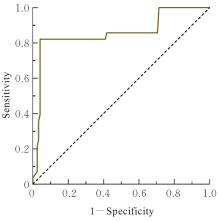
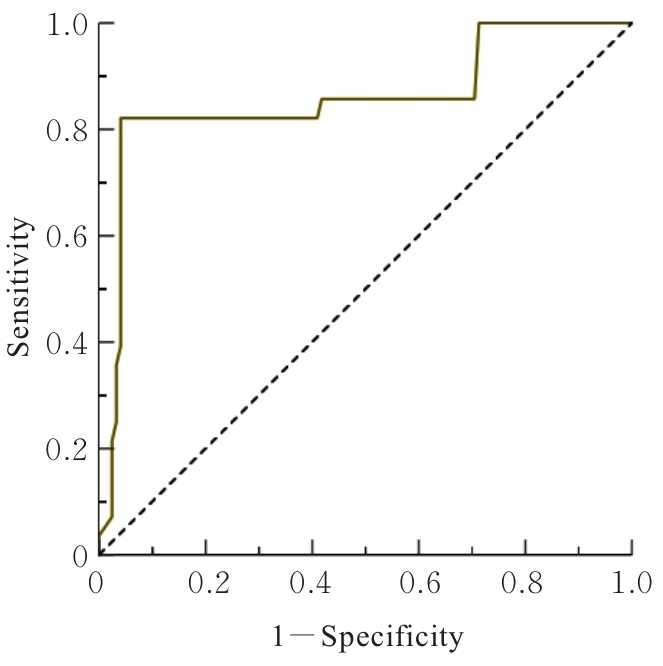
| [1] |
Di QIN,Lihong HUAGN,Qingshuang ZHENG,Jingjing SUN,Weimin XU.
Analysis on correlation between serum pro-inflammatory cytokines and muscle mass in elderly patients with sarcopenic obesity and diabetes
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(5): 1293-1302.
|
| [2] |
Xiaoyu WANG,Bing LI,Guohui LIU.
Research progress in application of inflammatory markers in diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1173-1181.
|
| [3] |
Tong SHEN,Yang WANG,Wei JIN,Zhihui LIN,Li YAN.
Risk factors analysis and risk model construction of cognitive frailty in elderly patients with chronic diseases
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1304-1309.
|
| [4] |
Cong FU,Yang YANG,Mingtu XU,Zeying QIN,Jingyang LI.
Analysis on related influencing factors of life quality of inpatients with coronary heart disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 478-486.
|
| [5] |
Yang YU,Yang YANG,Mingtu XU,Zeying QIN,Cong FU,Jingyang LI.
Mediating effect of perceived social support between self-esteem and anxiety in patients with coronary heart disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 216-221.
|
| [6] |
XU Xiaoyan, SONG Zikai, ZHANG Yang, QIN Ling.
Changes of serum NT-pro BNP and Lp(a) levels in patients with acute myocardial infarction after emergency PCI and their clinical significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 132-137.
|
| [7] |
XING Xunjing, QIN Ling, TANG Minglong, YANG Shuo, XU Guoliang.
Effectiveness and securities of ticagrelor and clopidogrel in antiplatelet therapy for coronary heart disease in old people: A Meta-analysis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 123-129.
|
| [8] |
ZHANG Tao, ZHANG Guoming, YAN Fei, LIU Zheng, HUO Qiang.
Values of evaluation of heart rate variability in major adverse cardiac events in patients with acute myocardial infarction after PCI
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(04): 780-785.
|
| [9] |
ZHU Tao, ZHANG Guoming, YAN Fei, LIU Zheng, HUO Qiang.
Comparison of diagnostic values between myocardial perfusion imaging and dual source CT coronary angiography in coronary artery stenosis in patients with diabetes complicated with coronary heart disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 425-430.
|
| [10] |
ZHU Hongling, GENG Wentao, XIE Jinfang, LI Xueyang, YIN Shuo, BI Chongcai.
Evaluation on clinical effect of CAD/CAM restorations in repairing posterior tooth defects in elderly people
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(01): 157-161.
|
| [11] |
ZHENG Dongchun, ZHANG Tianrong, LIU Hongbo, CHEN Huaiji, WANG Qi, XU Feng, ZHANG Yuezhu, ZHOU Liting, YE Lin.
Association between genetic variations in 9p21 region and coronary heart disease in Chinese Han population
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(01): 142-146.
|
| [12] |
WANG Xu, JI Mingxin, HAO Mingyue, JIA Lina, YANG Tongwei.
Influence of methylprednisolone in respiratory mechanics parameters in elderly patients with general anesthesia and its clinical significance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(02): 361-364.
|
| [13] |
LIU Yingli, YANG Libin, ZHANG Shushi, ZHANG Shuyan.
Therapeutic effect of ButylphthalideInjection inelderly patients with acute cerebral infarction and its influence incerebral hemodynamics andcerebral vascular reserve
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(02): 344-348.
|
| [14] |
ZHANG Yang, WANG Junfeng, CAOHongyan, QIN Ling, XU Guoliang.
Effectiveness and safety of Dengzhanhuasu and Dansheng Injection in treatment of patients with angina pectoris of coronary heart disease:A Meta-analysis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(02): 317-321.
|
| [15] |
JIANG Wenping, HOU Sen, LIN Qiuyu, GU Li, ZHAO Hongguang.
Value of adenosine triphosphate stressand rest nuclide myocardial perfusion imaging in diagnosis of female patients with coronary heart disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(02): 370-374.
|
 ),Xuan LI,Chaopu ZHANG,Shu DING,Jianwei ZHAO
),Xuan LI,Chaopu ZHANG,Shu DING,Jianwei ZHAO