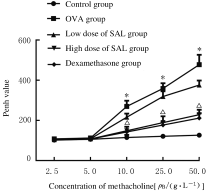
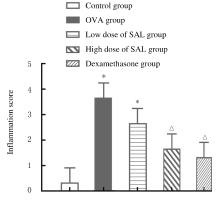
| 1 | CLOUTIER M M,DIXON A E,KRISHNAN J A,et al.Managing asthma in adolescents and adults: 2020 asthma guideline update from the national asthma education and prevention program[J]. JAMA, 2020, 324(22): 2301-2317. |
| 2 | PIJNENBURG M W, FLEMING L. Advances in understanding and reducing the burden of severe asthma in children[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2020, 8(10): 1032-1044. |
| 3 | 朴玉华, 王知广, 朴艺花, 等. 虎杖苷对实验性哮喘小鼠气道炎症的影响及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(6): 1111-1116,1345. |
| 4 | MANGAN M S J, OLHAVA E J, ROUSH W R,et al. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2018, 17(9): 688. |
| 5 | 姜 华, 闫宜青, 江 维, 等. NLRP3炎症小体活化、调控机制及相关疾病机制[J]. 中国科学:生命科学,2017,47(1):125-131. |
| 6 | 刘 雯, 郭文洁, 徐 强, 等. NLRP3炎症小体调控机制研究进展[J]. 药学学报, 2016, 51(10): 1505-1512. |
| 7 | MARIATHASAN S, WEISS D S, NEWTON K, et al. Cryopyrin activates the inflammasome in response to toxins and ATP[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7081): 228-232. |
| 8 | BRUCHARD M, REBé C, DERANGèRE V, et al. The receptor NLRP3 is a transcriptional regulator of TH2 differentiation[J]. Nat Immunol, 2015,16(8): 859-870. |
| 9 | BOGEFORS J, RYDBERG C, UDDMAN R, et al. Nod1, Nod2 and Nalp3 receptors, new potential targets in treatment of allergic rhinitis?[J].Allergy,2010,65(10):1222-1226. |
| 10 | BESNARD A G, GUILLOU N, TSCHOPP J, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome is required in murine asthma in the absence of aluminum adjuvant[J]. Allergy, 2011, 66(8): 1047-1057. |
| 11 | CHEN L, LAN Z. Polydatin attenuates potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway[J]. Food Funct, 2017, 8(5): 1785-1792. |
| 12 | QI Z L, ZHANG Y, QI S M, et al. Salidroside inhibits HMGB1 acetylation and release through upregulation of SirT1 during inflammation[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2017, 2017: 9821543. |
| 13 | LAN K C, CHAO S C, WU H Y, et al. Salidroside ameliorates sepsis-induced acute lung injury and mortality via downregulating NF-κB and HMGB1 pathways through the upregulation of SIRT1[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 12026. |
| 14 | YAN G H, CHOI Y H. Salidroside attenuates allergic airway inflammation through negative regulation of nuclear factor-kappa B and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase[J]. J Pharmacol Sci, 2014, 126(2): 126-135. |
| 15 | CAI H, WANG J, MO Y Q, et al. Salidroside suppresses group 2 innate lymphoid cell-mediated allergic airway inflammation by targeting IL-33/ST2 axis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 81: 106243. |
| 16 | LEE K S, PARK H S, PARK S J, et al. An antioxidant modulates expression of receptor activator of NF-kappaB in asthma[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2006, 38(3): 217-229. |
| 17 | KERZERHO J, MAAZI H, SPEAK A O, et al. Programmed cell death ligand 2 regulates TH9 differentiation and induction of chronic airway hyperreactivity[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2013, 131(4): 1048-1057. |
| 18 | PAPI A, BRIGHTLING C, PEDERSEN S E, et al. Asthma[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10122): 783-800. |
| 19 | 高龙霞, 阎 玥, 包海鹏, 等. 咳嗽变异性哮喘现代研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(9): 4171-4174. |
| 20 | EVON MUTIUS, SMITS H H. Primary prevention of asthma: from risk and protective factors to targeted strategies for prevention[J]. Lancet, 2020,396(10254): 854-866. |
| 21 | EL-HUSSEINI Z W, GOSENS R, DEKKER F, et al. The genetics of asthma and the promise of genomics-guided drug target discovery[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2020, 8(10): 1045-1056. |
| 22 | LAMKANFI M, DIXIT V M. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes[J]. Cell, 2014,157(5): 1013-1022. |
| 23 | GUO H T, CALLAWAY J B, TING J P. Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics[J]. Nat Med, 2015, 21(7): 677-687. |
| 24 | HOWRYLAK J A, NAKAHIRA K. Inflammasomes: key mediators of lung immunity[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2017, 79: 471-494. |
| 25 | PINKERTON J W, KIM R Y, ROBERTSON A A B, et al. Inflammasomes in the lung[J]. Mol Immunol, 2017, 86: 44-55. |
| 26 | RITTER M, STRAUBINGER K, SCHMIDT S,et al. Functional relevance of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated interleukin (IL)-1β during acute allergic airway inflammation[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2014, 178(2): 212-223. |
| 27 | 柳亚慧,时国朝.支气管哮喘的精准治疗[J].中国实用内科杂志,2020,40(5):371-376. |
| 28 | EISENBARTH S C,COLEGIO O R,O’CONNOR W,et al. Crucial role for the Nalp3 inflammasome in the immunostimulatory properties of aluminium adjuvants[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7198): 1122-1126. |
| 29 | LI H, YANG T, WU R, et al. Salidroside inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced proliferation and migration of airway smooth muscle cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(4): 6642-6650. |
| 30 | WANG J, JIN R G, XIAO L, et al. Anti-asthma effects of synthetic salidroside through regulation of Th1/Th2 balance[J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2014, 12(7): 500-504. |
 )
)