Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 257-264.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210202
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effect of calcitriol on hepatic fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in mice and its mechanism
Rongjun JIA1,Liman MA2,Lihua LI1( )
)
- 1.Department of Cell Biology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
2.Department of Clinical Medicine,School of Medical Sciences,Taizhou University,Taizhou 31800,China
-
Received:2020-09-17Online:2021-03-28Published:2021-03-25 -
Contact:Lihua LI E-mail:2744900797@qq.com
CLC Number:
- R575.2
Cite this article
Rongjun JIA,Liman MA,Lihua LI. Protective effect of calcitriol on hepatic fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in mice and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 257-264.
share this article
Tab.1
Activities of serum ALT and AST and levels of TBA, TBIL and Hyp of mice in various groups"
| Group | ALT[λB/(U·L-1)] | AST[λB/ (U·L-1)] | TBA[cB/ (μmol·L-1)] | TBIL[cB/ (μmol·L-1)] | Hyp [ρB/ (mg·L-1)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham operation | 50.22±4.72 | 26.53±2.34 | 4.21±1.02 | 36.02±4.28 | 1.73±0.16 |
| Model | 187.43±27.30* | 146.94±16.58* | 12.26±1.43* | 266.22±39.05* | 3.22±0.18* |
| Treatment | 122.56±7.38*△ | 66.68±5.96*△ | 5.38±1.20*△ | 135.78±12.44*△ | 2.05±0.26*△ |
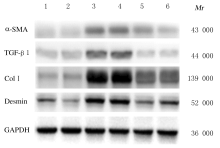
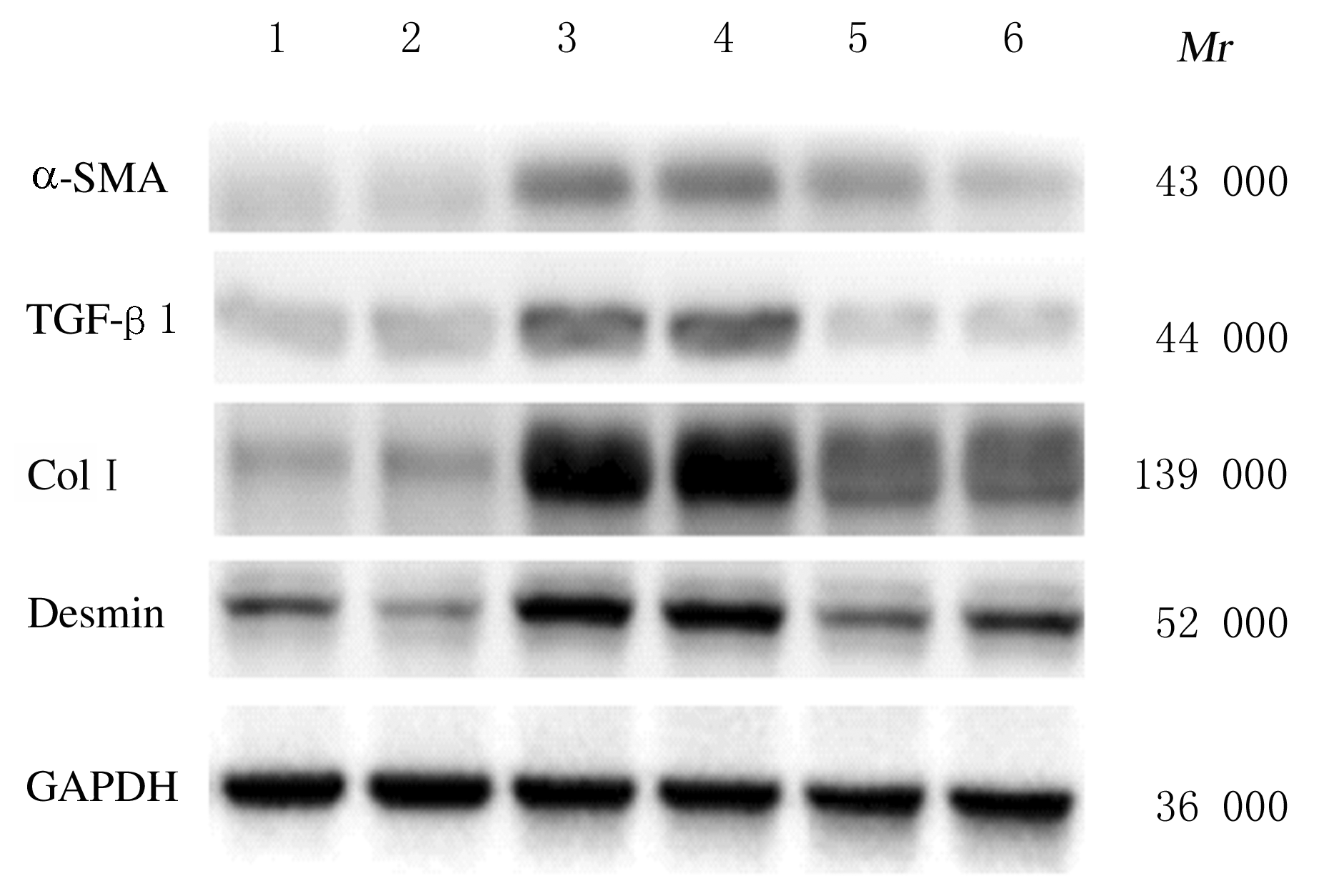
Tab.2
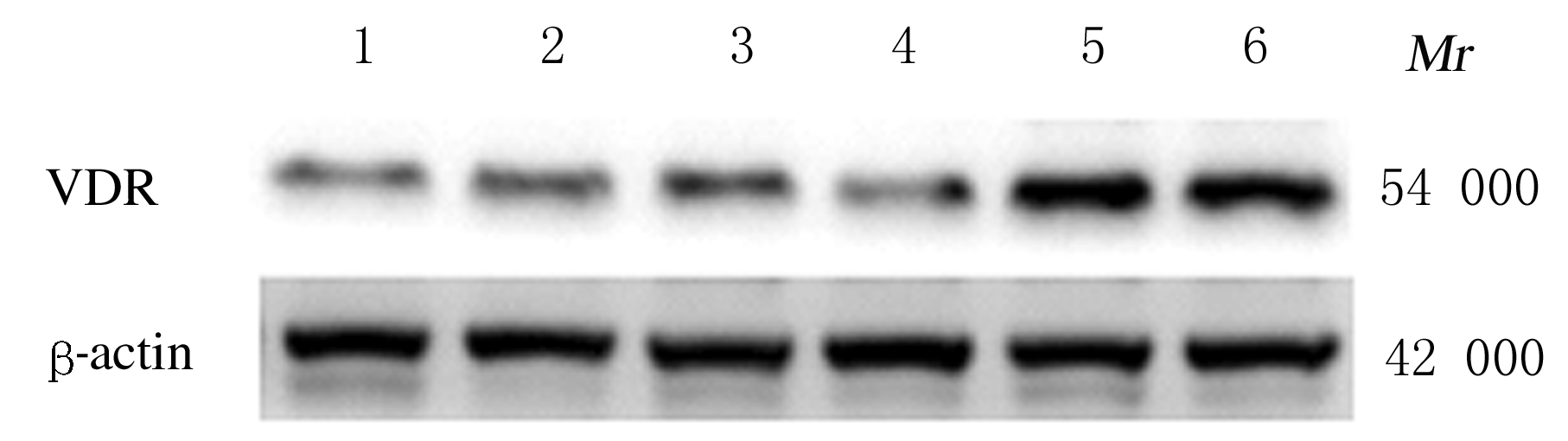
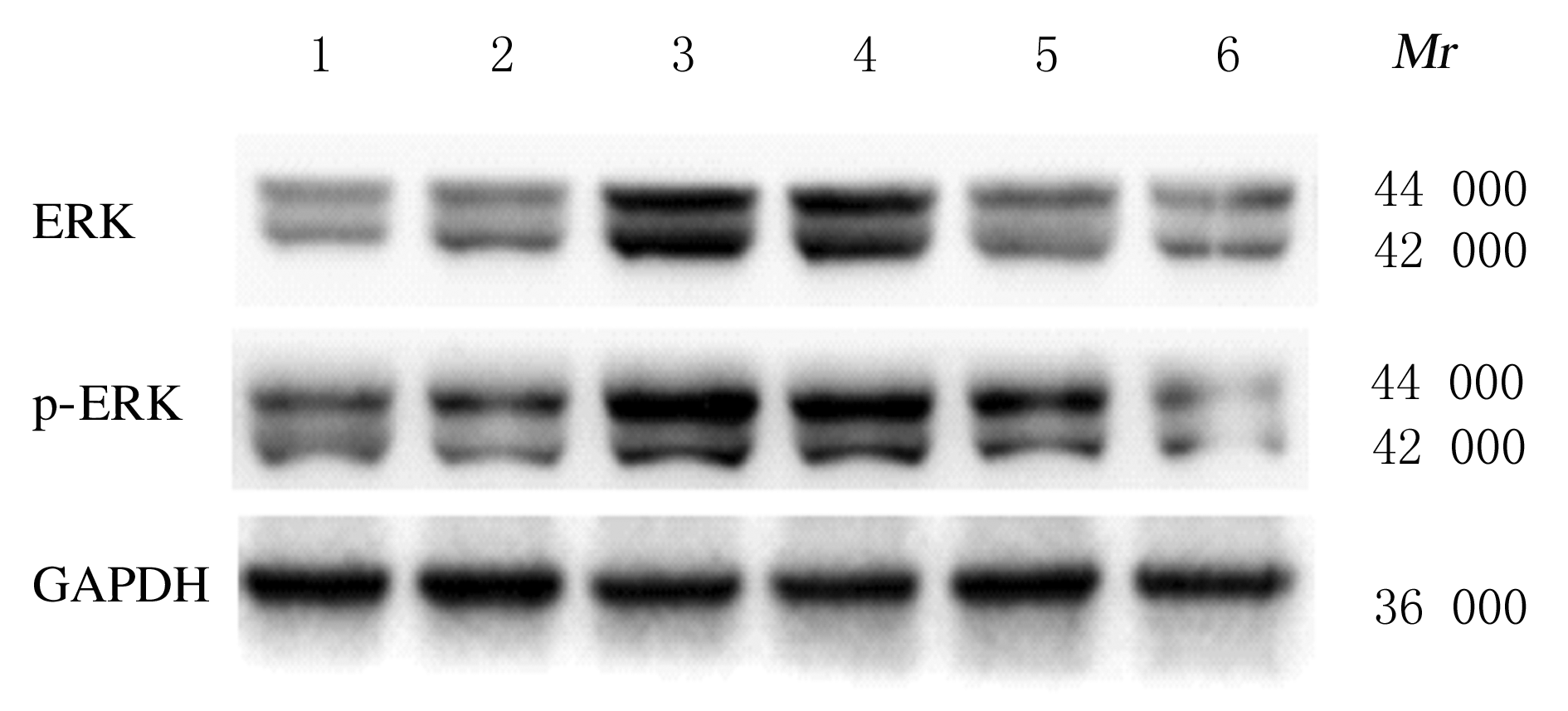
Expression levels of ERK,p-ERK,α-SMA, TGF-β1, Col Ⅰ and Desmin proteins in liver tissue of mice in various groups"
| Group | ERK | p-ERK | α-SMA | TGF-β1 | Col Ⅰ | Desmin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham operation | 0.58±0.02 | 0.63±0.01 | 0.14±0.02 | 0.22±0.04 | 0.30±0.02 | 0.49±0.11 |
| Model | 1.15±0.04* | 1.27±0.03* | 0.40±0.03* | 0.49±0.07* | 1.66±0.03* | 0.83±0.02* |
| Treatment | 0.61±0.02△ | 0.66±0.05△ | 0.27±0.09△ | 0.26±0.01△ | 0.55±0.01△ | 0.61±0.06△ |
| 1 | AYDIN MM, AKÇALI KC. Liver fibrosis [J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2018, 29 (1):14-21. |
| 2 | FRIEDRICH-RUST M, WANGER B, HEUPEL F, et al. Influence of antibiotic-regimens on intensive-care unit-mortality and liver-cirrhosis as risk factor [J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(16):4201-4210. |
| 3 | SEKI E, BRENNER D A. Recent advancement of molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis [J]. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci, 2015, 22(7):512-518. |
| 4 | LI J, LI X, XU W, et al. Antifibrotic effects of luteolin on hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by targeting AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and TGFβ/Smad signalling pathways [J]. Liver Int, 2015, 35(4):1222-1233. |
| 5 | TSUCHIDA T, FRIEDMAN S L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation [J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 14(7):397-411. |
| 6 | YANG J H, KIM S C, KIM K M, et al. Isorhamnetin attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad signaling and relieving oxidative stress [J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2016, 783:92-102. |
| 7 | SHANY S, SIGAL-BATIKOFF I, LAMPRECHT S. Vitamin D and myofibroblasts in fibrosis and cancer: At cross-purposes with TGF-β/SMAD signaling [J]. Anticancer Res, 2016, 36(12):6225-6234. |
| 8 | DURAN A, HERNANDEZ E D, REINA-CAMPOS M, et al. p62/SQSTM1 by binding to vitamin D receptor inhibits hepatic stellate cell activity, fibrosis, and liver cancer [J]. Cancer Cell, 2016, 30(4):595-609. |
| 9 | TRIANTOS C, AGGELETOPOULOU I, KALAFATELI M, et al. Prognostic significance of vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms in liver cirrhosis [J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1):14065. |
| 10 | MAESTRO M A, MOLNÁR F, CARLBERG C. Vitamin D and its synthetic analogs [J]. J Med Chem, 2019, 62(15):6854-6875. |
| 11 | REITER F P, YE L, BOSCH F, et al. Antifibrotic effects of hypocalcemic vitamin D analogs in murine and human hepatic stellate cells and in the CCl4 mouse model [J]. Lab Invest, 2019, 99(12):1906-1917. |
| 12 | ZERR P, VOLLATH S, PALUMBO-ZERR K, et al. Vitamin D receptor regulates TGF-β signalling in systemic sclerosis [J].Ann Rheum Dis,2015,74(3):e20. |
| 13 | CAI F F, WU R, SONG Y N, et al. Yinchenhao decoction alleviates liver fibrosis by regulating bile acid metabolism and TGF-β/Smad/ERK signalling pathway [J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1):15367. |
| 14 | LI X Q, ZHANG H, PAN L J, et al. Puerarin alleviates liver fibrosis via inhibition of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in thioacetamideinduced hepatic fibrosis in rats [J]. Exp Therapeut Med, 2019, 18(1):133-138. |
| 15 | REITER F P, HOHENESTER S, NAGEL J M, et al. 1,25-(OH)2-vitamin D3 prevents activation of hepatic stellate cells in vitro and ameliorates inflammatory liver damage but not fibrosis in the Abcb4(‒/‒) model [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2015, 459(2):227-233. |
| 16 | CAMPANA L, IREDALE J. Regression of liver fibrosis [J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2017, 37(1):001-010. |
| 17 | TAG C G, SAUER-LEHNEN S, WEISKIRCHEN S, et al. Bile duct ligation in mice: induction of inflammatory liver injury and fibrosis by obstructive cholestasis [J]. JoVE, 2015(96):52438. |
| 18 | SATO K, MARZIONI M, MENG F, et al. Ductular reaction in liver diseases: pathological mechanisms and translational significances[J].Hepatology,2019,69(1):420-430. |
| 19 | SATO K, MENG F Y, GIANG T, et al. Mechanisms of cholangiocyte responses to injury [J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018, 1864:1262-1269. |
| 20 | MARADANA M R, YEKOLLU S K, ZENG B, et al. Immunomodulatory liposomes targeting liver macrophages arrest progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [J]. Metab Clin Exp, 2018, 78:80-94. |
| 21 | GUO J, MA Z, MA Q, et al. 1, 25(OH)2D3 Inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma development through reducing secretion of inflammatory cytokines from immunocytes[J].Curr Med Chem, 2013, 20(33):4131-4141. |
| 22 | CHRISTAKOS S, DHAWAN P, VERSTUYF A, et al. Vitamin D: Metabolism, molecular mechanism of action, and pleiotropic effects [J]. Physiol Rev, 2016, 96(1):365-408. |
| 23 | ZHANG J, YANG S, XU B, et al. p62 functions as an oncogene in colorectal cancer through inhibiting apoptosis and promoting cell proliferation by interacting with the vitamin D receptor[J].Cell Prolif,2019,52(3):e12585. |
| 24 | ROWE I A. Lessons from epidemiology: The burden of liver disease [J]. Dig Dis, 2017, 35(4):304-309. |
| 25 | FABREGAT I, CABALLERO-DÍAZ D. Transforming growth factor-β-induced cell plasticity in liver fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis [J]. Front Oncol, 2018, 8:357. |
| 26 | RAMIREZ A M, WONGTRAKOOL C, WELCH T, et al. Vitamin D inhibition of pro-fibrotic effects of transforming growth factor β1 in lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells [J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2010, 118(3):142-150. |
| 27 | KIM S J, ISE H, GOTO M, et al. Interactions of vimentin-or desmin-expressing liver cells with N-acetylglucosamine-bearing polymers [J]. Biomaterials, 2012, 33(7):2154-2164. |
| 28 | WANG Y, DEB D K, ZHANG Z, et al. Vitamin D receptor signaling in podocytes protects against diabetic nephropathy [J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2012, 23(12):1977-1986. |
| 29 | ROSKOSKI R. ERK1/2 MAP kinases: structure, function, and regulation [J].Pharmacol Res,2012,66(2):105-143. |
| 30 | LONG T, WANG L, YANG Y, et al. Protective effects of trans-2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene 2-O-β-D-glucopyranoside on liver fibrosis and renal injury induced by CCl4 via down-regulating p-ERK1/2 and p-Smad1/2[J].Food Funct, 2019, 10(8):5115-5123. |
| [1] | YANG Fan, LI Lihua. Effect of vitamin D receptor activation on hepatic fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 722-727. |
| [2] | XIE Jing, LI Lihua. Inhibitory effect of dehydroandrographolide on hepatocyte apoptosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in hepatic fibrosis model mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1009-1014. |
| [3] | BAI Jie, JI Wenjing, DING Yongnian, PENG Yuanyuan, CHEN Yuanwen. Changes of levelsof endogenous AcSDKP and its regulatory factors in liver tissue of model rats with liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 999-1004. |
| [4] | CHANG Caifang, HOU Yong, CONG Gang. Therapeutic effect of α-2b interferon on inflammation of liver tissue and liver fibrosis in hepatitis B model ducks [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(01): 11-15. |
| [5] | YANG Kun, TIAN Zhenzhen, WANG Shuhua, XIU Ming, GUO Xiangling, QI Lina, LI Min, SUN Li, GAO Runping. Effect of LPS-TLR4 pathway in hepatic fibrogenesis of rats with chronic alcohol intake [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(04): 751-755. |
| [6] | HAO Xiaofang, ZHANG Ronghua, WANG Lin, WANG Meimei, ZHEN Yongzhan, ZHANG Guangling, CHEN Jing. Therapeutic effect of rhein lysinate on liver fibrosis in cholestatic model rats and its molecular mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(03): 481-485. |
| [7] | ZHONG Zhi-hong,YAN Wen-zhen,DAI Dong,CHEN Tu-ming,HU Zu-chao. Therapeutic effect of rapamycin on liver fibrosis model rats induced by carbon tetrachloride oil [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1224-1227. |
| [8] | RUAN Li,HUA Xing,LI Zheng-ming . Association analysis between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(3): 570-573. |
| [9] |
XU Jin-rui, NA Xiao-fei, YANG Yi.
Relevance analysis on polymorphisms of four SNPs of VDR gene and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ningxia Han population [J]. J4, 2012, 38(5): 985-989. |
| [10] | DAI Yong-Mei, CAI Li-Mian, LIN Ling. Inhibitory effect of octreotide on prolieration of rat hepatic stellate cells [J]. J4, 2009, 35(6): 1052-1056. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yi-ning, NIU Jun-qi, DING Yan-hua, WANG Feng. Anti-oxidative stress effects of Taurine on rat hepatic stellate cells [J]. J4, 2005, 31(2): 179-181. |
| [12] | SUN Min-dan, LIN Cheng-he, ZOU Hong-bin ,CHI Bao- rong. Study on distribution of vitamin D receptor (Bsm I)gene polymorphism in Chinese pre-menopausalHan women in Changchun [J]. J4, 2004, 30(5): 756-758. |
| [13] | LI Xian-hui, CHENG Yi, LIU Ya-wen , WANG Gang, LI Ji-sheng. Expression of nerve growth factor gene in astrocytescultured in 1,25-(OH)2D3 defined medium [J]. J4, 2004, 30(3): 398-400. |