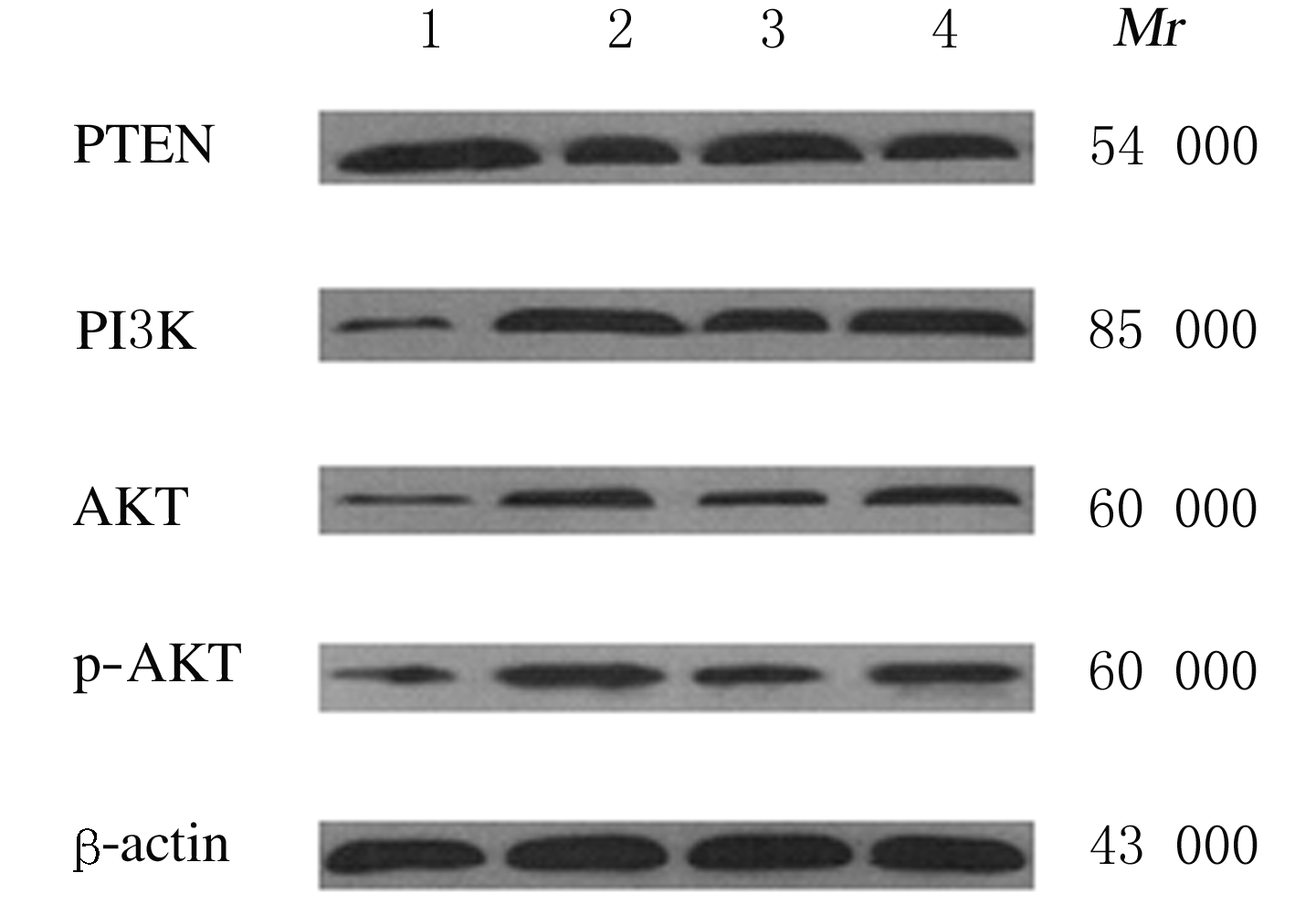
| 1 |
武占成, 赵 晶, 朱秀惠, 等. 类风湿关节炎的骨病变从络病论治[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(5): 760-765.
|
| 2 |
BANERJEE S, SANGWAN V, MCGINN O, et al. Triptolide-induced cell death in pancreatic cancer is mediated by O-GlcNAc modification of transcription factor Sp1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(47): 33927-33938.
|
| 3 |
LI X, LU Q, XIE W, et al. Anti-tumor effects of triptolide on angiogenesis and cell apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells by inducing autophagy via repressing Wnt/β-Catenin signaling[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 496(2): 443-449.
|
| 4 |
陈颖婷, 何柯新, 王云秀, 等. 雷公藤内酯醇对类风湿关节炎大鼠TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的调控作用研究[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2019, 40(17): 2053-2057.
|
| 5 |
陈柏松, 徐玉东, 钟淑琦, 等. 大鼠佐剂性关节炎模型的建立与评价[J]. 哈尔滨医科大学学报, 2005, 39(6): 489-491.
|
| 6 |
陈颖婷, 何柯新, 王云秀, 等. 雷公藤内酯醇对类风湿关节炎大鼠TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的调控作用研究[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2019, 40(17): 2053-2057.
|
| 7 |
陈璐璐, 钟晓岚, 朱颖敏, 等. 雌性Lewis大鼠佐剂诱导关节炎模型的建立与评价[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2019, 50(10): 1453-1460.
|
| 8 |
CHEN Z, WANG H, XIA Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal cell-derived miRNA-150-5p-expressing exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis mediated by the modulation of MMP14 and VEGF[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 201(8): 2472-2482.
|
| 9 |
LEE Y H, BAE S C. Correlation between circulating VEGF levels and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis[J]. Z Rheumatol, 2018, 77(3): 240-248.
|
| 10 |
SHEVCHENKO AV, PROKOFYEV VF, KOROLEV MA,et al.Polymorphism in the regulatory regions -С2578A and +C936T of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) gene in Russian women with rheumatoid arthritis[J].Ter Arkh,2017,89(5):60-64.
|
| 11 |
CHEN C Y, SU C M, HSU C J, et al. CCN1 promotes VEGF production in osteoblasts and induces endothelial progenitor cell angiogenesis by inhibiting miR-126 expression in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2017, 32(1): 34-45.
|
| 12 |
郑栩良, 张郜晨茜, 张 烁. 鲁贤昌教授治疗类风湿性关节炎经验[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报, 2018, 42(5): 370-373.
|
| 13 |
曾克勤, 武 剑, 郭雨凡, 等. 雷公藤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床疗效与安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国血液流变学杂志, 2017, 27(3): 284-287.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG F Z, HO D H, WONG R H. Triptolide, a HSP90 middle domain inhibitor, induces apoptosis in triple manner[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(32): 22301-22315.
|
| 15 |
胡伟锋, 王昌兴. 雷公藤内酯醇对类风湿关节炎大鼠的治疗作用及其网络药理学研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2016, 19(12): 1408-1413.
|
| 16 |
王 进, 李 森, 张友朋, 等. 雷公藤内酯醇联合顺铂对荷膀胱癌T24细胞裸鼠免疫功能及血管生长作用的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2016, 33(6): 1448-1450.
|
| 17 |
LIU Y, PAN Y F, XUE Y Q, et al. uPAR promotes tumor-like biologic behaviors of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in patients with rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2018, 15(2): 171-181.
|
| 18 |
JIAO Y, DING H, HUANG S, et al. Bcl-XL and Mcl-1 upregulation by calreticulin promotes apoptosis resistance of fibroblast-like synoviocytes via activation of PI3K/Akt and STAT3 pathways in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2018, 36(5): 841-849.
|
| 19 |
LIN J, HE Y, WANG B, et al. Blocking of YY1 reduce neutrophil infiltration by inhibiting IL-8 production via the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2019, 195(2): 226-236.
|
| 20 |
ZHANG L, LIU X, LIU J, et al. miR-26a promoted endometrial epithelium cells (EECs) proliferation and induced stromal cells (ESCs) apoptosis via the PTEN-PI3K/AKT pathway in dairy goats[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(6): 4688-4706.
|
| 21 |
DAI Y X, WAN Y K, QIU M K, et al. lncRNA MEG3 suppresses the tumorigenesis of hemangioma by sponging miR-494 and regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 51(6): 2872-2886.
|
| 22 |
LI N N, MENG X S, BAO Y R, et al. Evidence for the involvement of COX-2/VEGF and PTEN/Pl3K/AKT pathway the mechanism of oroxin B treated liver cancer[J]. Pharmacogn Mag, 2018, 14(54): 207-213.
|
| 23 |
刘 斐, 谭布珍. 雷公藤内酯醇联合紫杉醇对COC1/DDP细胞凋亡的影响及其对PI3K/AKT/GSK3β信号通路的调控[J]. 现代妇产科进展, 2013, 22(12): 945-950.
|
| 24 |
戴小娜,林 进.老年起病类风湿关节炎研究进展[J].中国实用内科杂志,2019,39(6):562-567.
|