Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1571-1583.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250613
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
Synthesis of novel visible-light-activated vanadium and silicon co-doped TiO2 coating and its antibacterial property evaluation
Duo CHEN1,2,Peipei DUAN3,Xueping KANG4,Shiman CHEN1,2,Jiayue HE1,2,Yuxin LIU1,2,Luoxin LI1,2,Yufeng SHEN5( ),Zheng ZHOU1(
),Zheng ZHOU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Prosthodontics,First Affiliated Hospital,Corps Stomatology Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
2.School of Medical Sciences,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
3.Department of Prosthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430079,China
4.Department of Orthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Xi’an Jiaotong University,Xi’an 710004,China
5.Department of Orthodontics,First Affiliated Hospital,Corps Stomatology Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
-
Received:2025-01-12Accepted:2025-02-17Online:2025-11-28Published:2025-12-15 -
Contact:Yufeng SHEN,Zheng ZHOU E-mail:shenyf1016@163.com;shzuzzheng0526@163.com
CLC Number:
- R783.1
Cite this article
Duo CHEN,Peipei DUAN,Xueping KANG,Shiman CHEN,Jiayue HE,Yuxin LIU,Luoxin LI,Yufeng SHEN,Zheng ZHOU. Synthesis of novel visible-light-activated vanadium and silicon co-doped TiO2 coating and its antibacterial property evaluation[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(6): 1571-1583.
share this article
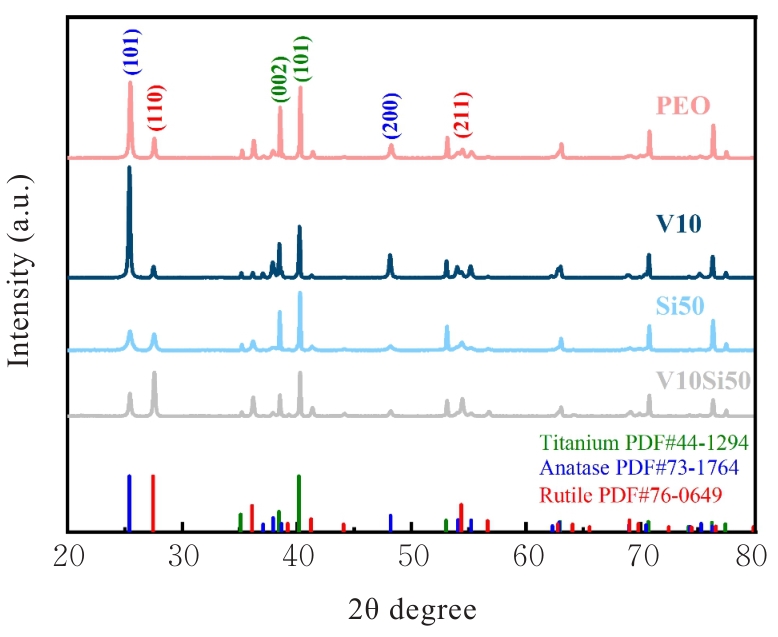
Tab.1
Compositions of electrolyte of coating materials during micro-arc oxidation process"
| Group | Solution electrolyte concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na3PO4 | NaOH | Na2SiO3·9H2O | NaVO3 | |
| PT | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.000 |
| PEO | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.000 |
| V10 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.010 |
| Si50 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.000 |
| V5Si50 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.005 |
| V10Si50 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.010 |
| V15Si50 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.015 |
Tab.2
Cell proliferation activities and cell survival rates in various groups"
| Group | Cell proliferation activity | Cell survival rate (η/%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/d) 1 | 2 | 4 | (t/d) 1 | 2 | 4 | |
| Control | 0.251±0.008 | 0.328±0.005 | 1.122±0.009 | 100.00±0.00 | 100.00±0.00 | 100.00±0.00 |
| V5Si50 | 0.258±0.008 | 0.321±0.005* | 1.099±0.005* | 107.40±9.29 | 94.80±1.24* | 97.54±1.44* |
| V10Si50 | 0.261±0.004* | 0.359±0.009* | 1.232±0.002* | 110.00±6.42* | 122.36±7.62* | 111.66±1.25* |
| V15Si50 | 0.252±0.001 | 0.286±0.004* | 0.702±0.002* | 100.88±10.36 | 69.57±1.30* | 55.45±0.52* |
Tab.5
Numbers of S.aureus colonies in various groups under visible light irradiation combined with coating materials"
| Group | Number of S. aureus colonies | |
|---|---|---|
| Dark 2 h | Light 2 h | |
| PT | 603.67±17.47 | 603.67±13.20 |
| PEO | 598.67±26.58 | 606.67±9.71 |
| V10 | 301.00±22.11*△# | 20.00±7.00*△# |
| Si50 | 602.67±12.86 | 593.33±21.08 |
| V10Si50 | 413.00±6.56*△# | 40.67±2.52*△# |
| [1] | TING M, SUZUKI J B. Peri-implantitis[J]. Dent J, 2024, 12(8): 251. |
| [2] | MEYLE J, FISCHER-WASELS L. Non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis[J]. Br Dent J, 2024, 237(10): 780-785. |
| [3] | YIN W W, YANG Y M, BAO R, et al. Necessity of removing implant-supported prostheses when conducting supportive peri-implant therapy: A clinical study[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2024: S0022-S3913(24)00653-X. |
| [4] | IONESCU C, KAMAL F Z, CIOBICA A, et al. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of oral cancer[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12(6): 1150. |
| [5] | CHEN T, YANG D, LEI S X, et al. Photodynamic therapy-a promising treatment of oral mucosal infections[J]. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther, 2022, 39: 103010. |
| [6] | AZZAWI Z G M, HAMAD T I, KADHIM S A, et al. Osseointegration evaluation of laser-deposited titanium dioxide nanoparticles on commercially pure titanium dental implants[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2018, 29(7): 96. |
| [7] | ZOU X S, VADELL R B, LIU Y W, et al. Photophysical study of electron and hole trapping in TiO2 and TiO2/Au nanoparticles through a selective electron injection[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2022, 126(50): 21467-21475. |
| [8] | ŠULIGOJ A, POVIRK N, MAVER K, et al. Transparent vanadium doped titania-silica films: Structural characterization and self-cleaning properties[J]. J Environ Chem Eng, 2024, 12(5): 113904. |
| [9] | DEEPA M J, ARUNIMA S R, ELIAS L, et al. Development of antibacterial V/TiO2-based galvanic coatings for combating biocorrosion[J]. ACS Appl Bio Mater, 2021, 4(4): 3332-3349. |
| [10] | NGWA H A, AY M, JIN H J, et al. Neurotoxicity of vanadium[A].Neurotoxicity of Metals[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 287-301. |
| [11] | MIGUEZ-PACHECO V, HENCH L L, BOCCACCINI A R. Bioactive glasses beyond bone and teeth: Emerging applications in contact with soft tissues[J]. Acta Biomater, 2015, 13: 1-15. |
| [12] | ZHANG X E, ZHANG X, ZHOU W C, et al. Modified multilayered porous titanium scaffolds with silicon-doped coating surface-loaded BMP-2 prepared by microarc oxidation for bone defect repair[J]. Surf Coat Technol, 2025, 495: 131570. |
| [13] | RASHAD M M, MOSTAFA A G, RAYAN D A. Structural and optical properties of nanocrystalline mayenite Ca12Al14O33 powders synthesized using a novel route[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2016, 27(3): 2614-2623. |
| [14] | LI L Y, ZHAO H, NI N, et al. Study on the origin of linear deviation with the Beer-Lambert law in absorption spectroscopy by measuring sulfur dioxide[J]. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 2022, 275: 121192. |
| [15] | LIU W B, ZHANG K, SUN Y, et al. Multidimensional treatment of periprosthetic joint infection using fusion peptide-grafted chitosan coated porous tantalum scaffold[J]. Bioact Mater, 2025, 44: 15-33. |
| [16] | MORALES-VALENZUELA A A, SCOUGALL-VILCHIS R J, LARA-CARRILLO E, et al. Enhancement of fluoride release in glass ionomer cements modified with titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. Medicine, 2022, 101(44): e31434. |
| [17] | ZHANG Y J, ZHANG Y L, KONG T T, et al. Effects of titanium nano-foveolae surfaces on human gingival fibroblasts[J]. J Nanosci Nanotechnol, 2020, 20(2): 673-679. |
| [18] | WANG S Y, ZHAO X, HSU Y, et al. Surface modification of titanium implants with Mg-containing coatings to promote osseointegration[J]. Acta Biomater, 2023, 169: 19-44. |
| [19] | PAPADIAMANTIS A G, JÄNES J, VOYIATZIS E, et al. Predicting cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles using isalos analytics platform[J]. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(10): 2017. |
| [20] | HANNIBAL V D, GREB L. Tetra-amido macrocyclic ligand (TAML) at silicon(Ⅳ): a structurally constrained, water-soluble silicon lewis superacid[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2024, 146(37): 25727-25737. |
| [21] | RASUL M G, AHMED S, SATTAR M A, et al. Hydrodynamic performance assessment of photocatalytic reactor with baffles and roughness in the flow path:a modelling approach with experimental validation[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(9): e19623. |
| [22] | XUE Y, WANG Z, KANG J T, et al. The effect of doping donor ions in the dielectric properties of (In0.5 B0.5)0.1Ti0.9O2 (BV, Nb, Ta) ceramics[J]. Ceram Int, 2024, 50(23): 51848-51857. |
| [23] | HU H Y, LIN Y, HU Y H. Phase role of white TiO2 precursor in its reduction to black TiO2 [J]. Phys Lett A, 2019, 383(24): 2978-2982. |
| [24] | ZAHID SHAFIQ M, SHAHID W, SHAHID S, et al. Enhancing photocatalytic efficiency of type Ⅱ V2O5/TiO2 heterojunctions for malachite green dye using solar simulator irradiation[J]. J Saudi Chem Soc, 2024, 28(3): 101869. |
| [25] | MA E H, SUN G L, DUAN F L, et al. Visible-light-responsive Z-scheme heterojunction MoS2 NTs/CuInS2 QDs photoanode for enhanced photoelectrocatalytic degradation of tetracycline[J]. Appl Mater Today, 2022, 28: 101504. |
| [26] | CHEN Q F, WANG K Y, GAO G M, et al. Singlet oxygen generation boosted by Ag–Pt nanoalloy combined with disordered surface layer over TiO2 nanosheet for improving the photocatalytic activity[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2021, 538: 147944. |
| [27] | ZOU X R, WEI Y Y, JIANG S, et al. ROS stress and cell membrane disruption are the main antifungal mechanisms of 2-phenylethanol against botrytis cinerea[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(45): 14468-14479. |
| [28] | KOTHANDAN S, SHEELA A. DNA Interaction and Cytotoxic studies on Mono/Di-Oxo and Peroxo- Vanadium (V) complexes - A Review[J]. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2021, 21(14): 1909-1924. |
| [29] | DOBSON N L, KLEEBERGER S R, BURKHOLDER A B, et al. Vanadium pentoxide exposure causes strain-dependent changes in mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy, copy number, and lesions, but not nuclear DNA lesions[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19): 14507. |
| [30] | LIU X C, HOU Y B, YANG M X, et al. N-acetyl-l-cysteine-derived carbonized polymer dots with ROS scavenging via Keap1-Nrf2 pathway regulate alveolar bone homeostasis in periodontitis[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2023, 12(26): e2300890. |
| [1] | Ziyang XU,Ruolin WANG,Yifan GUO,Yuji LIU,Min LIU. Research progress in mechanism of antimicrobial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles and its influencing factors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 1129-1136. |
| [2] | Lieqian SUN,Mengyu GU,Jie YANG,Kaiyi WANG,Gaoshuai GUO,Hongbo ZHANG,Siyi ZHANG,Tanglong WANG,Zhiwei YANG,Yanni HE,Chao YANG. Effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on mitochondrial autophagy in rats with vascular dementia through ROS/Nrf2 signaling and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 610-620. |
| [3] | Jing DENG,Xuan WANG,Changyu SHI,Siqi YANG,Qinling ZOU,Ming JIN. Effect of securinine on proliferation and apoptosis of human colon cancer SW620 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 307-316. |
| [4] | Qiao WANG,Ziling ZENG,Xing WANG,Ning MA,Zhibin WANG,Guofeng XU,Xiefang YUAN,Xiaoyun WANG,Yuejiao LI,Hongmei TANG,Yun ZHANG. Effect of Aspergillus fumigatus on DNA damage and IL-33 expression in human bronchial epithelial cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1205-1216. |
| [5] | Hongmei TANG,Yuejiao LI,Xing WANG,Zhibin WANG,Xiefang YUAN,Xiaoyun WANG. Effect of Jiegeng Yuanshen Tang on airway inflammation and mucus secretion in allergic asthmatic mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 10-17. |
| [6] | Naixu SHI,Miao HAO,Tianfu ZHANG,Kelin ZHAO,Ziyan HUANG,Chunyan LI,Xiaofeng WANG. Inhibitory effect of baicalein on proliferation of human tongue squamous cell carcinoma CAL27 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 985-993. |
| [7] | Bo HUANG,Jie DING,Hongrong GUO,Hongjuan WANG,Jianqun XU,Quan ZHENG. Effects of HIF-1α/ROS on apoptosis and invasion of lung cancer A549 cells under hypoxia and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 682-690. |
| [8] | Xuechun DU,Baosheng LI,Shuwei QIAO,Yanzhen OU,Zhen LI,Weiyan MENG. Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis-LPS on expression levels of ferroptosis-related factors in macrophages [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1148-1155. |
| [9] | Haixin QU,Erwei YUAN,Weiping GUO,Yajing ZHANG,Wenxia MA,Dan WU. Improvement effect of luteolin on acute respiratory distress syndrome by inhibiting ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling pathway activation in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 676-683. |
| [10] | Yang ZHOU,Xuguang MI,Wenxing PU,Wentao WANG,Meng JING,Fankai MENG. Ameliorative effect of melatonin on oxidative stress of human neuroblastoma SHSY5Y cells induced by hydrogen peroxide and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 340-347. |
| [11] | Yinong LIU,Qiang ZHANG,Li XU. Improvement effect of atorvastatin on vascular endothelial dysfunction induced by Ox-LDL/β2GPⅠ/anti-β2GPⅠ complex and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 317-323. |
| [12] | Dan MAO,Zhishuang LI,Jiaxin CHENG,Ping HOU. Effect of Shenxianshengmai Oral Liquid on ROS expression in mice with sick sinus syndrome and its regulation on HCN4 ion channel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1353-1361. |
| [13] | Ying YANG, Wei ZHAO, Dan LYU. Effect of C19ORF12 on proliferation and chemo-sensitivity of gastric cancer MKN45 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 687-693. |
| [14] | ZHANG Cong, LIU Di, ZHANG Hanxue, ZHANG Hao, KONG Fanli, FENG Xianmin. Protective effect of ginsenoside on hydrogen peroxide-induced HepG2 cell injury [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 985-991. |
| [15] | YU Lei, WANG Ce, HAN Bing, LI Xin, HAN Yuchen, SUN Yuying, GUO Xiangshu, LIU Weiwu, WANG Zhicheng. Enhancement of mitochondria-targeted KillerRed in autophagy caused by radiation in HeLa cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 693-698. |
|
||