Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1293-1302.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250516
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Analysis on correlation between serum pro-inflammatory cytokines and muscle mass in elderly patients with sarcopenic obesity and diabetes
Di QIN,Lihong HUAGN( ),Qingshuang ZHENG,Jingjing SUN,Weimin XU
),Qingshuang ZHENG,Jingjing SUN,Weimin XU
- Department of Geriatrics and General Medicine,China-Japan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
-
Received:2025-01-02Accepted:2025-03-04Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-11-05 -
Contact:Lihong HUAGN E-mail:lhhuang@jlu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R592
Cite this article
Di QIN,Lihong HUAGN,Qingshuang ZHENG,Jingjing SUN,Weimin XU. Analysis on correlation between serum pro-inflammatory cytokines and muscle mass in elderly patients with sarcopenic obesity and diabetes[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(5): 1293-1302.
share this article
Tab.1
Comparison of clinical data of subjects in four groups"
| Characteristic | BMI (kg·m-2) | ASM(m/kg) | ASMI (kg·m-2) | GS(m/kg) | FM(m/kg) | BFP(η/%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 25.14±2.56 | 28.97±4.15 | 7.89±1.15 | 33.71±7.86 | 23.16±2.44 | 29.45±5.58 |
| OD | 29.25±2.03* | 27.79±3.34 | 7.36±0.84 | 30.86±4.52 | 28.79±2.25* | 33.81±6.24* |
| SO | 29.06±3.29* | 27.95±4.08 | 7.73±1.12 | 31.59±6.84 | 28.14±3.67* | 37.84±7.02* |
| SOD | 29.14±3.37* | 22.17±3.40*△# | 5.27±0.81*△# | 20.45±4.13*△# | 27.31±3.84* | 37.08±6.85* |
| t | 65.477 | 52.547 | 107.669 | 70.368 | 53.774 | 24.734 |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Tab.2
Clinical data and laboratory indexes of subjects in normal group and sarcopenia group"
| Characteristic | Normal group (n=183) | Sarcopenia group (n=46) | t | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 72.58±12.47 | 73.05±12.64 | 0.275 | 0.784 |
| BMI (kg·m-2) | 25.14±2.27 | 25.63±2.31 | 1.568 | 0.118 |
| ASM (m/kg) | 28.36±4.11 | 22.09±2.81 | 13.692 | <0.001 |
| ASMI (kg·m-2) | 7.76±1.21 | 5.33±0.96 | 16.812 | <0.001 |
| GS (m/kg) | 32.42±6.16 | 20.18±4.73 | 16.908 | <0.001 |
| SBP (P/mmHg) | 140.56±19.88 | 141.95±20.24 | 0.508 | 0.612 |
| DBP (P/mmHg) | 71.27±11.36 | 70.48±11.13 | 0.517 | 0.606 |
| FPG [cB/(mmol·L-1)] | 6.08±1.49 | 6.15±1.44 | 0.352 | 0.725 |
| TC [cB/(mmol·L-1)] | 5.14±1.10 | 5.05±0.93 | 0.663 | 0.508 |
| TG [cB/(mmol·L-1)] | 1.33±1.59 | 1.40±0.59 | 0.475 | 0.636 |
| RBC (1012 L-1) | 4.54±1.57 | 4.37±1.42 | 0.845 | 0.399 |
| WBC (109 L-1) | 7.18±3.38 | 7.25±3.47 | 0.150 | 0.881 |
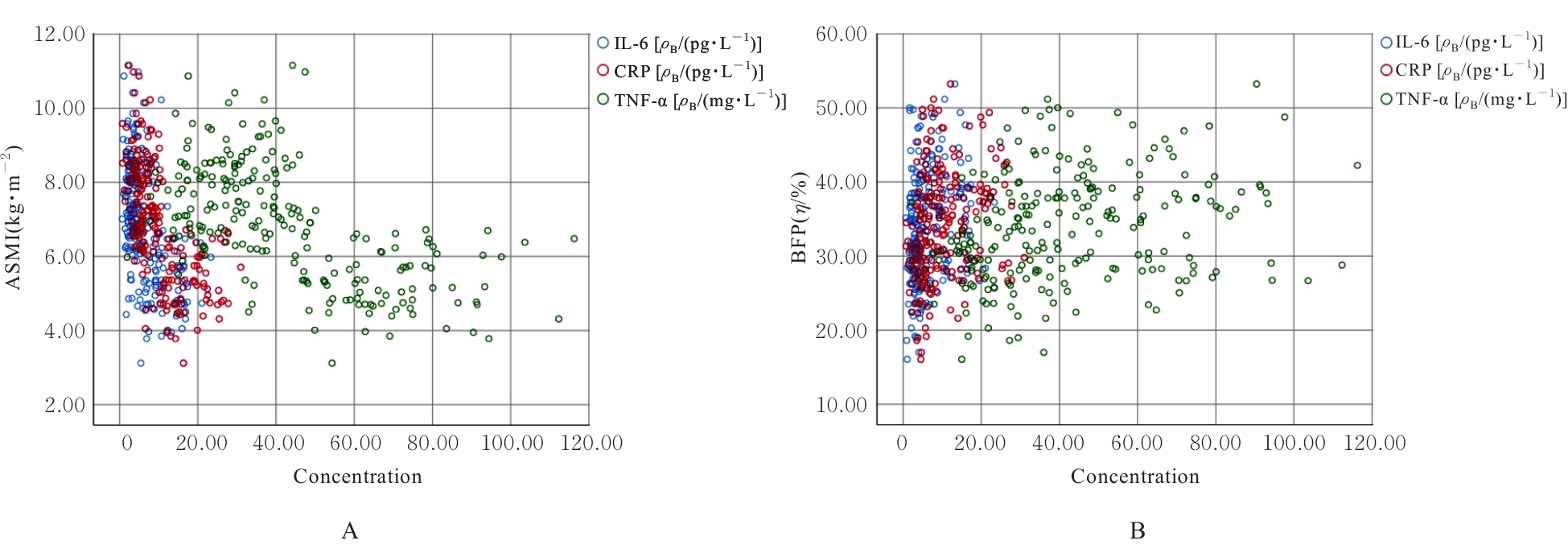
| IL-6 [ρB/(pg·L-1)] | 3.55±1.85 | 11.64±3.73 | 18.848 | <0.001 |
| CRP [ρB/(pg·L-1)] | 5.58±1.57 | 16.75±4.87 | 20.729 | <0.001 |
| TNF-α [ρB/(mg·L-1)] | 28.94±9.41 | 65.77±17.17 | 18.378 | <0.001 |
| Na+ [cB/(mmol·L-1)] | 140.23±12.15 | 142.45±12.52 | 1.317 | 0.189 |
| K+ [cB/(mmol·L-1)] | 4.16±0.88 | 4.23±0.92 | 0.568 | 0.571 |
| Ca2+ [cB/(mmol·L-1)] | 4.47±0.29 | 4.55±0.36 | 1.753 | 0.081 |
| PLT (109 L-1) | 233.54±32.84 | 237.49±34.19 | 0.861 | 0.390 |
Tab.5
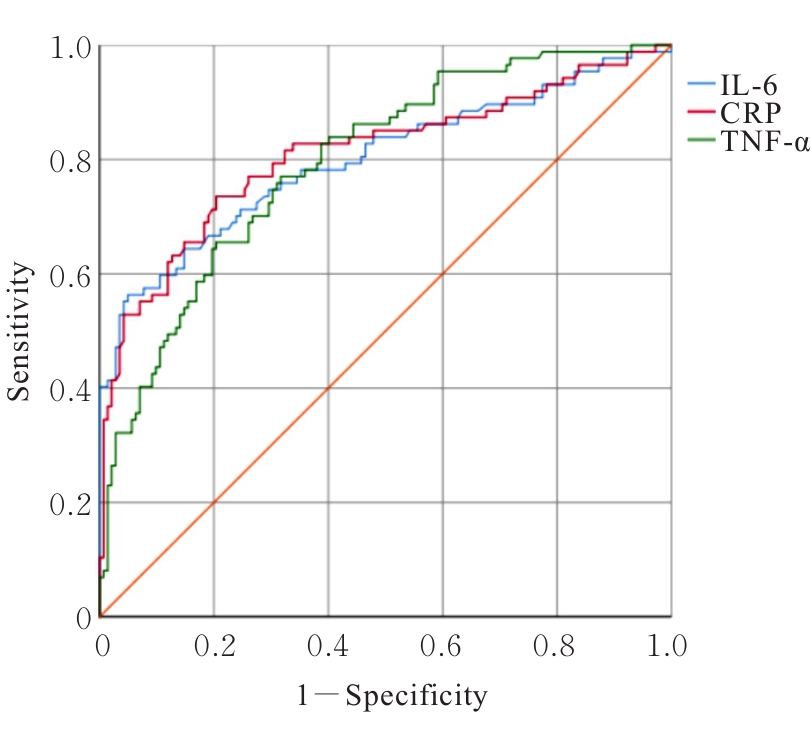
Predictive values of levels of IL-6, CRP and TNF-α on sarcopenia"
| Characteristic | AUC | Cut-off | 95% CI | P | Specificity | Sensitivity | Youden index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 0.799 | 6.795 pg·L-1 | 0.751-0.874 | <0.001 | 0.725 | 0.724 | 0.449 |
| CRP | 0.809 | 11.465 pg·L-1 | 0.739-0.866 | <0.001 | 0.718 | 0.736 | 0.454 |
| TNF-α | 0.796 | 47.460 mg·L-1 | 0.785-0.902 | <0.001 | 0.831 | 0.747 | 0.578 |
| [1] | PAPADOPOULOU S K. Sarcopenia: a contemporary health problem among older adult populations[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(5): 1293. |
| [2] | DAI S Y, SHU D B, MENG F J, et al. Higher risk of sarcopenia in older adults with type 2 diabetes: NHANES 1999-2018[J]. Obes Facts, 2023, 16(3): 237-248. |
| [3] | 王金涛, 胡 坚. 老年人2型糖尿病与肌少症的关系研究进展[J]. 实用老年医学, 2024, 38(5): 529-532. |
| [4] | DE CARVALHO F G, JUSTICE J N, DE FREITAS E C, et al. Adipose tissue quality in aging: how structural and functional aspects of adipose tissue impact skeletal muscle quality[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(11): 2553. |
| [5] | WANG M N, TAN Y, SHI Y F, et al. Diabetes and sarcopenic obesity: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatments[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2020, 11: 568. |
| [6] | 杜怡宁, 杨 青. 老年肌少症性肥胖研究进展[J]. 国际老年医学杂志, 2023, 44(6): 734-738. |
| [7] | KARANTH S D, WASHINGTON C, CHENG T D, et al. Inflammation in relation to sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity among older adults living with chronic comorbidities: results from the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999-2006[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(11): 3957. |
| [8] | BATSIS J A, MACKENZIE T A, JONES J D, et al. Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity and inflammation: results from the 1999-2004 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey[J]. Clin Nutr, 2016, 35(6): 1472-1483. |
| [9] | KANG M G, JUNG H W, KIM B J. A link between systemic low-grade inflammation and frailty in older adults: clinical evidence from a nationwide population-based study[J]. Korean J Intern Med, 2024, 39(6): 1011-1020. |
| [10] | BIOLO G, CEDERHOLM T, MUSCARITOLI M. Muscle contractile and metabolic dysfunction is a common feature of sarcopenia of aging and chronic diseases: from sarcopenic obesity to cachexia[J]. Clin Nutr, 2014, 33(5): 737-748. |
| [11] | KOSHIKAWA M, HARADA M, NOYAMA S, et al. Association between inflammation and skeletal muscle proteolysis, skeletal mass and strength in elderly heart failure patients and their prognostic implications[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2020, 20(1): 228. |
| [12] | LIVSHITS G, KALINKOVICH A. A cross-talk between sestrins, chronic inflammation and cellular senescence governs the development of age-associated sarcopenia and obesity[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2023, 86: 101852. |
| [13] | CHEN L K, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2020, 21(3): 300-307. |
| [14] | GARVEY W T, MECHANICK J I, BRETT E M, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists and American college of endocrinology comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for medical care of patients with obesity[J]. Endocr Pract, 2016, 22(): 1-203. |
| [15] | LYNCH G M, MURPHY C H, DE MARCO CASTRO E, et al. Inflammation and metabolism: the role of adiposity in sarcopenic obesity[J]. Proc Nutr Soc, 2020: 1-13. |
| [16] | CLEASBY M E, JAMIESON P M, ATHERTON P J. Insulin resistance and sarcopenia: mechanistic links between common co-morbidities[J]. J Endocrinol, 2016, 229(2): R67-R81. |
| [17] | YING L, ZHANG Q, YANG Y M, et al. A combination of serum biomarkers in elderly patients with sarcopenia: a cross-sectional observational study[J]. Int J Endocrinol, 2022, 2022: 4026940. |
| [18] | TEIXEIRA L A C, AVELAR N C P, PARENTONI A N, et al. Inflammatory biomarkers in older women with obesity, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic obesity[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2023, 24(10): 1562-1564. |
| [19] | 杜 婧, 赵家军. 非酒精性脂肪肝合并肌少症研究进展[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024,44(5): 424-430, 440. |
| [20] | AKASH M S H, REHMAN K, LIAQAT A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha: role in development of insulin resistance and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(1): 105-110. |
| [21] | LEVINE M E, CRIMMINS E M. The impact of insulin resistance and inflammation on the association between sarcopenic obesity and physical functioning[J]. Obesity, 2012, 20(10): 2101-2106. |
| [22] | MOHAMMAD I J, KASHANIAN S, RAFIPOUR R, et al. Evaluation of the relationship of cytokines concentrations tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and C-reactive protein in obese diabetics and obese non-diabetics: a comparative study[J]. Biotechnol Appl Biochem, 2024, 71(2): 272-279. |
| [23] | EBRAHIMI M, HEIDARI-BAKAVOLI A R, SHOEIBI S, et al. Association of serum hs-CRP levels with the presence of obesity, diabetes mellitus, and other cardiovascular risk factors[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2016, 30(5): 672-676. |
| [24] | 孙家镇, 高静媛, 盛丽春, 等. 中老年2型糖尿病合并肌少症与NLR等炎症标志物的相关性[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2024, 30(5): 679-683. |
| [25] | BIAN A L, HU H Y, RONG Y D, et al. A study on relationship between elderly sarcopenia and inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2017, 22(1): 25. |
| [26] | 黄安乐, 卜子涵, 薛梦婷, 等. 肌少症患者外周血炎性因子的Meta分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2021, 27(7): 969-975. |
| [27] | HE Y, DUAN W R, XU P, et al. Exploring the impact of interleukins on sarcopenia development: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2024, 193: 112480. |
| [28] | YANG C W, LI C I, LI T C, et al. Correction: association of sarcopenic obesity with higher serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in Chinese older males-a community-based study (Taichung community health study-elderly, TCHS-E)[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0136069. |
| [29] | MALISZEWSKA K, ADAMSKA-PATRUNO E, KRĘTOWSKI A. The interplay between muscle mass decline, obesity, and type 2 diabetes[J]. Pol Arch Intern Med, 2019, 129(11): 809-816. |
| [30] | TRINH B, RASMUSSEN S J, BRØGGER-JENSEN M E, et al. Inhibition of basal IL-6 activity promotes subcutaneous fat retention in humans during fasting and postprandial states[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2025, 6(4): 102042. |
| [31] | FAN J J, KOU X J, YANG Y, et al. microRNA-regulated proinflammatory cytokines in sarcopenia[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2016, 2016: 1438686. |
| [32] | 柯义兵, 阿布都克热木·达吾提, 郭浩然, 等. 骨骼肌萎缩相关分子机制及信号通路研究进展[J]. 生理学报, 2024, 76(6): 1056-1068. |
| [33] | 刘 竞, 丁国宪. 骨骼肌肌间脂肪浸润在代谢相关疾病中的研究进展[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 44(5): 719-725. |
| [1] | Shuang LI,Jiayu GE,Xianzhu CONG,Aimin WANG,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG. Analysis on influencing factors for occurrence of angina pectoris in diabetic mellitus patients and its Bayesian network risk prediction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 1028-1038. |
| [2] | Yixuan GAO,Peng WANG,Silong ZHANG,Ruijuan GAO,Yingfang MA,Keke ZHANG,Dan FENG,Zongqi HUANG,Ketao MA,Li LI,Junqiang SI. Inhibitory effect of safranal on proliferation, migration and phenotypic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells of rats induced by high glucose in vitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 948-957. |
| [3] | Qi WANG,Lingyu JIANG,Xiangrong LIU. Research progress in application of weight-adjusted waist circumference index in risk prediction and evaluation of obesity-related diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 848-854. |
| [4] | Meng QU,Rui HUANG,Xinda JU,Yuxin LIU,Jichen XIA,Jiaxin HUANG,Chunyan YU,Zhiheng DONG. Ameliorative effect of ginsenoside Rh1 on kidney injury in diabetic mice through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1565-1571. |
| [5] | Jingshun ZHANG,Yinggang ZOU,Lianwen ZHENG. Effect of over-expression SLC7A5 on apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1526-1534. |
| [6] | Yanbin ZHANG,Guangye GUO,Caihua ZHENG,Xinyan LIU. Research progress in association between Helicobacter pylori and metabolic syndrome and its effect on occurrence and development of metabolic syndrome [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1757-1762. |
| [7] | Zhifei LIU,Yaru BI,Chenglin SUN,Suyan TIAN. Mendelian randomization analysis based on causal relationship between gut microbiota and gestational diabetes mellitus [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1381-1389. |
| [8] | Jing TANG,Huan LI,Shuo ZHANG,Ligang JING. Analysis on association between serum homocysteine and inflammatory response and oxidative stress in patients with acute ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 786-790. |
| [9] | Xue FANG,Yu KANG,Xiaoxi SHA,Zhifen HAN,Yan ZHANG. Detection of gastrocnemius muscle hardness of diabetic patients under different functional states by ultrasonic shear wave elastography and its clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 451-456. |
| [10] | Jiaxin WANG,Zhenqi WANG,Xuan ZHANG. Expressions of CDKAL1 gene and its splice isomers in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and their clinical significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1290-1295. |
| [11] | Zhe LIN,Taidong WANG,Xiaowei HUANG,Chao MA,Xuefeng ZHUANG,Yuchen WANG,He LIN,Junqi GUO,Guangfu LYU. Improvement effect of Saposhnikoviae Radix wild product on rheumatoid arthritis in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 617-624. |
| [12] | Jing GUAN,Shen HA,Hao YUAN,Ying CHEN,Pengju LIU,Zhi LIU,Shuang JIANG. Protective effect of Modified Xiao-Xian-Xiong Decoction on liver injury in rats with type 2 diabete mellitus and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 608-616. |
| [13] | Xiaowei HUANG,Siqi ZHANG,Yixin ZHANG,Bo LIU,Xin WANG,Fenglan JI,Runze YANG,Huibo XU,Tao DING. Relationship between syndrome manifestations and differentially expressed genes in rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus with Qi and Yin deficiency explored through transcriptomics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 625-633. |
| [14] | Xiaojuan ZHU,Haitao DAI,Yan LI,Lingxin CUI,Ya WANG,Jiang XU,Nan WU. Improvement effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on periodontal inflammation in diabetic periodontitis rats and its influence on expression levels of TLR4 and NF-κB in periodontal tissue [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 31-38. |
| [15] | Junxiong ZHAO,Qian WU,Liangui NIE,Shengquan LIU,Zhentao JIANG,Jian CHEN,Ting XIAO,Jun YANG. Ameliorative effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 8-14. |
|
||