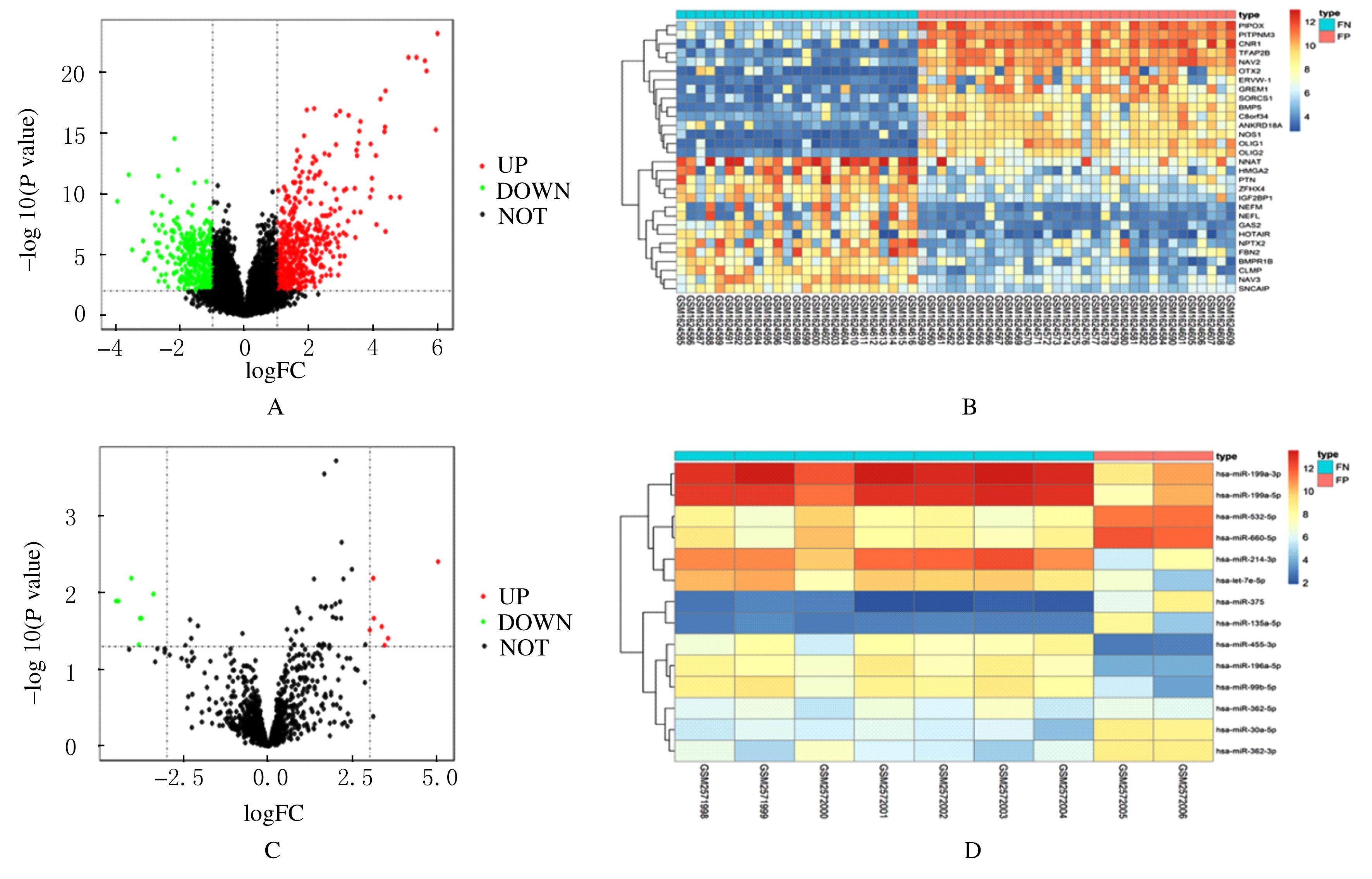
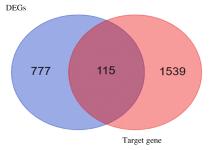
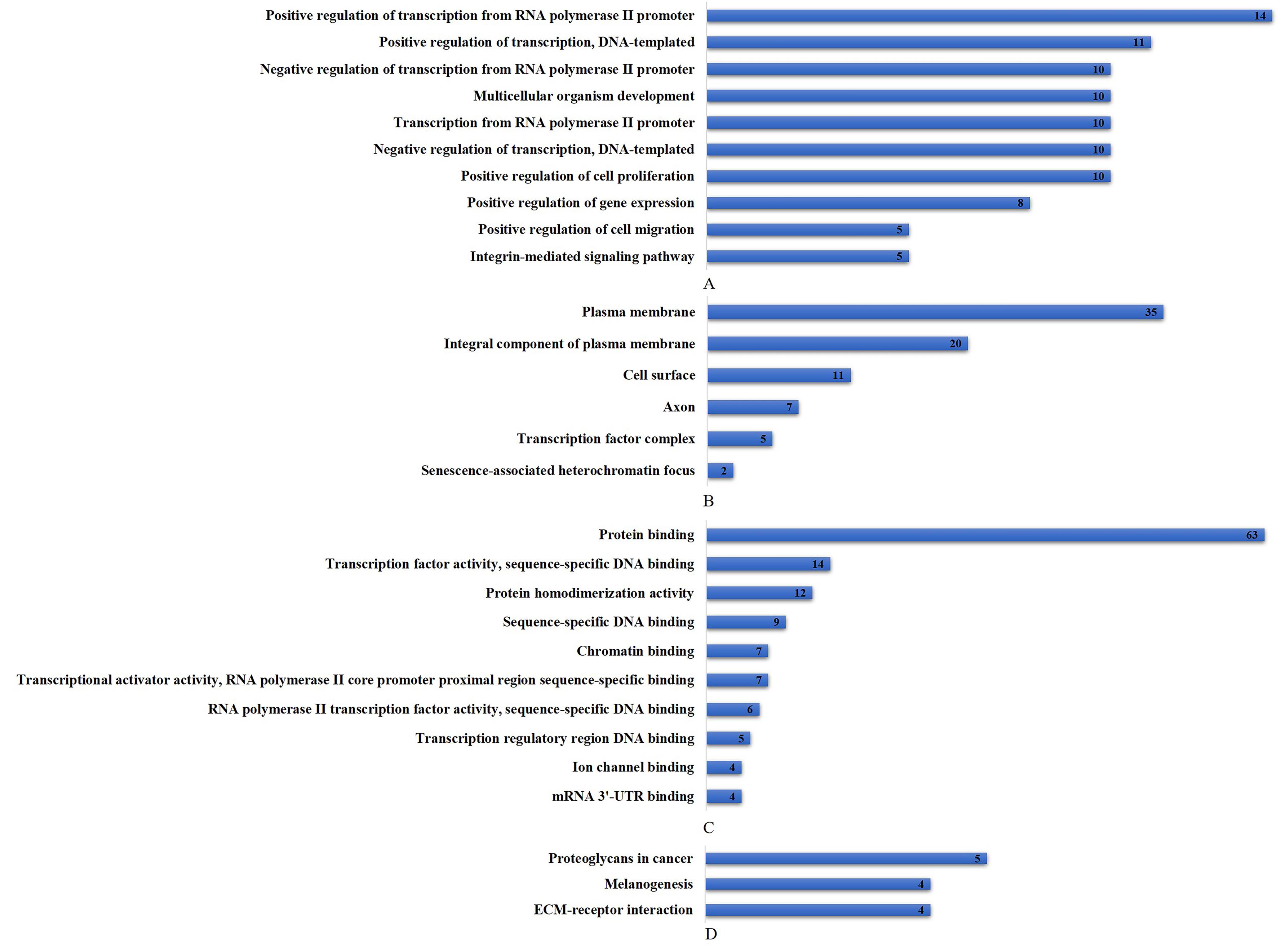
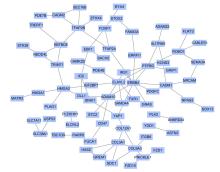
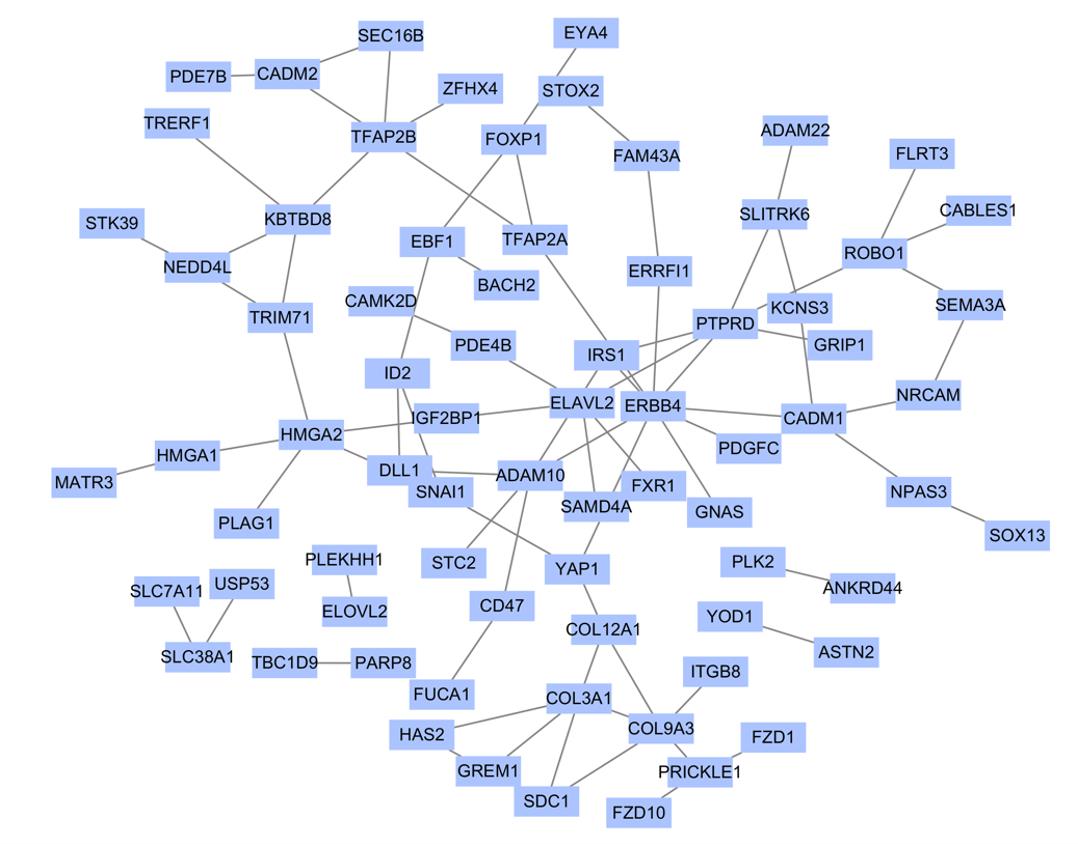
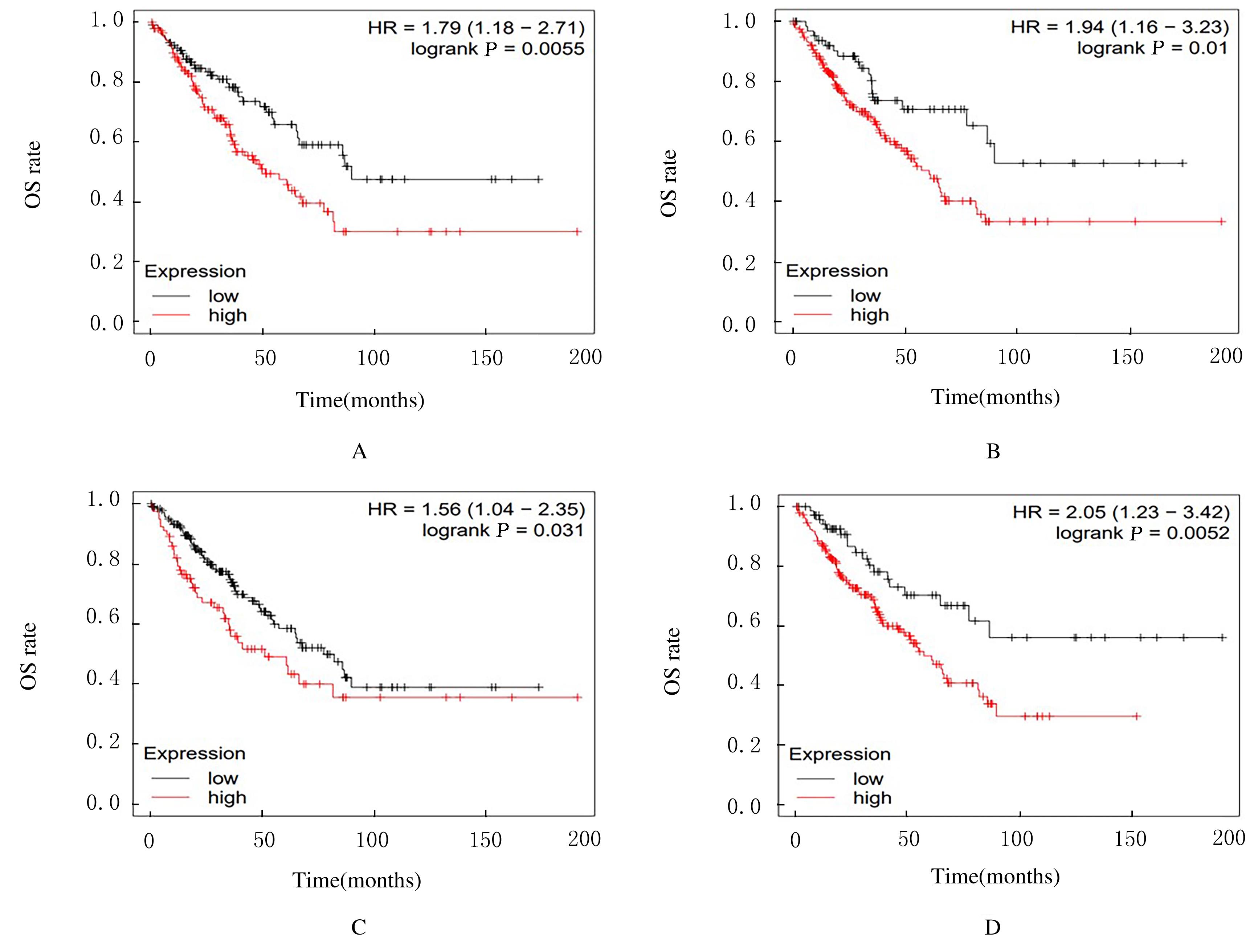
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 154-162.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220119
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics analysis on miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks based on fusion genes acting in rhabdomyosarcoma
Zhijuan ZHAO1,Lian MENG1,Chunxia LIU1,2( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathology,First Affiliated Hospital,College of Medical Sciences,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832002,China
2.Department of Pathology,Second Affiliated Hospital,Guangzhou Medical University,Guangzhou 510260,China
-
Received:2021-05-21Online:2022-01-28Published:2022-01-17 -
Contact:Chunxia LIU E-mail:liuliu2239@sina.com
CLC Number:
- R738.6
Cite this article
Zhijuan ZHAO,Lian MENG,Chunxia LIU. Bioinformatics analysis on miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks based on fusion genes acting in rhabdomyosarcoma[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 154-162.
share this article
Tab.1
Differentially expressed miRNA screened in this study"
| miRNA_ID | P | logFC |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-375 | 0.003 942 | 5.03 |
| hsa-miR-30a-5p | 0.006 482 | 3.11 |
| hsa-miR-362-5p | 0.021 800 | 3.13 |
| hsa-miR-532-5p | 0.027 706 | 3.36 |
| hsa-miR-362-3p | 0.030 996 | 3.00 |
| hsa-miR-660-5p | 0.039 330 | 3.55 |
| hsa-miR-135a-5p | 0.048 080 | 3.45 |
| hsa-miR-196a-5p | 0.006 482 | -4.05 |
| hsa-miR-199a-3p | 0.010 458 | -3.39 |
| hsa-miR-455-3p | 0.012 873 | -4.43 |
| hsa-miR-214-3p | 0.012 873 | -4.50 |
| hsa-miR-199a-5p | 0.021 800 | -3.80 |
| hsa-miR-99b-5p | 0.021 800 | -3.75 |
| hsa-let-7e-5p | 0.047 928 | -3.84 |
| 1 | SKAPEK S, FERRARI A, GUPTA A, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma [J].Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2019, 5(1): 2. |
| 2 | SORENSEN P H, LYNCH J C, QUALMAN S J,et al. PAX3-FKHR and PAX7-FKHR gene fusions are prognostic indicators in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the children's oncology group[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2002, 20(11): 2672-2679. |
| 3 | MISSIAGLIA E, SHEPHERD C J, ALADOWICZ E, et al. MicroRNA and gene co-expression networks characterize biological and clinical behavior of rhabdomyosarcomas[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 385: 251-260. |
| 4 | ZHANG L, PANG Y W, CUI X B, et al. MicroRNA-410-3p upregulation suppresses proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 18(1): 936-943. |
| 5 | SHANG H, LIU Y, LI Z Z, et al. MicroRNA-874 functions as a tumor suppressor in rhabdomyosarcoma by directly targeting GEFT[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2019, 9(4): 668-681. |
| 6 | ESPINOZA-SÁNCHEZ N A, GÖTTE M. Role of cell surface proteoglycans in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2020, 62: 48-67. |
| 7 | MACHACKOVA T, VYCHYTILOVA-FALTEJSKOVA P, SOUCKOVA K, et al. MiR-215-5p reduces liver metastasis in an experimental model of colorectal cancer through regulation of ECM-receptor interactions and focal adhesion[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2020, 12(12): E3518. |
| 8 | THEOCHARIS A D, KARAMANOS N K. Proteoglycans remodeling in cancer: Underlying molecular mechanisms[J]. Matrix Biol, 2019, 75/76: 220-259. |
| 9 | ZHAO X, WANG Q Y, LIN F F, et al. RNA sequencing of osteosarcoma gene expression profile revealed that miR-214-3p facilitates osteosarcoma cell proliferation via targeting ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein 1 (UQCRC1)[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 4982-4991. |
| 10 | PHATAK P, BYRNES K A, MANSOUR D, et al. Overexpression of miR-214-3p in esophageal squamous cancer cells enhances sensitivity to cisplatin by targeting survivin directly and indirectly through CUG-BP1 [J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(16): 2087-2097. |
| 11 | HUANG H J, LIU J, HUA H, et al. MiR-214 and N-ras regulatory loop suppresses rhabdomyosarcoma cell growth and xenograft tumorigenesis[J]. Oncotarget, 2014, 5(8): 2161-2175. |
| 12 | VEERIAH S, BRENNAN C, MENG S S, et al. The tyrosine phosphatase PTPRD is a tumor suppressor that is frequently inactivated and mutated in glioblastoma and other human cancers[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009, 106(23): 9435-9440. |
| 13 | MEEHAN M, PARTHASARATHI L, MORAN N, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor delta acts as a neuroblastoma tumor suppressor by destabilizing the aurora kinase A oncogene[J]. Mol Cancer, 2012, 11: 6. |
| 14 | SOLOMON D A, KIM J S, CRONIN J C, et al. Mutational inactivation of PTPRD in glioblastoma multiforme and malignant melanoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2008, 68(24): 10300-10306. |
| 15 | FUNATO K, YAMAZUMI Y, ODA T, et al. Tyrosine phosphatase PTPRD suppresses colon cancer cell migration in coordination with CD44[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2011, 2(3): 457-463. |
| 16 | WANG M, ZHAO Y, YU Z Y, et al. Glioma exosomal microRNA-148a-3p promotes tumor angiogenesis through activating the EGFR/MAPK signaling pathway via inhibiting ERRFI1 [J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2020, 20: 518. |
| 17 | YU Y, CHEN Q Y, ZHANG X L, et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL promotes the malignant progression of cholangiocarcinoma by epigenetically repressing ERRFI1 expression[J]. Cancer Sci, 2020, 111(7): 2297-2309. |
| 18 | YAN J W, LIN J S, HE X X. The emerging role of miR-375 in cancer[J]. Int J Cancer, 2014, 135(5): 1011-1018. |
| 19 | YIN L H, ZHENG X Q, LI H Y, et al. Epigenetic deregulated miR-375 contributes to the constitutive activation of JAK2/STAT signaling in myeloproliferative neoplasm[J].Leuk Res, 2015,39(4):471-478. |
| 20 | HE X X, CHANG Y, MENG F Y, et al. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo [J]. Oncogene, 2012, 31(28): 3357-3369. |
| 21 | HE J, CAO Y N, SU T W, et al. Downregulation of miR-375 in aldosterone-producing adenomas promotes tumour cell growth via MTDH[J]. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2015, 83(4): 581-589. |
| 22 | MAO Q Q, QUAN T, LUO B, et al. MiR-375 targets KLF4 and impacts the proliferation of colorectal carcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(1): 463-471. |
| 23 | LIU W, ZHAO X T, ZHANG Y J, et al. MicroRNA-375 as a potential serum biomarker for the diagnosis, prognosis, and chemosensitivity prediction of osteosarcoma[J]. J Int Med Res, 2018,46(3): 975-983. |
| 24 | XU X D, LIU Y, LI Y, et al. Selective exosome exclusion of miR-375 by glioma cells promotes glioma progression by activating the CTGF-EGFR pathway[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 40(1): 16. |
| 25 | SZCZYRBA J, NOLTE E, WACH S, et al. Downregulation of Sec23A protein by miRNA-375 in prostate carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2011, 9(6): 791-800. |
| 26 | ZHAO W S, YAN W P, CHEN D B, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR activation screening identifies a role of ELAVL2-CDKN1A axis in paclitaxel resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2019, 9(6): 1183-1200. |
| 27 | LI L, MOU Y P, WANG Y Y, et al. MiR-199a-3p targets ETNK1 to promote invasion and migration in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2019, 215(9): 152511. |
| 28 | WANG X M, ZOU J L, CHEN H J, et al. Long noncoding RNA NORAD regulates cancer cell proliferation and migration in human osteosarcoma by endogenously competing with miR-199a-3p[J]. IUBMB Life, 2019, 71(10): 1482-1491. |
| 29 | LIU F, ZHUANG L, WU R X, et al. MiR-365 inhibits cell invasion and migration of triple negative breast cancer through ADAM10[J]. J BUON, 2019, 24(5): 1905-1912. |
| 30 | WANG Y J, ZHOU N, LI P, et al. EphA8 Acts as an oncogene and contributes to poor prognosis in gastric cancer via regulation of ADAM10[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(11): 20408-20419. |
| 31 | ZHAO R, NI D J, TIAN Y, et al. Aberrant ADAM10 expression correlates with osteosarcoma progression[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2014, 19: 9. |
| [1] | Liantao HU,Wenjun DENG,Shizhen LU,Luo SUN,Xuebing LI,Chuhao LI,Xinran WANG,chunbing ZHANG,Yue LI,Weiqun WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on CC chemokine ligand 20 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and its effect on prognostic assessment of liver hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1010-1017. |
| [2] | Qian LIU,Guoping QI,Huayi YU,Yuyang DAI,Wenbin LU,Jianhua JIN. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of colon cancer core genes and independent prognostic factors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 755-765. |
| [3] | Xiaoyan LI,Wei ZHANG,Jie HE. Promotion effect of REG1A on proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 444-453. |
| [4] | Ying ZHAO,Danyu ZHAO,Chao LIU. Bioinformatics analysis on prognostic evaluation value of TXNDC11 gene in pan-cancer and its immunity regulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 142-153. |
| [5] | Shuqing FENG,Yanhong YAO,Yue SHI,Zhibin LIU,Feng GAO. Application of real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR for detection of BCR/ABL gene expression in peripheral blood in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation therapy in patients with Ph + acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 180-187. |
| [6] | Nan LI,Lei CHEN,Tianmin XU,Kun ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of extracellular matrix related genes in patients with endometriosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 188-194. |
| [7] | Hao DONG,Haizhen JIANG,Chao LI,Dengke GAO,Yaping JIN,Huatao CHEN. Construction of mouse NR1D1 gene overexpression vector and its bioinformatics analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 94-103. |
| [8] | Xiaofeng REN,Yunzheng YAN,Wei LI,Yuexiang LI,Junhai XIAO,Ruiyuan CAO,Yonggang LI. Antiviral activity of remdesivir against human rhabdomyosarcoma cells and ICR suckling mice infected with enterovirus 71 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1446-1454. |
| [9] | Yang YU,Sainan LIU,Yunkai LIU,Yong LI,Yichun QIAO,Yi CHENG. Bioinformatic analysis on expression characteristics of PRPS2 and its relationship with prognosis of breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1229-1236. |
| [10] | Yuqing PAN, Yunyan SUN, Yixun LI, Liying WANG, Zhuoma SINAN, Rui CHEN, Xi ZHANG, Yan DU. Construction and analysis of competitive endogenous RNA networks in acute myeloid leukemia based on high-throughput microarray [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 669-676. |
| [11] | Lan ZHENG,Songzhe PIAO,Ran XU,Xinyue WANG,Yixuan WANG,Zhenhua LIN,Yang YANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of expression levels of m6A regulators on immune infiltration and prognosis of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 438-452. |
| [12] | Yao LIN,Chunlin LIN,Qin WANG,Bin ZHANG,Shaoyu WANG,Guangwei ZHU. Expressions of minichromosome maintenance proteins and structural maintenance of chromosomes 4 genes in cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissue and bioinformation analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 430-437. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xi, ZHAI Li, SUN Yunyan, YANG Wei, GAO Yanzhang, LEI Ming, PAN Yuqing. Bioinformatics analysis of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia based on high-throughput microarray [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1036-1042. |
| [14] | WANG Zhi, HONG Li, LI Suting, ZENG Wanling. Analysis on endometrial cancer-related genes and candidate pathways based on GEO database bioinformatics methods [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 804-809. |
| [15] | SHANG Hao, LI Chunsen, LI Feng, LIU Chunxia. Effect of microRNA-9-5p targeting MEF2C on biological behaviors of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 482-491. |