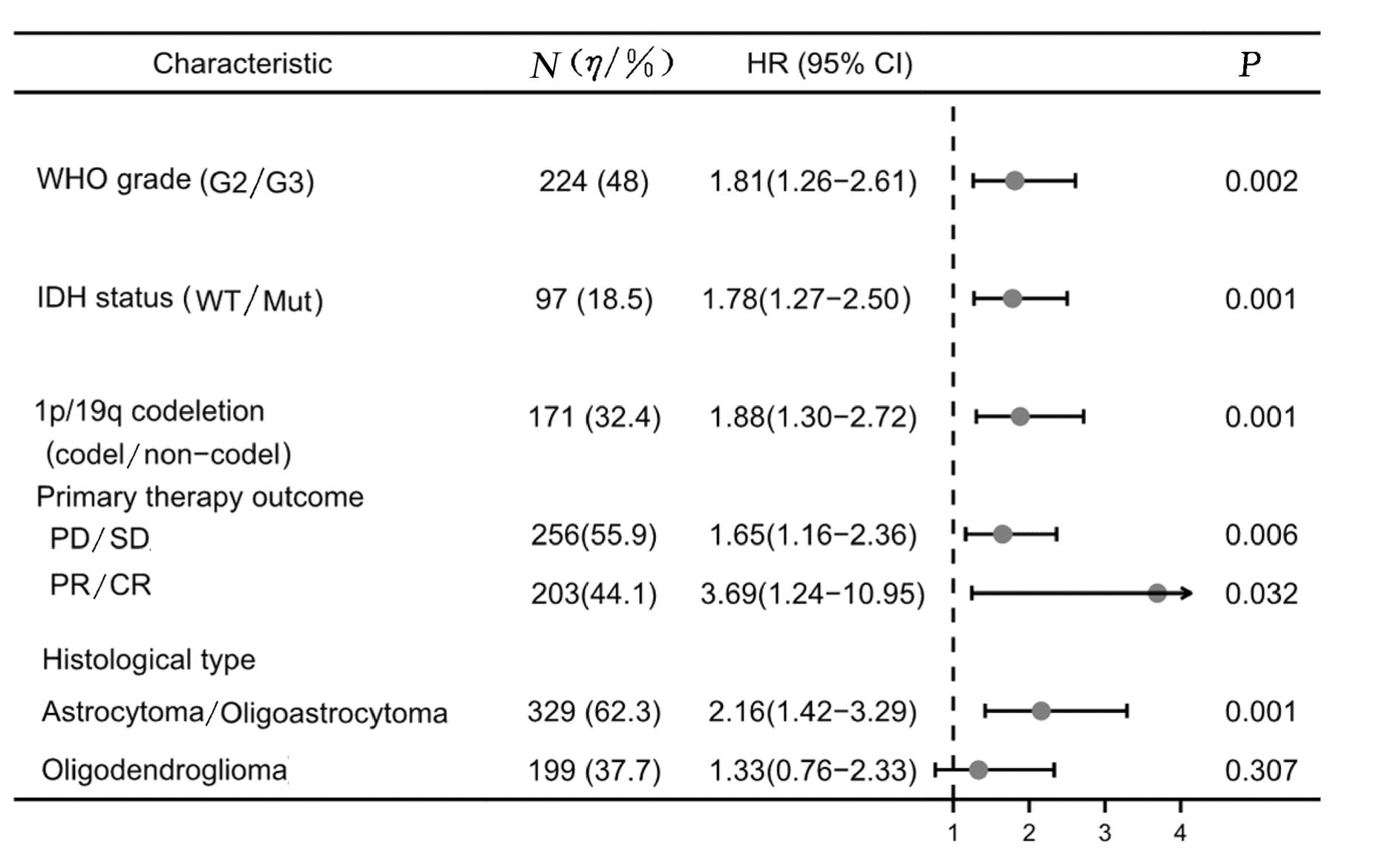
| 1 |
OSTROM Q T, GITTLEMAN H, FARAH P, et al. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006-2010[J]. Neuro Oncol,2013,15():ii1-ii56.
|
| 2 |
LOUIS D N, PERRY A, WESSELING P, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary[J].Neuro Oncol, 2021,23(8): 1231-1251.
|
| 3 |
BUSH N A O, CHANG S M, BERGER M S. Current and future strategies for treatment of glioma[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2017, 40(1): 1-14.
|
| 4 |
LIU L, LIU Z X, WANG H, et al. 14-3-3β exerts glioma-promoting effects and is associated with malignant progression and poor prognosis in patients with glioma[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 15(3): 2381-2387.
|
| 5 |
BURSTEIN E, HOBERG J E, WILKINSON A S, et al. COMMD proteins, a novel family of structural and functional homologs of MURR1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(23): 22222-22232.
|
| 6 |
YOU N, LI J, GONG Z B, et al. COMMD7 functions as molecular target in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J].Mol Carcinog,2017,56(2):607-624.
|
| 7 |
YOU N, LI J, HUANG X B, et al. COMMD7 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating CXCL10[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2017, 88: 653-657.
|
| 8 |
ZHENG L, DENG C L, WANG L, et al. COMMD7 is correlated with a novel NF-κB positive feedback loop in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(22): 32774-32784.
|
| 9 |
ZHENG L, YOU N, HUANG X, et al. COMMD7 regulates NF-κB signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma stem-like cells[J]. Mol Ther Oncolytics, 2019, 12: 112-123.
|
| 10 |
LI K F, CHEN L G, ZHANG H, et al. High expression of COMMD7 is an adverse prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2021, 13(8): 11988-12006.
|
| 11 |
LOVE M I, HUBER W, ANDERS S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2[J]. Genome Biol,2014,15(12): 550.
|
| 12 |
NAVANI S. Manual evaluation of tissue microarrays in a high-throughput research project: the contribution of Indian surgical pathology to the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) project[J]. Proteomics,2016,16(8):1266-1270.
|
| 13 |
TANG Z F, LI C W, KANG B X, et al. GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(W1): W98-W102.
|
| 14 |
YU G C, WANG L G, HAN Y Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J]. OMICS, 2012, 16(5): 284-287.
|
| 15 |
RU B B, WONG C N, TONG Y, et al. TISIDB: an integrated repository portal for tumor-immune system interactions[J].Bioinformatics,2019,35(20):4200-4202.
|
| 16 |
YU S H, LEE C M, HA S H, et al. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by tomentosin in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 and Huh7 cells[J]. Hum Exp Toxicol, 2021, 40(2): 231-244.
|
| 17 |
KOO K H, KWON H. MicroRNA miR-4779 suppresses tumor growth by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through direct targeting of PAK2 and CCND3[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(2): 77.
|
| 18 |
ZHU Y W, GU J N, LI Y, et al. MiR-17-5p enhances pancreatic cancer proliferation by altering cell cycle profiles via disruption of RBL2/E2F4-repressing complexes[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 412: 59-68.
|
| 19 |
SHAPIRO G I. Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment[J].J Clin Oncol,2006,24(11): 1770-1783.
|
| 20 |
WANG M Y, CHEN B H, ZHANG W R, et al. Dematin inhibits glioblastoma malignancy through RhoA-mediated CDKs downregulation and cytoskeleton remodeling[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2022, 417(1): 113196.
|
| 21 |
WANG J, LI B Q, WANG C Z, et al. Long noncoding RNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes glioma cell cycle progression and proliferation through the FOXD2-AS1/miR-31/CDK1 pathway[J].J Cell Biochem,2019,120(12): 19784-19795.
|
| 22 |
陈 骅, 黄 强, 翟德忠, 等. 周期蛋白依赖性激酶1在胶质瘤组织中的表达及其沉默对胶质瘤细胞恶性表型的影响[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2007, 29(7): 484-488.
|
| 23 |
HIRAOKA D, AONO R, HANADA S, et al. Two new competing pathways establish the threshold for cyclin-B-Cdk1 activation at the meiotic G2/M transition[J]. J Cell Sci, 2016, 129(16): 3153-3166.
|
| 24 |
ZHANG Z Y, WANG C Z, DU G J, et al. Genistein induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via ATM/p53-dependent pathway in human colon cancer cells[J]. Int J Oncol, 2013, 43(1): 289-296.
|
| 25 |
YAO G D, QI M, JI X L, et al. ATM-p53 pathway causes G2/M arrest, but represses apoptosis in pseudolaric acid B-treated HeLa cells[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2014, 558: 51-60.
|
| 26 |
ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG Z M. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2020, 17(8): 807-821.
|
| 27 |
ISHIKAWA E, MIYAZAKI T, TAKANO S, et al. Anti-angiogenic and macrophage-based therapeutic strategies for glioma immunotherapy[J]. Brain Tumor Pathol, 2021, 38(3): 149-155.
|
| 28 |
SOKRATOUS G, POLYZOIDIS S, ASHKAN K. Immune infiltration of tumor microenvironment following immunotherapy for glioblastoma multiforme[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2017, 13(11): 2575-2582.
|
| 29 |
ZHENG G R, HAN T, HU X M, et al. NCAPG promotes tumor progression and modulates immune cell infiltration in glioma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 770628.
|
| 30 |
NOOR H, ZAMAN A, TEO C, et al. PODNL1 methylation serves as a prognostic biomarker and associates with immune cell infiltration and immune checkpoint blockade response in lower-grade glioma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(22): 12572.
|
| 31 |
WANG W M, GREEN M, CHOI J E, et al. CD8+T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7755): 270-274.
|
| 32 |
GAO M H, MONIAN P, QUADRI N, et al. Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis[J]. Mol Cell, 2015, 59(2): 298-308.
|
| 33 |
LIU T Q, ZHU C, CHEN X, et al. Ferroptosis, as the most enriched programmed cell death process in glioma, induces immunosuppression and immunotherapy resistance[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2022, 24(7): 1113-1125.
|
 )
)