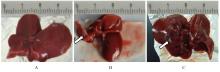
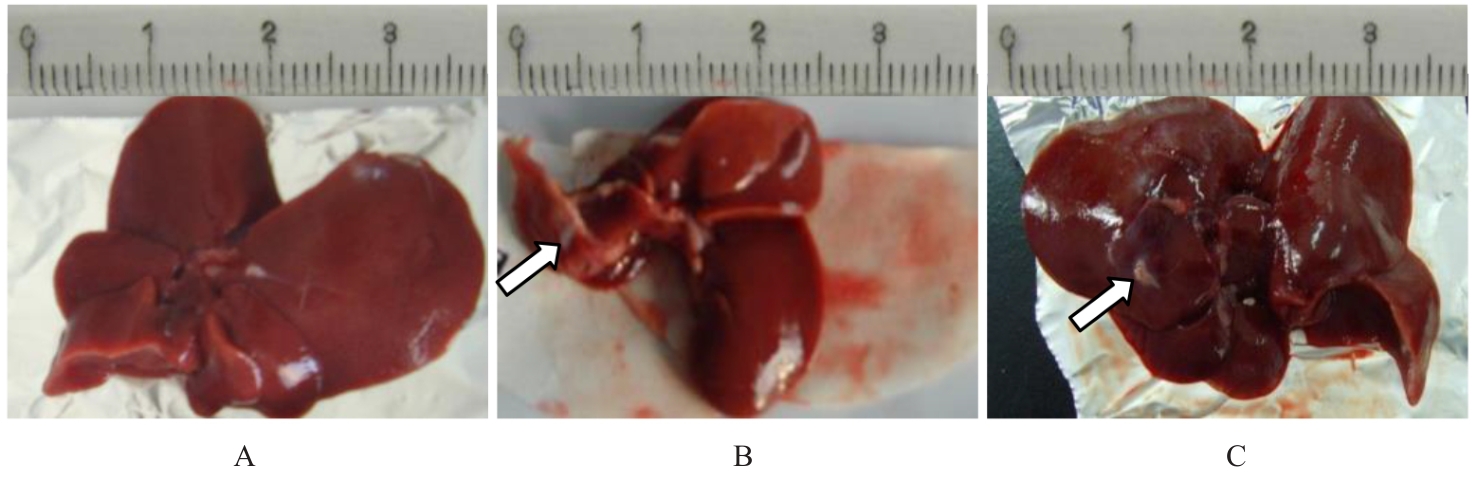
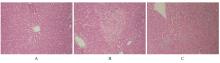
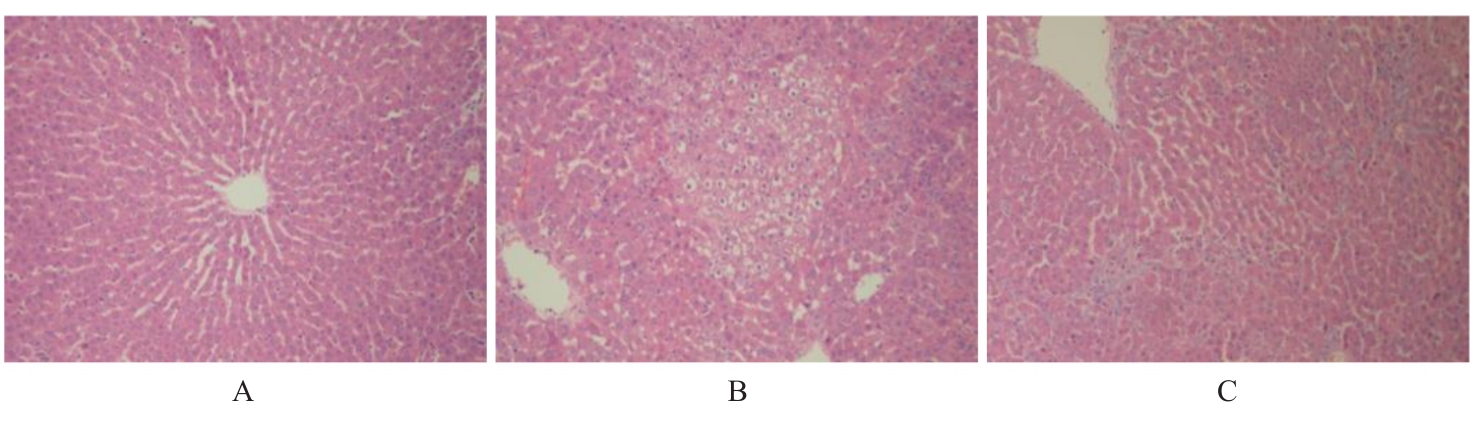
| [1] |
Feina WANG,Xuguang MI,Xiuying LIN,Jianhua FU,Lei LIU,Xinyue YU,Huanhuan ZANG,Linjun LIU,Shiling CHEN,Yanqiu FANG.
Effect of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway inhibitor MSAB on fibrogenic responses of human endometrial stromal cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1266-1274.
|
| [2] |
Yuwei KANG,Wei YANG,Shijie MA,Wei ZHOU,Fei DENG.
Levels of sICAM-1 and sVCAM-1 and activity of SOD in serum and their relationships with coronary artery calcification in patients with maintenance hemodialysis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 812-818.
|
| [3] |
Jia ZHOU,Zhidong QIU,Zhe LIN,Guangfu LYU,Jiaming XU,He LIN,Kexin WANG,Yuchen WANG,Xiaowei HUANG.
Effect of chelerythrine on migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 25-32.
|
| [4] |
Meng QYU,Yuzhu JIANG,Rui HUANG,Zhenzhuo MA,Jichen XIA,Yuan ZHANG,Zhiheng DONG.
Protective effect of ginsenoside Rh2 on kidney injury in rats with diabetic kidney lesions and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1168-1173.
|
| [5] |
Lingyao XU,Shutang WEI,Yong DONG,Zhenglu SUN,Junbo ZHAO,Dazheng HAN.
Regulatory effect of lncRNA MALAT1 on activation of hepatic stellate cell and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 697-705.
|
| [6] |
Junxiong ZHAO,Qian WU,Liangui NIE,Shengquan LIU,Zhentao JIANG,Jian CHEN,Ting XIAO,Jun YANG.
Ameliorative effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 8-14.
|
| [7] |
Meng QYU,Hong ZHENG,Yan LI,Boxue CHEN,Yuzhu JIANG,Shenggao WANG,Chunyan YU,Zhiheng DONG.
Inhibitory effect of fermented red ginseng total saponins high glucose-induced renal tubular cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1182-1189.
|
| [8] |
Mingliu GU,Fengyuan LIN,Xuefeng WU,Jianing ZHOU,Xuechun LU,Peige DU,Liping AN.
Improvement effect of Phellinus igniarius acidic polysaccharide on liver fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1167-1174.
|
| [9] |
Zhouguang WU,Bin WANG,Zhen CHENG,Wenjie ZHANG,Taoyan ZUO,Siqi CHEN,Jingru FU.
Analysis on correlation of GPC3 and α-SMA expressions with liver function-related indexes in liver tissue of children with biliary atresia
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1237-1243.
|
| [10] |
Yang ZHENG,Jiahui WANG,Yue PENG,Xianling YUAN,Lei WANG,Tiejian ZHAO.
Influence of curcumol in structure of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells of mice and its inhibitiory effect on intrahepatic angiogenesis
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1124-1130.
|
| [11] |
Rongjun JIA,Liman MA,Lihua LI.
Protective effect of calcitriol on hepatic fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 257-264.
|
| [12] |
Xiangteng LIU,Guilan WANG,Jiayan RONG,Juan HUANG,Jiabiao LIN,Dongming HUANG,Bingjie WANG.
Analysis on correlations between serum level of TGF-β1 and severity of bronchiolitis and pulmonary function indexes
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1293-1297.
|
| [13] |
YANG Fan, LI Lihua.
Effect of vitamin D receptor activation on hepatic fibrosis induced by bile duct ligation in mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 722-727.
|
| [14] |
DONG Zhuo, LI Jiale, CHEN Xiaoyi, WANG Rui, YI Junxuan, WEI Xinfeng, JIN Shunzi.
Effect of NRP1 gene knockout on process of radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(01): 26-34.
|
| [15] |
ZHOU Licheng, LIU Xianfa, LI Qiang, LI Rong, HUANG Jiagan, ZHANG Qiong, LI Xiaofei.
Anti-atherosclerosis effect of berberine combined with simvastatin in atherosclerosis model rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 849-854.
|
 ),Feng ZHENG1,3(
),Feng ZHENG1,3( )
)