |
Yufei FENG,Shan JIN,Yubing WANG,Yinfei LU,Lijuan PANG,Kejian LIU.
Bioinformatics analysis based on immune-related genes and immune cell infiltration of in-stent restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 749-758.
|
| [5] |
Yueying SONG,Chao GAO,Wenjun CHEN,Aiyu SHAO,Yichun QIAO,Zhuolin LI.
Screening of miRNAs related to prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer and its gene network based on TCGA Database
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 392-399.
|
| [6] |
Na NI,Hongliang DONG,Haiyang GAO,Weiwei CHEN,Xinyu MENG,Bingjie CUI,Jing DU.
Construction of human lncRNA-GACAT2 over-expression vector and its effect on proliferation and stemness of lung cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1147-1153.
|
| [7] |
Yaqi XU,Yanyu WANG,Wenjing ZHANG,Mei HAN,Huaxia MU,Xi YANG,Weixiao BU,Zikun TAO,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG.
Bioinformatics analysis on screening of key genes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with prognosis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1243-1252.
|
| [8] |
Haikang CUI,Xudong ZHANG,Xiaoning LI,Xi YANG,Lan YANG,Wenjie ZHANG.
Bioinformatics analysis on predition effect of subtypes of cell pyroptosis and APOD on prognosis of gastric cancer patients
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1268-1279.
|
| [9] |
Jingjing LI, REZIWANGULI·Aisikaier,Wanyi XING,Yinggang ZOU.
Primary dedifferentiated liposarcoma of unilateral ovary: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1040-1045.
|
| [10] |
Renyi YANG,Shuwang PENG,Yongheng WANG,Yuxuan DONG,Shanshan DUAN.
Construction of ferroptosis prognostic risk model of thyroid cancer and bioinformatics analysis on its potential mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 402-413.
|
| [11] |
Xiaoyan WANG,Yihong HU,Yucheng HAN,Xianqiong ZOU.
Bioinformatics analysis on mechanism of COMMD7 in occurrence and development of brain low-grade glioma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 414-424.
|
| [12] |
Haiwei QUAN,Yali ZHANG,Han WANG,Yijiu AI,Yutong ZOU,Wei XIA.
Detection of expression level of miR-4286 in exosome in peripheral blood of patients with acute myeloid leukemia and its diagnostic value
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 460-466.
|
| [13] |
Yang BAI,Chenxi YANG,Xiaoqiang LIU,Yu LIU,Qian XING.
Changes of follicular helper T lymphocytes in peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus during pregnancy and its significance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 166-172.
|
| [14] |
Liantao HU,Wenjun DENG,Shizhen LU,Luo SUN,Xuebing LI,Chuhao LI,Xinran WANG,chunbing ZHANG,Yue LI,Weiqun WANG.
Bioinformatics analysis on CC chemokine ligand 20 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its effect on prognostic assessment of liver hepatocellular carcinoma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1010-1017.
|
| [15] |
Shan GAO,Yutong WANG,Minqiu LU,Lei SHI,Bin CHU,Yuehua DING,Mengzhen WANG,Li BAO.
Analysis on causes for early death and its risk factors of patients with multiple myeloma in era of novel drugs
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 783-789.
|
 ),Yanhua WU(
),Yanhua WU( )
)