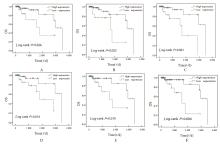
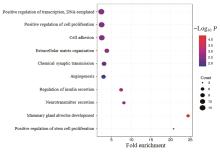
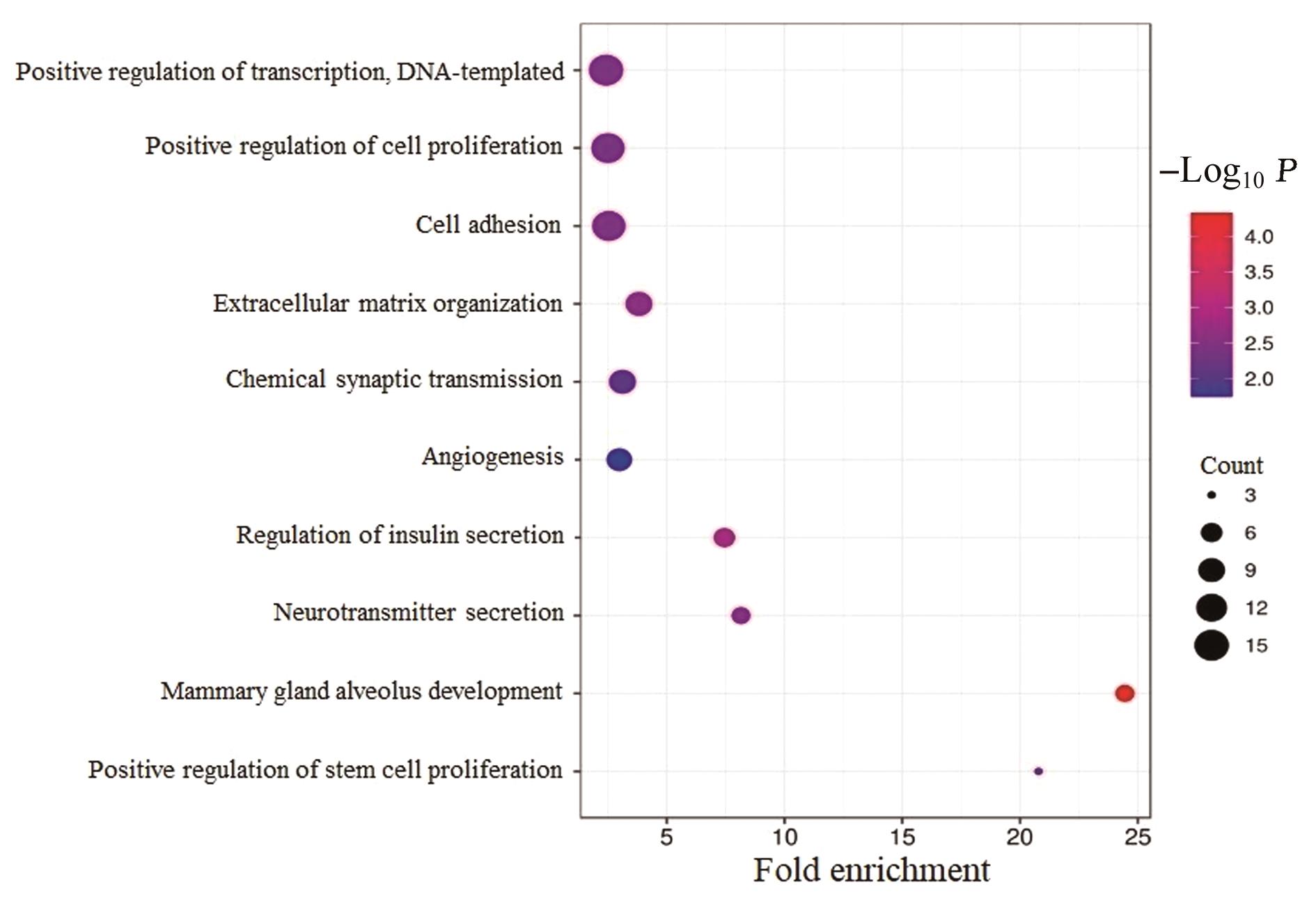
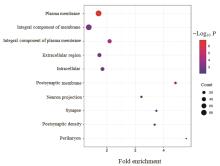
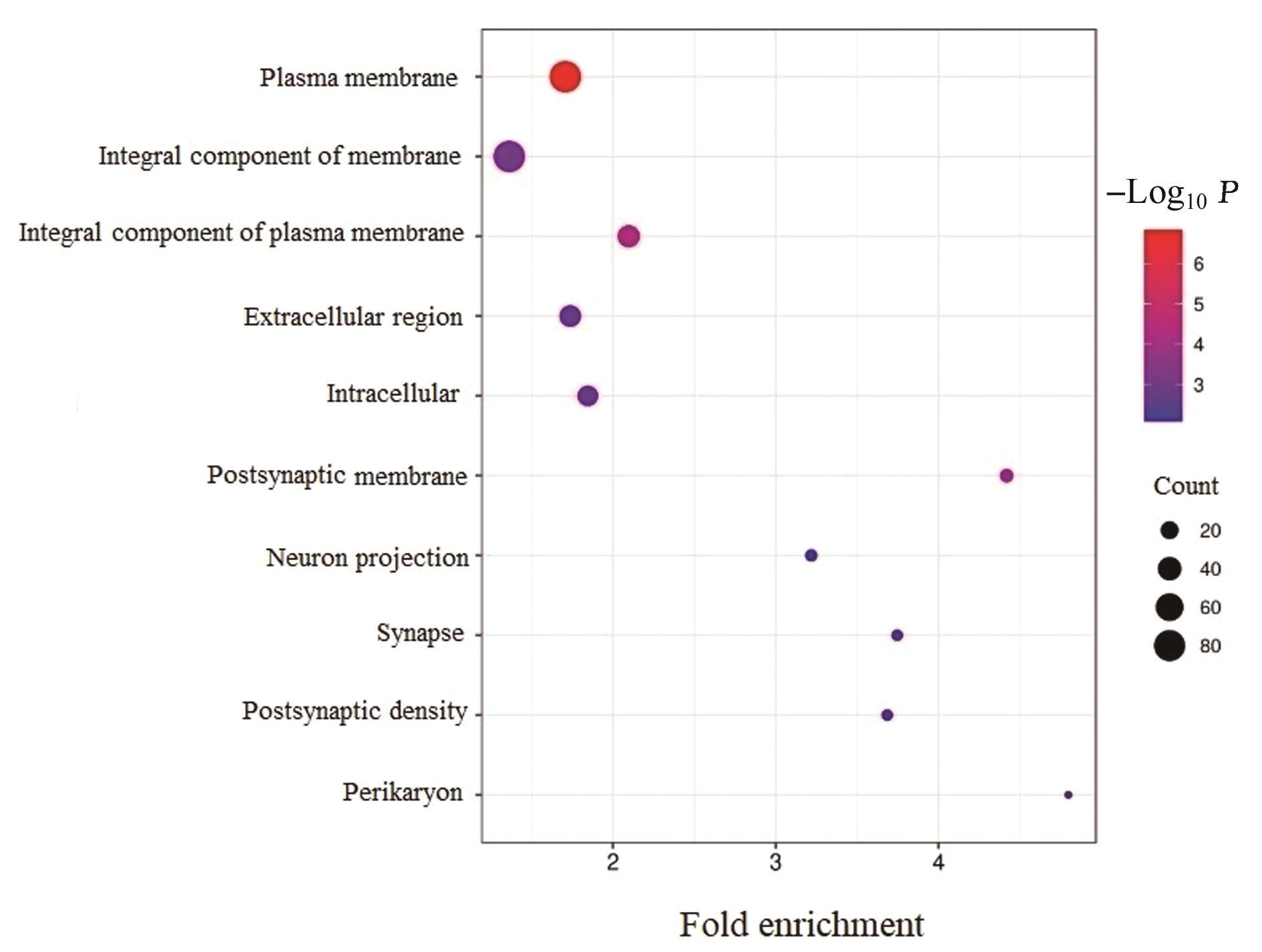
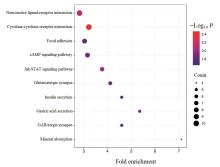
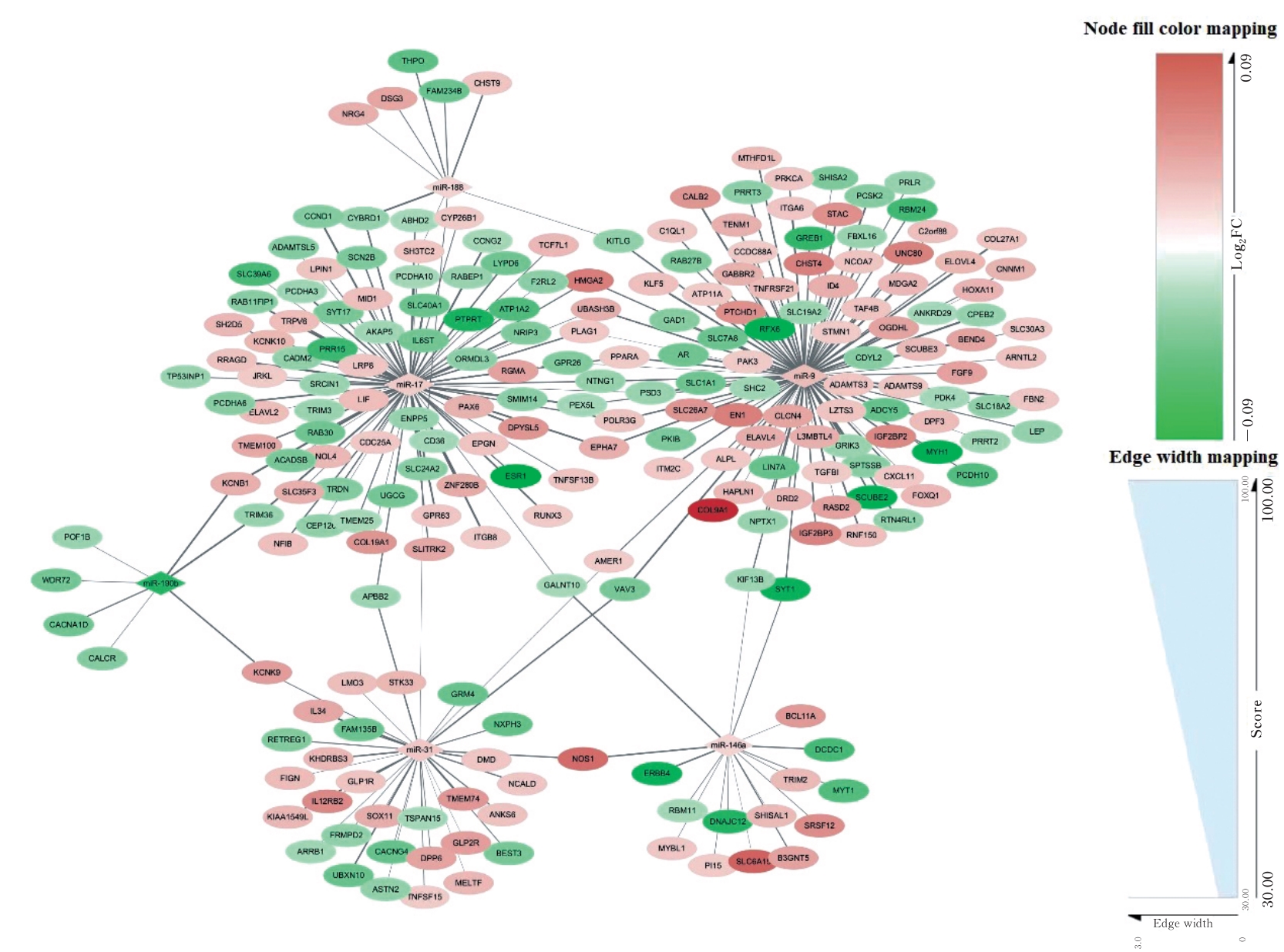
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 392-399.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240212
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Screening of miRNAs related to prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer and its gene network based on TCGA Database
Yueying SONG1,Chao GAO2,Wenjun CHEN2,Aiyu SHAO2,Yichun QIAO2( ),Zhuolin LI2(
),Zhuolin LI2( )
)
- 1.Center for Disease Control and Prevention Institure of School Health and Prevention of Common Student Diseases,Changchun City,Jilin Province,Changchun 130033,China
2.Department of Epidemiology and Health Statistics,School of Public Health,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Received:2022-10-31Online:2024-03-28Published:2024-04-28 -
Contact:Yichun QIAO,Zhuolin LI E-mail:qiaoyichun@jlu.edu.cn;lizhuolin425@jlu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R737.9
Cite this article
Yueying SONG,Chao GAO,Wenjun CHEN,Aiyu SHAO,Yichun QIAO,Zhuolin LI. Screening of miRNAs related to prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer and its gene network based on TCGA Database[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 392-399.
share this article
Tab.1
Differentially expressed miRNAs in patients with TNBC and non-TNBC"
| Gene ID | Log2FC | P | Gene expression status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hsa-miR-34c | 1.02 | 3.55E-08 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-30a | 1.04 | 8.15E-10 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-887 | 1.06 | 4.66E-09 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-182 | 1.06 | 4.86E-15 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-196a-2 | 1.06 | 1.13E-06 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-342 | 1.48 | 7.62E-27 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-153-2 | 1.59 | 7.98E-13 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-10a | 1.79 | 2.97E-21 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-149 | 1.88 | 1.14E-23 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-375 | 2.13 | 9.27E-17 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-653 | 2.34 | 9.83E-20 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-184 | 3.43 | 1.19E-17 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-190b | 3.46 | 6.87E-47 | Low expression |
| Hsa-miR-877 | 1.00 | 4.99E-10 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-130b | 1.01 | 9.70E-25 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-511 | 1.03 | 2.52E-12 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-188 | 1.03 | 1.33E-13 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-146a | 1.05 | 1.79E-15 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-942 | 1.07 | 2.55E-19 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-937 | 1.17 | 3.56E-08 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-19a | 1.24 | 6.77E-20 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-17 | 1.26 | 9.58E-30 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-31 | 1.31 | 5.37E-11 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-505 | 1.31 | 3.12E-32 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-455 | 1.51 | 6.81E-31 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-9-3 | 1.56 | 4.18E-11 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-9-1 | 1.57 | 3.58E-11 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-9-2 | 1.57 | 3.58E-11 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-584 | 1.62 | 7.46E-29 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-483 | 1.65 | 1.16E-13 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-224 | 1.84 | 1.76E-18 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-452 | 1.86 | 7.46E-29 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-18a | 1.92 | 7.34E-48 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-1269a | 2.23 | 3.35E-06 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-135b | 2.88 | 5.38E-34 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-577 | 3.37 | 9.58E-30 | High expression |
| Hsa-miR-934 | 4.78 | 8.82E-55 | High expression |
| 1 | KWAN M L, BERNARD P S, KROENKE C H, et al. Breastfeeding, PAM50 tumor subtype, and breast cancer prognosis and survival[J].J Natl Cancer Inst, 2015, 107(7): djv087. |
| 2 | YUAN Z Y, WANG S S, GAO Y, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer: a report of 305 cases[J].Ai Zheng,2008,27(6): 561-565. |
| 3 | EBERLEIN T J. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina breast cancer study[J]. Yearb Surg, 2007, 2007: 304-305. |
| 4 | NAKAJIMA H, FUJIWARA I, MIZUTA N, et al. Prognosis of Japanese breast cancer based on hormone receptor and HER2 expression determined by immunohistochemical staining[J]. World J Surg, 2008, 32(11): 2477-2482. |
| 5 | BABYSHKINA N, MALINOVSKAYA E, PATALYAK S, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for different molecular breast cancer subtypes: a retrospective study in Russian population[J]. Med Oncol, 2014, 31(9): 165. |
| 6 | GROUP I B C S, COLLEONI M, GELBER S, et al. Tamoxifen after adjuvant chemotherapy for premenopausal women with lymph node-positive breast cancer: international Breast Cancer Study Group Trial 13-93[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2006, 24(9): 1332-1341. |
| 7 | Straver M E, Rutgers E J T, Rodenhuis S,et al.The relevance of breast cancer subtypes in the outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J]. Annal surgical Oncol, 2010, 17(9):2411-2418. |
| 8 | RAKHAE A, EL-SAYEDM E, GREENA R, et al. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cancer, 2007, 109(1): 25-32. |
| 9 | XIONG B, LEI X F, ZHANG L, et al. miR-103 regulates triple negative breast cancer cells migration and invasion through targeting olfactomedin 4[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 89: 1401-1408. |
| 10 | LIANG Z X, BIAN X H, SHIM H. Downregulation of microRNA-206 promotes invasion and angiogenesis of triple negative breast cancer[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016, 477(3): 461-466. |
| 11 | LEE R C, FEINBAUM R L, AMBROS V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene Lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to Lin-14[J]. Cell, 1993, 75(5): 843-854. |
| 12 | SANTOVITO D, MEZZETTI A, CIPOLLONE F. microRNAs and atherosclerosis: new actors for an old movie[J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2012, 22(11): 937-943. |
| 13 | RUPAIMOOLE R, CALIN G A, LOPEZ-BERESTEIN G, et al. miRNA deregulation in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cancer Discov, 2016, 6(3): 235-246. |
| 14 | CHUA J H, ARMUGAM A, JEYASEELAN K. microRNAs: biogenesis, function and applications[J]. Curr Opin Mol Ther, 2009, 11(2): 189-199. |
| 15 | LING H, FABBRI M, CALIN G A. microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2013, 12(11): 847-865. |
| 16 | VOLINIA S, CALIN G A, LIU C G,et al.A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2006, 103(7): 2257-2261. |
| 17 | JANG M H, KIM H J, GWAK J M, et al. Prognostic value of microRNA-9 and microRNA-155 expression in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Hum Pathol, 2017, 68: 69-78. |
| 18 | FAN C N, LIU N, ZHENG D, et al. microRNA-206 inhibits metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by targeting transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 6755-6764. |
| 19 | BARONI S, ROMERO-CORDOBA S, PLANTAMURA I, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of miR-9 induces cancer-associated fibroblast-like properties in human breast fibroblasts[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2016, 7(7): e2312. |
| 20 | D'IPPOLITO E, PLANTAMURA I, BONGIOVANNI L,et al. miR-9 and miR-200 regulate PDGFRβ-mediated endothelial differentiation of tumor cells in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2016,76(18): 5562-5572. |
| 21 | JANG M H, KIM H J, GWAK J M, et al. Prognostic value of microRNA-9 and microRNA-155 expression in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Hum Pathol, 2017, 68: 69-78. |
| 22 | D'IPPOLITO E, PLANTAMURA I, BONGIOVANNI L,et al. miR-9 and miR-200 regulate PDGFRβ-mediated endothelial differentiation of tumor cells in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2016, 76(18): 5562-5572. |
| 23 | LI J, LAI Y H, MA J Y, et al. miR-17-5p suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by targeting ETV1 in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2017, 17(1): 745. |
| 24 | LUO L J, YANG F, DING J J, et al. miR-31 inhibits migration and invasion by targeting SATB2 in triple negative breast cancer[J]. Gene, 2016, 594(1): 47-58. |
| 25 | SI C S, YU Q, YAO Y F. Effect of miR-146a-5p on proliferation and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer via regulation of SOX5[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 15(5): 4515-4521. |
| 26 | ZAVALA V, PÉREZ-MORENO E, TAPIA T, et al. miR-146a and miR-638 in BRCA1-deficient triple negative breast cancer tumors, as potential biomarkers for improved overall survival[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2016, 16(1): 99-107. |
| 27 | NAOREM L D, MUTHAIYAN M, VENKATESAN A. Identification of dysregulated miRNAs in triple negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis approach[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(7): 11768-11779. |
| 28 | HAMILTON N, AUSTIN D, MÁRQUEZ-GARBÁN D, et al. Receptors for insulin-like growth factor-2 and androgens as therapeutic targets in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(11): 2305. |
| 29 | HAMILTON N, AUSTIN D, MÁRQUEZ-GARBÁN D,et al. Receptors for insulin-like growth factor-2 and androgens as therapeutic targets in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(11): 2305. |
| 30 | WANG Z S, LI Y F, XIAO Y J, et al. Integrin α9 depletion promotes β-catenin degradation to suppress triple-negative breast cancer tumor growth and metastasis[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 145(10): 2767-2780. |
| 31 | RIGIRACCIOLO D C, NOHATA N, LAPPANO R, et al. IGF-1/IGF-1R/FAK/YAP transduction signaling prompts growth effects in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(4): 1010. |
| 32 | SHAHEEN S, FAWAZ F, SSHA H,et al. Differential expression and pathway analysis in drug-resistant triple-negative breast cancer cell lines using RNASeq analysis[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2018,19(6):1810. |
| 33 | WANG S, XIA D, WANG X,et al. C/EBPβ regulates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. FEBS Open Bio, 2021, 11: 1250-1258. |
| [1] | Haifeng WEI,Zhiqiang NI,Yanhong WEI,Qilai WANG,Shouqing LI,Yinfu MA,Yan TAN,Yanqiu FANG. Effects of miR-126 over-expression and ADAM9 gene silencing on biological behavior of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 310-319. |
| [2] | Dandan WANG,Ning ZHOU,Dongqin LIU,Jie ZHAO,Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Yan WU. Effect of miR-491-5p over-expression on proliferation and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1134-1139. |
| [3] | Yaqi XU,Yanyu WANG,Wenjing ZHANG,Mei HAN,Huaxia MU,Xi YANG,Weixiao BU,Zikun TAO,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of key genes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with prognosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1243-1252. |
| [4] | Haikang CUI,Xudong ZHANG,Xiaoning LI,Xi YANG,Lan YANG,Wenjie ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis on predition effect of subtypes of cell pyroptosis and APOD on prognosis of gastric cancer patients [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1268-1279. |
| [5] | Jingjing LI, REZIWANGULI·Aisikaier,Wanyi XING,Yinggang ZOU. Primary dedifferentiated liposarcoma of unilateral ovary: A case report and literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 1040-1045. |
| [6] | Xuying WANG,Mingzhen JING,Jin YU,Rong FU,Ru YANG. Effects of miR-181a-5p and BACH2 expressions on apoptosis and invasion of leukemic CCRF-CEM cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 840-849. |
| [7] | AIKEREMUJIANG·Aerken, RIXIATI·Paerhati,Zheng ZHANG,Sheng ZHAI. Effect of miR-7 on osteogenic differentiation of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head cell model and mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 947-957. |
| [8] | Hongying LI,Chenyan WANG,Shichao GUO,Youwei ZHAO,Yanbo DONG,Jiancheng HUANG. Effect of down-regulation of miR-320a expression on proliferation and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 958-967. |
| [9] | Shan LIU,Zhaodong XING,Ping HUANG. Effect of expression of miR-17-5p in exosomes derived from colorectal cancer cells on chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 975-984. |
| [10] | Lingyao XU,Shutang WEI,Yong DONG,Zhenglu SUN,Junbo ZHAO,Dazheng HAN. Regulatory effect of lncRNA MALAT1 on activation of hepatic stellate cell and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 697-705. |
| [11] | Yunpeng LIU,Zihao LIU,Boming KANG,Zhiguang YANG. Regulatory effect of lncRNA SNHG17 on biological behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting AEG1 through miR-384 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 298-307. |
| [12] | Gaofeng ZHOU,Jing XIAO,Jia ZHOU,Junxiu LIU,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,He LIN,Xiaowei HUANG. Protective effect of Velvet antler polypeptide pretreatment on myocardial H9c2 cell injury induced by TBHP through regulating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway with miR-133a [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 369-376. |
| [13] | Renyi YANG,Shuwang PENG,Yongheng WANG,Yuxuan DONG,Shanshan DUAN. Construction of ferroptosis prognostic risk model of thyroid cancer and bioinformatics analysis on its potential mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 402-413. |
| [14] | Xiaoyan WANG,Yihong HU,Yucheng HAN,Xianqiong ZOU. Bioinformatics analysis on mechanism of COMMD7 in occurrence and development of brain low-grade glioma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 414-424. |
| [15] | Haiwei QUAN,Yali ZHANG,Han WANG,Yijiu AI,Yutong ZOU,Wei XIA. Detection of expression level of miR-4286 in exosome in peripheral blood of patients with acute myeloid leukemia and its diagnostic value [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 460-466. |
|
||