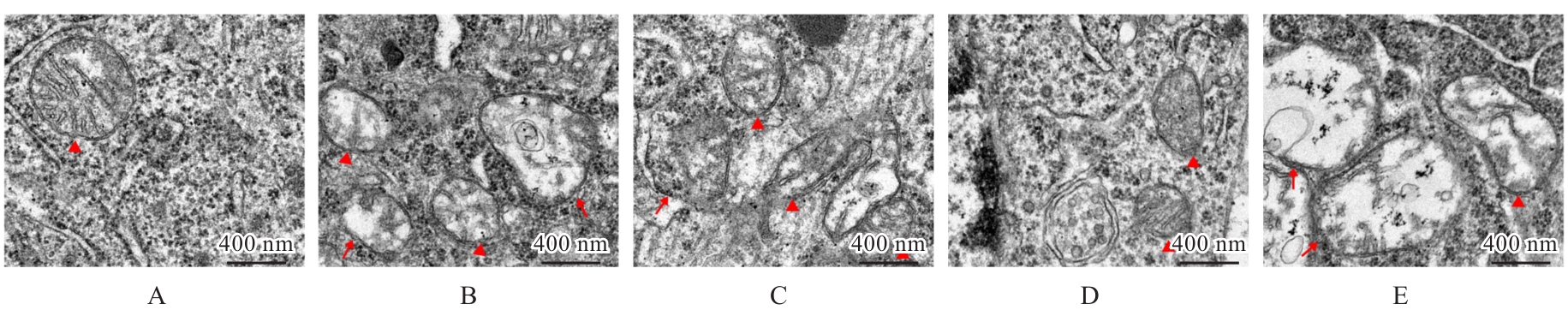
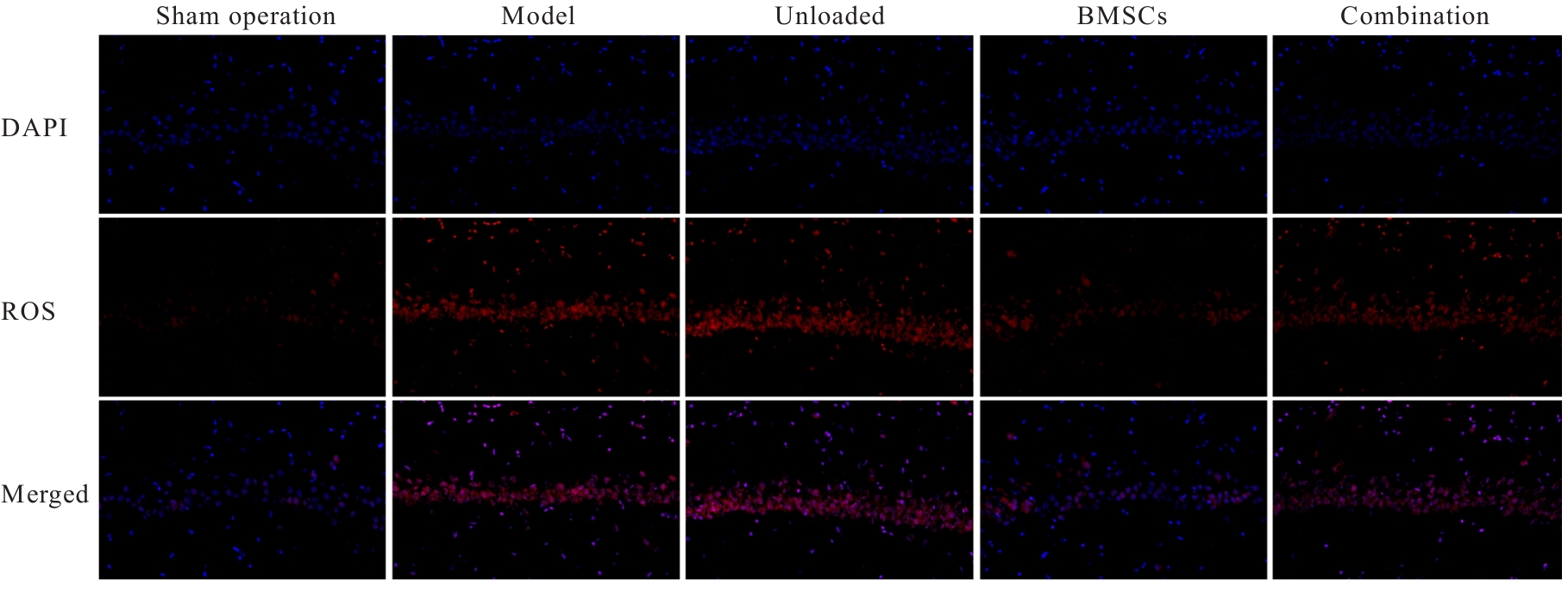
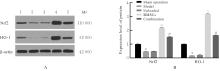
| [1] |
陈 昭, 吴 林, 蓝雪琳, 等. 血管性痴呆发病机制中西医研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2022, 24(1): 40-44.
|
| [2] |
RUNDEK T, TOLEA M, ARIKO T, et al. Vascular cognitive impairment (VCI)[J]. Neurotherapeutics, 2022, 19(1): 68-88.
|
| [3] |
WOLTERS F J, ARFAN IKRAM M. Epidemiology of vascular dementia[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2019, 39(8): 1542-1549.
|
| [4] |
INOUE Y, SHUE F, BU G J, et al. Pathophysiology and probable etiology of cerebral small vessel disease in vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2023, 18(1): 46.
|
| [5] |
PATHAN N, KHAROD M K, NAWAB S, et al. Genetic determinants of vascular dementia[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2024, 40(8): 1412-1423.
|
| [6] |
SANTOS M A O, BEZERRA L S, CORREIA C D C, et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in vascular dementia: epidemiologic and clinical aspects[J]. Dement Neuropsychol, 2018, 12(1): 40-44.
|
| [7] |
WANG D P, LI B W, WANG S C, et al. Engineered inhaled nanocatalytic therapy for ischemic cerebrovascular disease by inducing autophagy of abnormal mitochondria[J]. NPJ Regen Med, 2023, 8(1): 44.
|
| [8] |
杨 超, 杨 佳, 刘 玲. 涤痰汤对血管性痴呆大鼠海马NOX2/ROS通路、GSH、HO-1表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2019, 39(12): 3052-3055.
|
| [9] |
BONORA M, GIORGI C, PINTON P. Molecular mechanisms and consequences of mitochondrial permeability transition[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(4): 266-285.
|
| [10] |
HE Y Y, HE T T, LI H P, et al. Deciphering mitochondrial dysfunction: Pathophysiological mechanisms in vascular cognitive impairment[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 174: 116428.
|
| [11] |
HE S Z, WANG Q Q, CHEN L K, et al. miR-100a-5p-enriched exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance the anti-oxidant effect in a Parkinson’s disease model via regulation of Nox4/ROS/Nrf2 signaling[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 747.
|
| [12] |
TURANO E, SCAMBI I, VIRLA F, et al. Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells: towards novel therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2917.
|
| [13] |
PALANISAMY C P, PEI J J, ALUGOJU P, et al. New strategies of neurodegenerative disease treatment with extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)[J]. Theranostics, 2023, 13(12): 4138-4165.
|
| [14] |
TELI P, KALE V, VAIDYA A. Mesenchymal stromal cells-derived secretome protects Neuro-2a cells from oxidative stress-induced loss of neurogenesis[J]. Exp Neurol, 2022, 354: 114107.
|
| [15] |
JIANG X H, LI H F, CHEN M L, et al. Treadmill exercise exerts a synergistic effect with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on neuronal apoptosis and synaptic-axonal remodeling[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2023, 18(6): 1293-1299.
|
| [16] |
RADWAN R R, MOHAMED H A. Mechanistic approach of the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells on brain damage in irradiated mice: emphasis on anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects[J]. Int J Radiat Biol, 2023, 99(9): 1463-1472.
|
| [17] |
ZHUO Y, LI W S, LU W, et al. TGF-β1 mediates hypoxia-preconditioned olfactory mucosa mesenchymal stem cells improved neural functional recovery in Parkinson’s disease models and patients[J]. Mil Med Res, 2024, 11(1): 48.
|
| [18] |
LINH T T D, HSIEH Y C, HUANG L K, et al. Clinical trials of new drugs for vascular cognitive impairment and vascular dementia[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(19): 11067.
|
| [19] |
TIAN Z M, JI X M, LIU J. Neuroinflammation in vascular cognitive impairment and dementia: current evidence, advances, and prospects[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(11): 6224.
|
| [20] |
JOMOVA K, RAPTOVA R, ALOMAR S Y, et al. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2023, 97(10): 2499-2574.
|
| [21] |
LYU Y J, MENG Z P, HU Y Y, et al. Mechanisms of mitophagy and oxidative stress in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2024, 17: 1394932.
|
| [22] |
HE F, RU X L, WEN T. NRF2, a transcription factor for stress response and beyond[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(13): 4777.
|
| [23] |
YANG S X, XIE Z P, PEI T T, et al. Salidroside attenuates neuronal ferroptosis by activating the Nrf2/HO1 signaling pathway in Aβ1-42-induced Alzheimer’s disease mice and glutamate-injured HT22 cells[J]. Chin Med, 2022, 17(1): 82.
|
| [24] |
黄 健, 曹诗杰, 安红伟. 自噬与血管性痴呆关系研究进展[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 24(2): 219-221.
|
| [25] |
WEI P H, JIA M, KONG X Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate perioperative neurocognitive disorder by inhibiting inflammatory responses and activating BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling pathway in aged mice[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14(1): 263.
|
| [26] |
KAISAR M A, VILLALBA H, PRASAD S, et al. Offsetting the impact of smoking and e-cigarette vaping on the cerebrovascular system and stroke injury: Is Metformin a viable countermeasure?[J]. Redox Biol, 2017, 13: 353-362.
|
| [27] |
GEORGE M, THARAKAN M, CULBERSON J, et al. Role of Nrf2 in aging, Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2022, 82: 101756.
|
 )
)