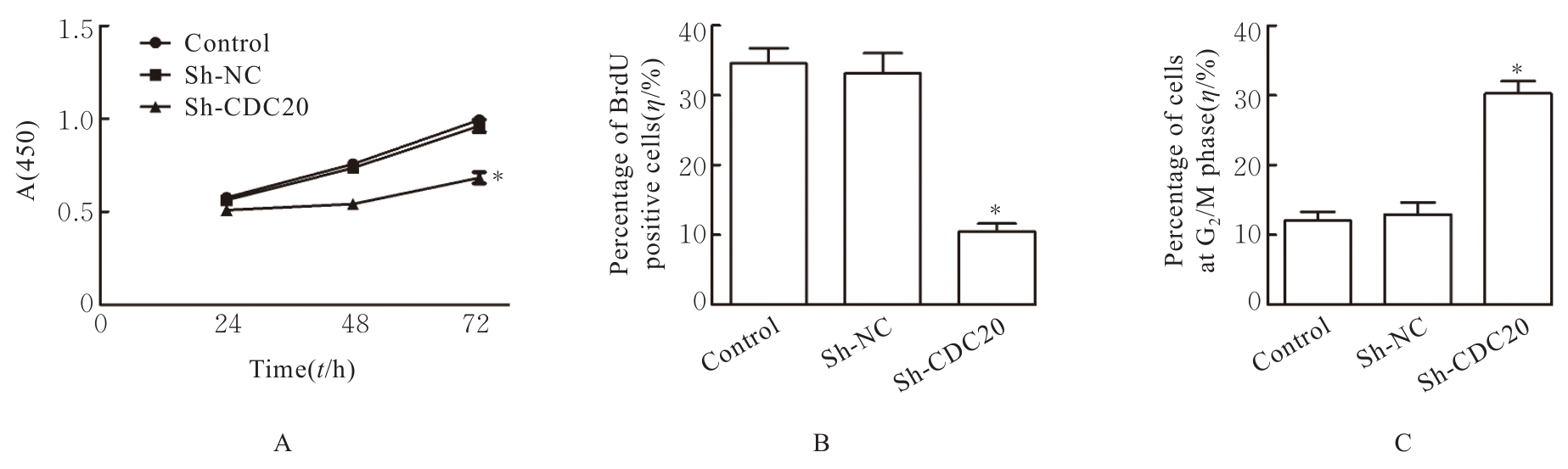
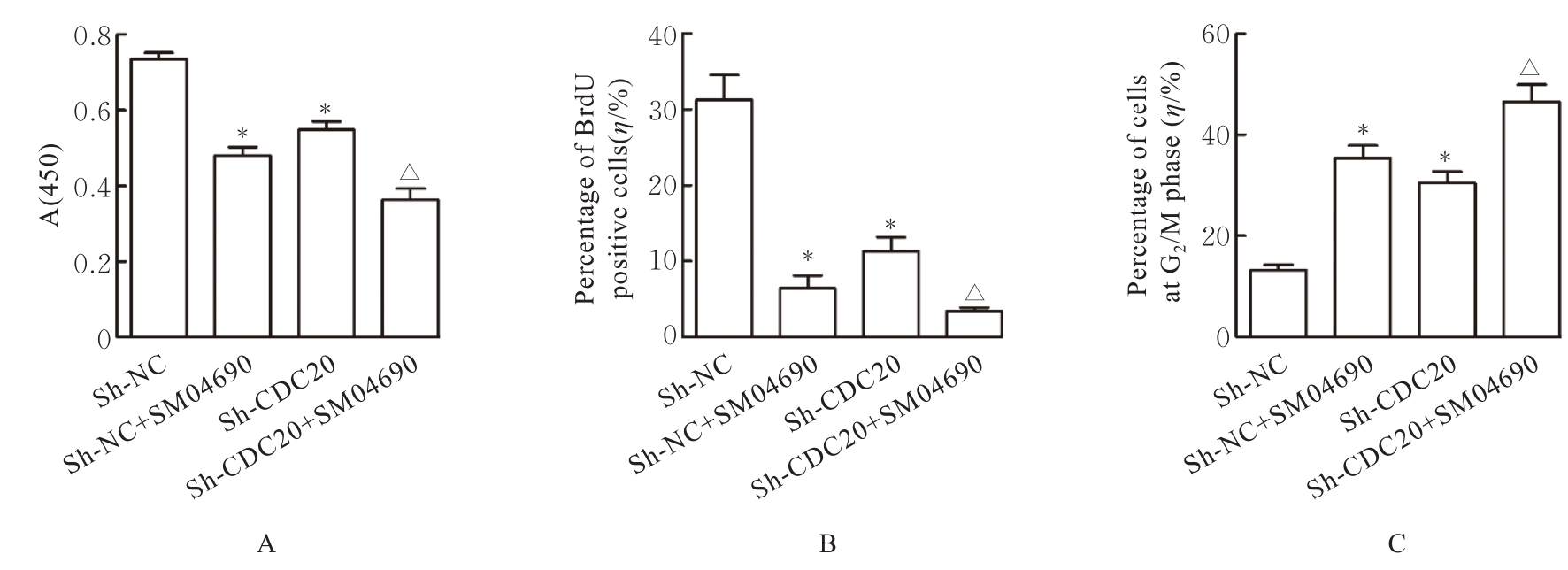
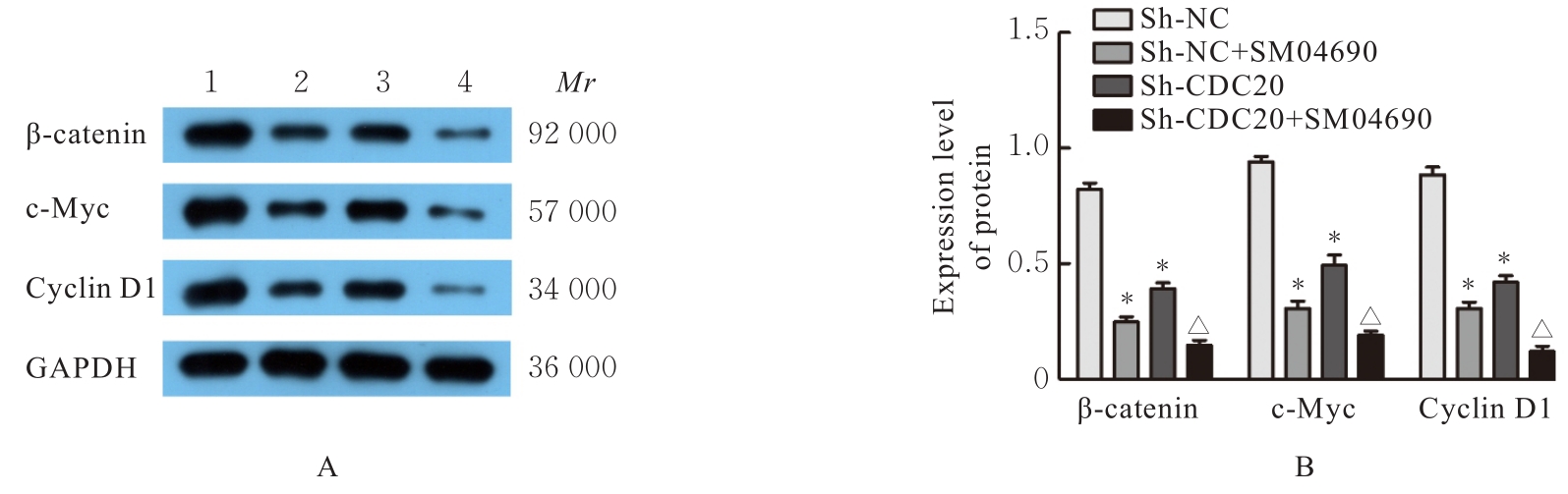
| [1] |
Changji ZHU,Xingzhe LIU,Yanhua XUAN.
Effect of hypoxia on expressions of Gli1 and Sox2 in cervical cancer SiHa cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 442-450.
|
| [2] |
Rongxia JIA,Xu ZHOU,Zhikun SHI,Meijing BAO,Guanqun WANG,Yuqing CHU,Yang LIN.
Analysis on risk factors for disease progression of patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia Ⅰ
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1528-1534.
|
| [3] |
Guowu WANG,Yuan YAO,Yu ZHANG,Na XU,Fang LIU.
Inhibitory effect of miR-152 on proliferation and invasion of endometrial carcinoma cells by reducing low-density lipoprotein receptor expression
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 591-599.
|
| [4] |
Xingyu ZHAO,Xin YANG,Zhihua ZHU,Han HE,Zitong SONG,Wei ZHANG.
Inhibitory effect of juglone on proliferation of cervical cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 348-355.
|
| [5] |
Aiping WEN,Le LUO,Zhiwei MENG,Jingji JIN,Honggui ZHOU,Jihong ZHU.
Expression of Tip60 protein in endometrial adenocarcinoma tissue and its clinical significance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1244-1249.
|
| [6] |
Dongli ZHANG,Ruifang FU,Guixia SUN.
Effect of oxymatrine on proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer SiHa cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 951-957.
|
| [7] |
Lijing QIN,Bing HAN,Zhongqi LI,Qi SUO,Zhen JIA,Hongli CUI,Weiqiang XU,Fang FANG,Zhicheng WANG.
Effects of targeting-silenced ATRX on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by radiation in cervical cancer HeLa cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 904-910.
|
| [8] |
Dan SU, Yi LIU, Manman CUI, Nian YANG, Yu HUANG, Wenjing HE.
Evaluation of clinical effect of screening chemotherapy regimens in treatment of ovarian cancer based on miniPDX animal models
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 731-739.
|
| [9] |
Lan ZHENG,Songzhe PIAO,Ran XU,Xinyue WANG,Yixuan WANG,Zhenhua LIN,Yang YANG.
Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of expression levels of m6A regulators on immune infiltration and prognosis of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 438-452.
|
| [10] |
Yao LIN,Chunlin LIN,Qin WANG,Bin ZHANG,Shaoyu WANG,Guangwei ZHU.
Expressions of minichromosome maintenance proteins and structural maintenance of chromosomes 4 genes in cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissue and bioinformation analysis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 430-437.
|
| [11] |
Jing WANG,Jing LIU,Xujing WEI,Yafei DU,Guiying FANG,Lin LI.
Effects of oridonin on proliferation, migration, invasion and expression of lncRNA CCAT1 of endometrial carcinoma HEC-1B cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 384-389.
|
| [12] |
Yinfeng CUI,Mengyu CHAI,Wanshan YANG,Ying PAN.
Effect of cardamonin on proliferation of cervical cancer HeLa cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1182-1186.
|
| [13] |
Xia WANG,Yujun YAO,Jing TANG,Kaihui LI.
Effect of lncRNA-CCAT2 on apoptosis of cervical cancer CaSki cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1247-1253.
|
| [14] |
GE Jing, XIE Lei, LI Lin, WEI Xujing, CHEN Ran, WANG Na.
Expression of integrin-linked kinase in endometrial carcinoma tissue and its effects on migration and invasion abilities of cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1011-1015.
|
| [15] |
WEI Xujing, LI Lin, ZHANG Hongzhen, WANG Jing, XU Jing.
Effects of LncRNA CCAT1 on proliferation,invasion and migration of endometrial cancer cells through TGF-β1/smad signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1016-1022.
|
 )
)