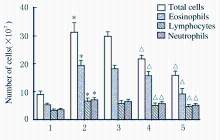
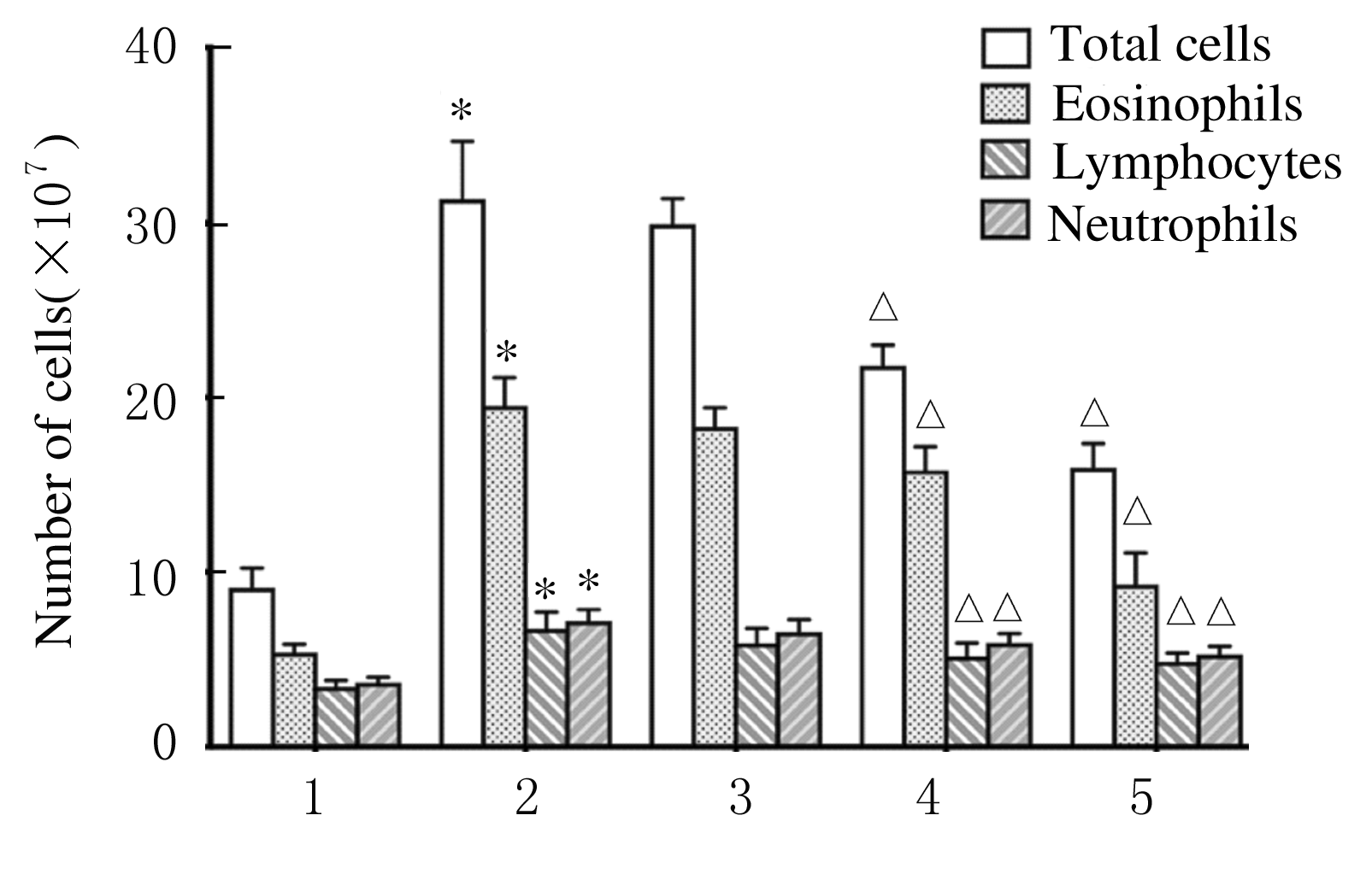
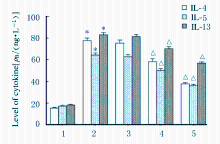
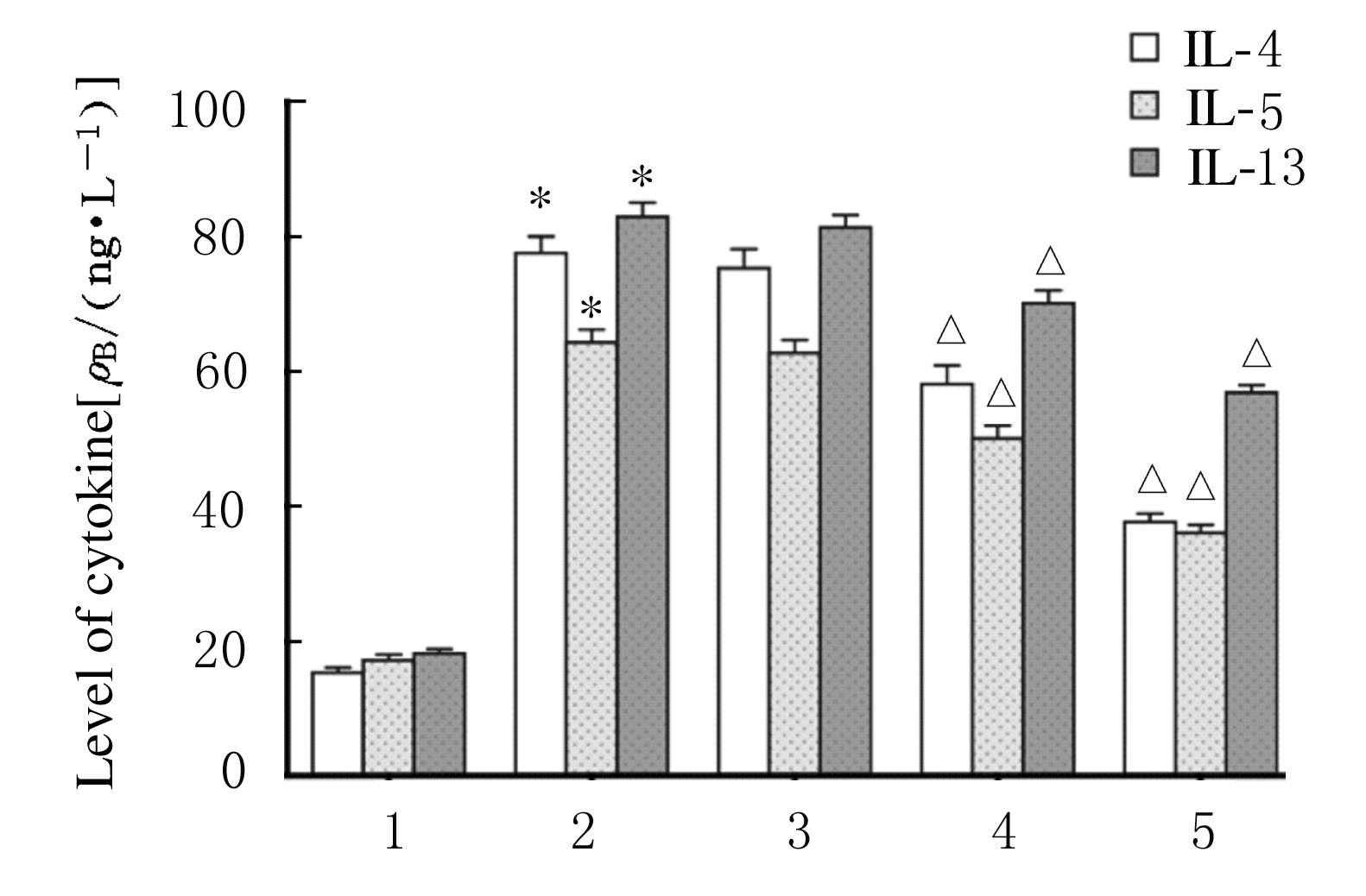
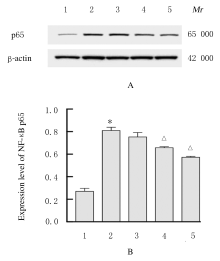
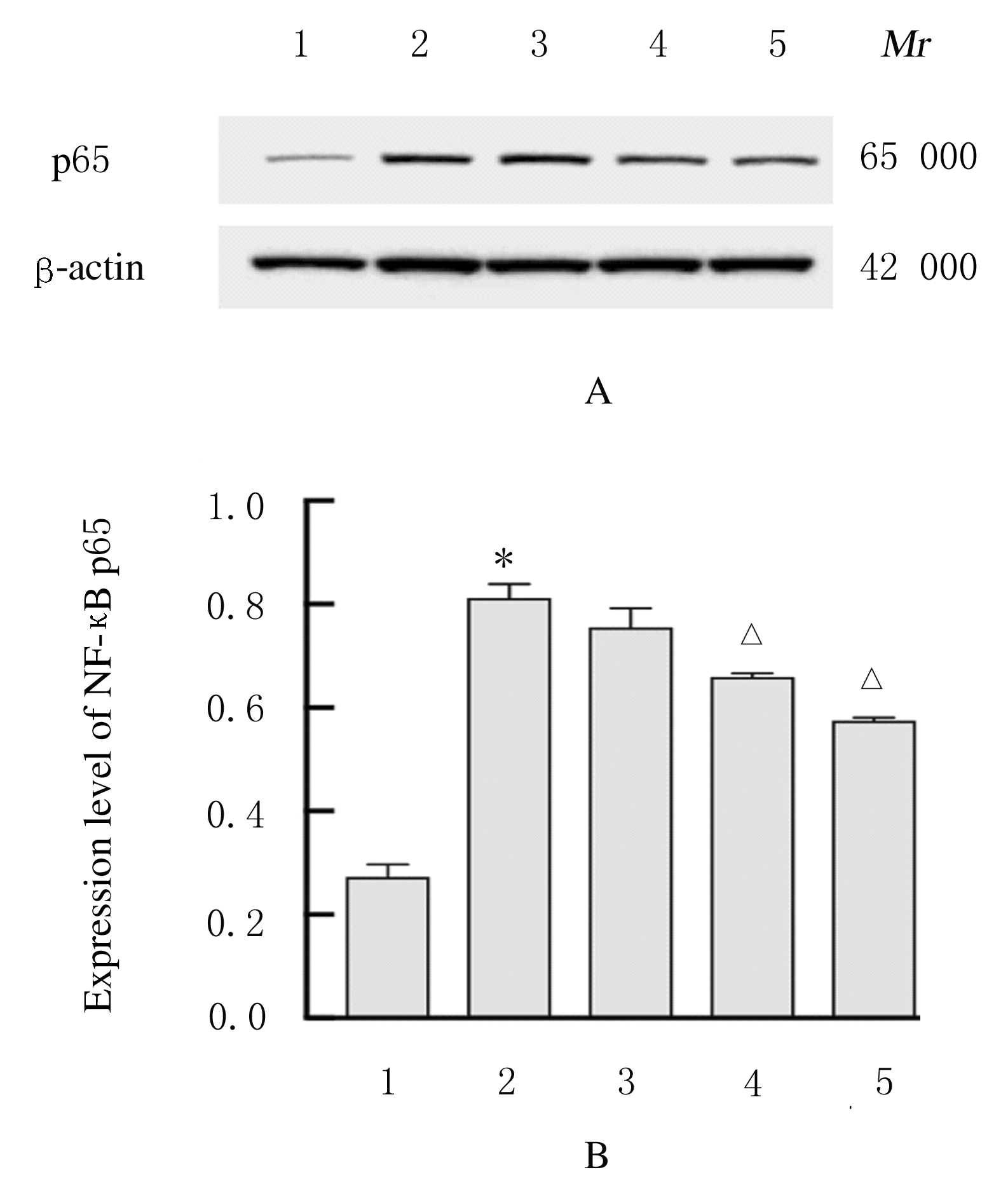
| [1] |
Jing WANG,Chang XU,Yilan SONG,Chongyang WANG,Jingzhi JIANG,Liangchang LI,Guanghai YAN,Liming SU.
Alleviation of esculentoside A on airway inflammation of asthmatic mice and its effect on expression levels of IL-6 and STAT3 in lung tissue
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 299-307.
|
| [2] |
Xue LUAN, Guanghai YAN, Haibo LI, Bo ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yuanyuan HUANG.
Effect of salidroside on airway inflammation in mice with asthma and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 537-544.
|
| [3] |
QIN Chao, DAI Xi, YANG Xiaoqiong, WANG Rongli, WANG Xing, LI Guoping.
Intervention effect of honokiol on inflammatory response in lung tissue of asthma mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 214-220.
|
| [4] |
WANG Yazhou, HE Peng, WANG Danhong.
Effects of montelukast on proliferation and apoptosis of airway smooth muscle cells in asthmatic rats by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 274-279.
|
| [5] |
LYU Xiuyun, YANG Ting, XU Lei, WANG Lihong.
Dynamic changes of MIP-1α and IL-13 levels of patients with severe asthma and their valuesin prognosis evaluation
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1401-1407.
|
| [6] |
WANG Tianyue, ZHOU Qianlan, SHANG Yunxiao.
Effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on airway inflammation and Treg/Th17 immune balance of mice with obese asthma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 491-497.
|
| [7] |
WANG Lihong, ZHANG Ying, LAN Kun, ZHANG Haiyu, CAO Xiaobei, LI Shanyu.
Inhibitory effect of astragalus polysaccharides on pulmonary inflammation in asthma model mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 313-318.
|
| [8] |
HU Bo, WANG Xiaowen, CAO Jianhui, SUN Xiaomin, CUI Yajie, SHI Congcong.
Changes of expressions of NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and IL-1β and IL-18 in serum in children with asthma and their significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(01): 111-116.
|
| [9] |
AN Beiying, LI Yanan, JU Yanghua, WANG Yingying, CHENG Hang.
Effects of serum vitamin D3 level on asthma control and pulmonary function in children with asthma and their clinical significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 1010-1013.
|
| [10] |
RAN Qin, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Yun, QIU Yuhuan, YUAN Xiefang, WANG Xiaoyun, TANG Hongmei, WANG Xing, LI Guoping.
Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on pulmonary inflammation in mice with neutrophilic asthma and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 897-902.
|
| [11] |
ZOU Fei, CHENG Zhihua, ZHANG Yuying, MA Ke.
Evaluation on efficacy of Huaiqihuang granules in treatment of children with asthma at non-acute attack stage
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 597-603.
|
| [12] |
CHEN Liyan, TANG Ying, ZHANG Li, SI Qin, XU Lijun.
Detection of interleukin -22 in peripheral blood of patients with bronchial asthma and its clinical significance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(02): 349-352.
|
| [13] |
WANG Guoqiang, WANG Yubo, ZHANG Weijie, WANG Xinran, ZHANG Wenjin, WU Tian, GUAN Xuewa, CHEN Fang, ZHENG Jingtong, WANG Fang.
Effects of Th17 transcription factors RORγt, BATF and Th17-related cytokines in pathogenesis of patients with neutrophilic asthma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(01): 106-110.
|
| [14] |
LI Yanfeng, WANG Hongbo, GAO Yang, ZHENG Yuxuan, LIU Li.
Change of serum periostinlevel in children with bronchial asthma and significance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(01): 101-105.
|
| [15] |
LI Guangxin, REN Lianzhu, YU Conghai, ZHAO Lijun.
Improvement effect of interval training on respiratory function and exercise performance of asthmatic children
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(05): 949-953.
|
 )
)